Abstract
Purpose
Adverse cutaneous reactions to antituberculous drugs (ATD), such as maculopapular eruption (MPE), are the most common causes of discontinuation of scheduled treatment of tuberculosis. We previously reported that tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α genetic polymorphism -308G/A is significantly associated with ATD-induced hepatitis. This study aimed to investigate associations between TNF-α -308G/A and ATD-induced MPE.
Methods
Patients with ATD-induced MPE and controls without any adverse reactions to ATD were recruited from the database of the Adverse Drug Reaction Pharmacogenomic Research Group database of Korea. We compared the genotype frequency of TNF-α-308G/A between patients with ATD-induced MPE and ATD-tolerant controls.
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Clinical characteristics of the study subjects
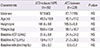
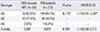
Table 2
TNF-α polymorphism -308G/A in patents with ATD-induced MPE and ATD-tolerant controls
References
1. Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention. Annual report on the tuberculosis cases notified in Korea 2012. Cheongwon: Korean Centers for Disease Control & Prevention;2013.
2. American Thoracic Society. CDC. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Treatment of tuberculosis. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2003; 52(RR-11):1–77.
3. Kim SH, Lee BH, Lee KD, Park JS, Kim YS, Jee YK, et al. The prevalence of adverse drug reactions to a short course anti-tuberculosis regimen. Korean J Med. 2007; 73:496–502.
4. Tan WC, Ong CK, Kang SC, Razak MA. Two years review of cutaneous adverse drug reaction from first line anti-tuberculous drugs. Med J Malaysia. 2007; 62:143–146.
5. Yee D, Valiquette C, Pelletier M, Parisien I, Rocher I, Menzies D. Incidence of serious side effects from first-line antituberculosis drugs among patients treated for active tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 167:1472–1477.

6. Dossing M, Wilcke JT, Askgaard DS, Nybo B. Liver injury during antituberculosis treatment: an 11-year study. Tuber Lung Dis. 1996; 77:335–340.

7. Roychowdhury S, Svensson CK. Mechanisms of drug-induced delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions in the skin. AAPS J. 2005; 7:E834–E846.

8. Kim SH, Kim SH, Yoon HJ, Shin DH, Park SS, Kim YS, et al. TNF-α genetic polymorphism -308G/A and antituberculosis drug-induced hepatitis. Liver Int. 2012; 32:809–814.

9. Kim SH, Kim SH, Yoon HJ, Shin DH, Park SS, Kim YS, et al. GSTT1 and GSTM1 null mutations and adverse reactions induced by antituberculosis drugs in Koreans. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2010; 90:39–43.

10. Lee YH, Harley JB, Nath SK. Meta-analysis of TNF-alpha promoter -308 A/G polymorphism and SLE susceptibility. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006; 14:364–371.

11. Elahi MM, Asotra K, Matata BM, Mastana SS. Tumor necrosis factor alpha -308 gene locus promoter polymorphism: an analysis of association with health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009; 1792:163–172.

12. Lu Z, Chen L, Li H, Zhao Y, Lin L. Effect of the polymorphism of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-308 G/A gene promoter on the susceptibility to ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. Digestion. 2008; 78:44–51.

13. Fernandez TD, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Cornejo-Garcia JA, Lopez S, Chaves P, et al. Cytokine and chemokine expression in the skin from patients with maculopapular exanthema to drugs. Allergy. 2008; 63:712–719.

14. Magee P. Drug-induced skin disorders. In : Walker R, Edwards C, editors. Clinical pharmacy and therapeutics. 3rd ed. Phildelphia: Churchill Livingstone;2003. p. 843–852.
15. Lehloenya RJ, Dheda K. Cutaneous adverse drug reactions to anti-tuberculosis drugs: state of the art and into the future. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012; 10:475–486.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download