Abstract
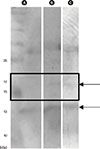
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA) is a specific variant of anaphylaxis that requires both vigorous physical activity and the ingestion of specific causative foods. In particular, occurrence for FDEIA is rarely associated with apples. A 17-year-old male experienced generalized urticaria, dyspnea, headache, vomiting, and presyncope after ingestion of an apple and then 2 hours of exercise. The skin prick test showed a strong positive reaction to apple crude allergen extract, whereas the results of an open food challenge and exercise provocation tests were negative. However, the exercise test after apple consumption provoked a positive reaction with generalized urticaria, dyspnea, and presyncope. We detected 17 kD IgE-reactive protein band in immunoblotting assay with apple crude extract and patient's serum.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Sharma R, Sinha R, Menon PS, Sirohi D. Management protocol for anaphylaxis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:855–862.

2. Im JH, Kwon HY, Ye YM, Park HS, Kim TB, Choi GS, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Korea: a multicenter retrospective case study. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:203–210.

3. Soyer OU, Sekerel BE. Food dependent exercise induced anaphylaxis or exercise induced anaphylaxis? Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2008; 36:242–243.

4. Muraro A, Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, Holzhauser T, Poulsen LK, Gowland MH, Akdis CA, et al. EAACI Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Guidelines. Protecting consumers with food allergies: understanding food consumption, meeting regulations and identifying unmet needs. Allergy. 2014; 69:1464–1472.

5. Du Toit G. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2007; 18:455–463.

6. Kaneko M, Yagi H, Koyama H, Nakajima N, Muramatu R, Takizawa T, et al. A case of apple allergy with initial symptoms like food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Arerugi. 2013; 62:698–703.
7. Romano A, Di Fonso M, Giuffreda F, Papa G, Artesani MC, Viola M, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: clinical and laboratory findings in 54 subjects. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001; 125:264–272.

8. Maulitz RM, Pratt DS, Schocket AL. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to shellfish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979; 63:433–434.

9. Yang MS. Epidemiologic study on food-dependent exercise induced anaphylaxis. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:179–180.

10. Cho HJ, Kim JH, Choi GS, Kim JE, Ye YM, Park HS. Clinical features of patients with apple allergy and identification of IgE-binding components of apple. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 30:116–122.
11. Gordins P, McLean-Tooke A, Spickett GP. The role of omega-5 gliadin-specific IgE test in diagnosing exercise-induced wheat allergy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011; 155:93–94.

12. Yang MS, Lee SH, Kim KM, Kwon HS, Kim DI, Park CH, et al. A case report of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis to apples. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 26:242–245.
13. Brockow K, Kneissl D, Valentini L, Zelger O, Grosber M, Kugler C, et al. Using a gluten oral food challenge protocol to improve diagnosis of wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 135:977–984.e4.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download