Abstract
Purpose
Cow's milk-specific IgE (CM-IgE) has been proposed as one of the valuable markers for diagnosis of clinical cow's milk (CM) allergy. In this study, we evaluated the additional usefulness of casein-specific IgE (casein-IgE) and IgG (casein-IgG) for the diagnosis of clinical CM allergy.
Methods
Fifty-eight subjects, aged from 3 months to 154 months, were enrolled. Thirty-four patients showed immediate-type of clinical CM allergy, and 24 patients were atopic controls. The serum levels of CM-IgE, casein-IgE, and casein-IgG were measured. Patients were divided into 2 groups: those aged under 12 months and those aged 12 months or over. The diagnostic values of each antibody were analyzed and compared using the Mann-Whitney U-test and receiver operating characteristic curves.
Results
CM allergy had significantly higher levels of CM-IgE and casein-IgE, and lower levels of casein-IgG/IgE ratio when compared to atopic controls in both age groups (P<0.05). CM-IgE and casein-IgE were shown to be better predictive markers for immediate-type CM allergy in patients under 12 months, while casein-IgG/IgE ratio was a more useful marker in those aged 12 months or over. Considering 100% positive predictive values, cutoff points were 1.04 kU/L for CM-IgE, 0.11 kU/L for casein-IgE, 19.5 for casein-IgG/IgE ratio in patients aged under 12 months, and 7.1 kU/L for CM-IgE, 1.41 kU/L for casein-IgE, 12.51 for casein-IgG/IgE ratio in those aged 12 months or over.
Figures and Tables
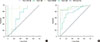 | Fig. 1Receiver operating characteristic curve represent sensitivity and specificity of cow's milk and casein antibodies for diagnosing clinical cow's milk allergy aged less than 12 months (A), aged 12 months or over 12 months (B). |
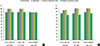 | Fig. 2Comparison of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of cow's milk and casein antibodies aged less than 12 months (A), aged 12 months or over 12 months (B). |
Table 1
Characteristics of study subjects
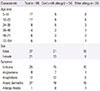
Table 2
Cow's milk and casein specific antibodies in subjects aged less than 12 months
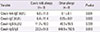
Table 3
Cow's milk and casein specific antibodies in subjects aged 12 months or over 12 months
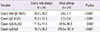
Table 4
Clinical decision points of cow's milk and casein specific antibodies obtained from receiver operating characteristic curves
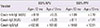
| Variable | 100% NPV | 100% PPV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age<12 mo | Age≥12 mo | Age<12 mo | Age≥12 mo | |
| Cow's milk IgE (kU/L) | ≤0.18 | ≤0.05 | ≥1.04 | ≥7.10 |
| Casein IgE (kU/L) | ≤0.07 | ≤0.05 | ≥0.11 | ≥1.41 |
| Casein IgG/IgE | ≥432.00 | ≥167.60 | ≤19.50 | ≤12.51 |
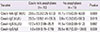
Table 5
Comparison of cow's milk and casein specific antibodies in subjects aged 12 months or over according to the presence of cow's milk anaphylaxis
References
1. Ahn K, Kim J, Hahm MI, Lee SY, Kim WK, Chae Y, et al. Prevalence of immediate-type food allergy in Korean schoolchildren: a population-based study. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012; 33:481–487.

2. Kim J, Chang E, Han Y, Ahn K, Lee SI. The incidence and risk factors of immediate type food allergy during the first year of life in Korean infants: a birth cohort study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011; 22:715–719.

4. Park M, Kim D, Ahn K, Kim J, Han Y. Prevalence of immediate-type food allergy in early childhood in seoul. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:131–136.

5. Host A, Halken S, Jacobsen HP, Christensen AE, Herskind AM, Plesner K. Clinical course of cow's milk protein allergy/intolerance and atopic diseases in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2002; 13:Suppl 15. 23–28.

6. Wood RA, Sicherer SH, Vickery BP, Jones SM, Liu AH, Fleischer DM, et al. The natural history of milk allergy in an observational cohort. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:805–812.

7. Rona RJ, Keil T, Summers C, Gislason D, Zuidmeer L, Sodergren E, et al. The prevalence of food allergy: a meta-analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:638–646.

8. Hochwallner H, Schulmeister U, Swoboda I, Spitzauer S, Valenta R. Cow's milk allergy: from allergens to new forms of diagnosis, therapy and prevention. Methods. 2014; 66:22–33.

9. Host A, Halken S. Cow's milk allergy: where have we come from and where are we going? Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2014; 14:2–8.

10. Nicolaou N, Tsabouri S, Priftis KN. Reintroduction of cow's milk in milk-allergic children. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2014; 14:54–62.

11. Ito K, Futamura M, Moverare R, Tanaka A, Kawabe T, Sakamoto T, et al. The usefulness of casein-specific IgE and IgG4 antibodies in cow's milk allergic children. Clin Mol Allergy. 2012; 10:1.

12. Garcia-Careaga M Jr, Kerner JA Jr. Gastrointestinal manifestations of food allergies in pediatric patients. Nutr Clin Pract. 2005; 20:526–535.

13. Garcia-Ara C, Boyano-Martinez T, Diaz-Pena JM, Martin-Munoz F, Reche-Frutos M, Martin-Esteban M. Specific IgE levels in the diagnosis of immediate hypersensitivity to cows' milk protein in the infant. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:185–190.

14. Ahrens B, Lopes de Oliveira LC, Grabenhenrich L, Schulz G, Niggemann B, Wahn U, et al. Individual cow's milk allergens as prognostic markers for tolerance development? Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 42:1630–1637.

15. Garcia-Ara MC, Boyano-Martinez MT, Diaz-Pena JM, Martin-Munoz MF, Martin-Esteban M. Cow's milk-specific immunoglobulin E levels as predictors of clinical reactivity in the follow-up of the cow's milk allergy infants. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:866–870.

16. Chatchatee P, Jarvinen KM, Bardina L, Beyer K, Sampson HA. Identification of IgE- and IgG-binding epitopes on alpha(s1)-casein: differences in patients with persistent and transient cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:379–383.

17. Buchanan AD, Green TD, Jones SM, Scurlock AM, Christie L, Althage KA, et al. Egg oral immunotherapy in nonanaphylactic children with egg allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:199–205.

18. Jones SM, Pons L, Roberts JL, Scurlock AM, Perry TT, Kulis M, et al. Clinical efficacy and immune regulation with peanut oral immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:292–300. 300.e1–300.e97.

19. van Neerven RJ, Knol EF, Ejrnaes A, Wurtzen PA. IgE-mediated allergen presentation and blocking antibodies: regulation of T-cell activation in allergy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2006; 141:119–129.

20. Savilahti EM, Saarinen KM, Savilahti E. Specific antibodies to cow's milk proteins in infants: effect of early feeding and diagnosis of cow's milk allergy. Eur J Nutr. 2010; 49:501–504.

21. Jarvinen KM, Westfall JE, Seppo MS, James AK, Tsuang AJ, Feustel PJ, et al. Role of maternal elimination diets and human milk IgA in the development of cow's milk allergy in the infants. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014; 44:69–78.

22. Sampson HA, Ho DG. Relationship between food-specific IgE concentrations and the risk of positive food challenges in children and adolescents. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 100:444–451.

23. Castro AP, Pastorino AC, Gushken AK, Kokron CM, Filho UD, Jacob CM. Establishing a cut-off for the serum levels of specific IgE to milk and its components for cow's milk allergy: Results from a specific population. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2014; 01. 29. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aller.2013.09.012.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download