Abstract
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a diffuse lung disease characterized by the accumulation of lipoproteins derived from surfactants in the distal air space. The lack of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor is believed to contribute to macrophage dysfunction and the impaired processing of surfactants. Because the prevalence of PAP in the general population is less than 1 in 200,000, and the typical age at presentation is 35 to 50 years, PAP is a very rare disease in children. To the best of our knowledge, there has been no Korean report on PAP in children. We describe here a patient who was diagnosed with PAP at the aged 15 years.
Figures and Tables
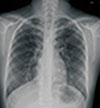 | Fig. 1The initial chest radiograph showing ground grass opacities and fine reticular infiltration both upper and middle lobes. |
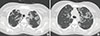 | Fig. 2The initial high resolution computed tomography revealing patchy and extensive ground-grass opacity lesions with crazy-paving appearance especially in the upper (A) and middle (B) lung zone. |
References
1. Trapnell BC, Whitsett JA, Nakata K. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:2527–2539.

2. Carey B, Trapnell BC. The molecular basis of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Clin Immunol. 2010; 135:223–235.

3. Froudarakis ME, Koutsopoulos A, Mihailidou HP. Total lung lavage by awake flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope in a 13-year-old girl with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Respir Med. 2007; 101:366–369.

4. Byun MK, Kim DS, Kim YW, Chung MP, Shim JJ, Cha SI, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in Korean population. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:393–398.

5. Suzuki T, Sakagami T, Rubin BK, Nogee LM, Wood RE, Zimmerman SL, et al. Familial pulmonary alveolar proteinosis caused by mutations in CSF2RA. J Exp Med. 2008; 205:2703–2710.

6. Woo DH, Park JE, Ryu YH, Kim HJ, Shin KC, Chung JH, et al. A case of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2010; 27:57–62.

7. Rosen SH, Castleman B, Liebow AA. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 1958; 258:1123–1142.

8. Stanley E, Lieschke GJ, Grail D, Metcalf D, Hodgson G, Gall JA, et al. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor-deficient mice show no major perturbation of hematopoiesis but develop a characteristic pulmonary pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994; 91:5592–5596.

9. Kitamura T, Tanaka N, Watanabe J, Uchida , Kanegasaki S, Yamada Y, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis as an autoimmune disease with neutralizing antibody against granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med. 1999; 190:875–880.

10. Suzuki T, Sakagami T, Young LR, Carey BC, Wood RE, Luisetti M, et al. Hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: pathogenesis, presentation, diagnosis, and therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010; 182:1292–1304.
11. Ceruti M, Rodi G, Stella GM, Adami A, Bolongaro A, Baritussio A, et al. Successful whole lung lavage in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis secondary to lysinuric protein intolerance: a case report. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007; 2:14.

12. Wang BM, Stern EJ, Schmidt RA, Pierson DJ. Diagnosing pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. A review and an update. Chest. 1997; 111:460–466.
13. Seymour JF, Presneill JJ, Schoch OD, Downie GH, Moore PE, Doyle IR, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in patients with idiopathic acquired alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:524–531.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download