Abstract
Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome (IHES) is a rare disorder defined by persistent blood eosinophilia, evidence of eosinophil-associated organ dysfunction and absence of secondary causes. Eosinophilic infiltration and its mediator release can cause damage to multiple organs. Although IHES can involve every organ system, bladder involvement is rarely evidenced. We recently reported a case of IHES with both bladder and gastrointestinal tract involvement. A 43-year-old woman visited Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital complaining of urinary frequency, abdominal pain, and diarrhea for several months. Abdominal pelvic computed tomographic scan showed diffuse wall thickenings in her bladder and colon with small pelvic ascites. Laboratory investigation showed a marked peripheral eosinophilia and tissue biopsies confirmed eosinophilic infiltration in the bladder wall, esophagus, and duodenum. The patient was treated with prednisolone and her eosinophilia and symptoms have gradually improved.
Figures and Tables
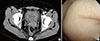 | Fig. 1(A) There is diffuse wall thickening of urinary bladder on the abdominal-pelvic computed tomography (axial view). (B) Cystoscopic examination finding shows edematous wall of bladder. |
References
1. Simon HU, Rothenberg ME, Bochner BS, Weller PF, Wardlaw AJ, Wechsler ME, et al. Refining the definition of hypereosinophilic syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:45–49.

2. Gotlib J. World Health Organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2014 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2014; 89:325–337.

3. Valent P, Klion AD, Horny HP, Roufosse F, Gotlib J, Weller PF, et al. Contemporary consensus proposal on criteria and classification of eosinophilic disorders and related syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 130:607–612.e9.

4. Ogbogu PU, Bochner BS, Butterfield JH, Gleich GJ, Huss-Marp J, Kahn JE, et al. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: a multicenter, retrospective analysis of clinical characteristics and response to therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:1319–1325.e3.

5. Lee SI, Park HS, Ha BK, Kim DH, Yoo JT, Choi SH. A case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis diagnosed by repeated abdominal pain with eosinophilic ascites and cystitis. Kosin Med J. 2011; 26:191–195.
6. Kim SS, Choi CH, Choi HS, Park IW, Gham CW, Cho HG, et al. A case of eosinophilic enterocolitis associated with eosinophilic ascites and cystitis. Korean J Med. 2005; 69:Suppl 3. S746–S752.
7. Roufosse F, Weller PF. Practical approach to the patient with hypereosinophilia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:39–44.

8. Podjasek JC, Butterfield JH. Mortality in hypereosinophilic syndrome: 19 years of experience at Mayo Clinic with a review of the literature. Leuk Res. 2013; 37:392–395.

9. Kojima K, Maeda J, Mikami S, Yamagishi H, Ide H, Hattori S, et al. Eosinophilic cystitis presented as a manifestation of hypereosinophilic syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. Nephron Extra. 2013; 3:30–35.

11. D M, T M K, M S, V R M, V G. Eosinophilic cystitis mimicking bladder tumour - a rare case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013; 7:2282–2283.
12. Ingle SB, Hinge Ingle CR. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: an unusual type of gastroenteritis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:5061–5066.

14. Cogan E, Roufosse F. Clinical management of the hypereosinophilic syndromes. Expert Rev Hematol. 2012; 5:275–289.

15. Helbig G. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of eosinophilia. Curr Opin Hematol. 2014; 21:3–7.

16. Razaq W, Beautyman E. Successful treatment of refractory idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome with etoposide. Am J Ther. 2009; 16:68–70.

17. Arefi M, Garcia JL, Briz MM, de Arriba F, Rodriguez JN, Martin-Nunez G, et al. Response to imatinib mesylate in patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome. Int J Hematol. 2012; 96:320–326.

18. Jeung YJ, Lee JY, Lee GY, Oh MJ, Lee BJ, Choi DC. A case of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome presenting with nocturia and dyspnea. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 30:241–245.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download