Abstract
Purpose
IgE is associated with allergic disease. However, insufficient research has been carried out regarding the levels of serum IgA in children with allergic disease. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the levels of serum immunoglobulin in Korean children with allergic disease and to identify significant correlations between such diseases and serum IgA levels.
Methods
We evaluated 338 children who visited the Pediatric Allergy Clinic, CHA Bundang Medical Center from March 2007 to July 2013. We assessed factors, such as sex, age, and family history of allergic diseases. Laboratory tests, including serum IgG, A, and M, total IgE, and specific IgE, were carried out on all patients. In addition, we compared serum IgA levels in allergic Korean children with normal reference ranges.
Results
The median (interquartile range) of serum IgA values was 31.1 mg/dL (14.3-50.6 mg/dL) in cases of food allergy and 44.3 mg/dL (25.7-94.2 mg/dL) in cases of atopic dermatitis. The serum IgA levels were lower in allergic Korean children aged 9-12 months and 25-72 months than in the normal mean reference values. Relationships between age and serum IgA levels were statistically significant in allergic children.
Figures and Tables
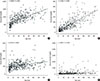 | Fig. 1Correlation of serum immunoglobulin levels to age. Serum IgG (A), IgA (B), IgM (C) were significantly correlated to age, but there was no correlation between serum IgE level and age (D). |
Table 1
Epidemiologic properties of the subjects (n=337)

Table 2
Level of immunoglobulin in all subjects sorted by morbidity

Table 3
Comparison of serum IgA level between Korean allergic childrens and Thai healthy children

SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval.
*Adapted from Sitcharungsi, et al. Microbiol Immunol 2012;56:117-22.31)
Table 4
Comparison of serum IgA level between Korean allergic children and Turkish healthy children

SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval.
*Adapted from Aksu, et al. Turk J Pediatr 2006;48:19.29)
Table 5
Comparison of normal serum IgA range
References
1. Seong HU, Cho SD, Park SY, Yang JM, Lim DH, Kim JH, et al. Nationwide survey on the prevalence of allergic diseases according to region and age. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012; 22:224–231.

2. Kim DI, Yang HJ, Park YM, Rha YH, Choung JT, Pyun BY. Clinical manifestations patterns of allergic disease in Korean children under the age of 6: multi-center study. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:640–645.

3. Park GH, Park JH, Hwang YH, Sung MS, Kim SW. The correlation between the severity of atopic dermatitis classified by SCORing atopic dermatitis index and the laboratory tests. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:79–83.

4. Anupama N, Sharma MV, Nagaraja H, Bhat MR. The serum immunoglobulin E level reflects the severity of bronchial asthma. Thai J Physiol Sci. 2005; 18:35–40.
6. Possin ME, Morgan S, DaSilva DF, Tisler C, Pappas TE, Roberg KA, et al. The relationships among immunoglobulin levels, allergic sensitization, and viral respiratory illnesses in early childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010; 21:990–996.

7. van Asperen PP, Gleeson M, Kemp AS, Cripps AW, Geraghty SB, Mellis CM, et al. The relationship between atopy and salivary IgA deficiency in infancy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985; 62:753–757.
8. Payette K, Weiss NS. Salivary IgA levels in atopic children. Ann Allergy. 1977; 39:328–331.
9. Gleeson M, Clancy RL, Hensley MJ, Cripps AW, Henry RL, Wlodarczyk JH, et al. Development of bronchial hyperreactivity following transient absence of salivary IgA. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996; 06. 153(6 Pt 1):1785–1789.

10. Kukkonen K, Kuitunen M, Haahtela T, Korpela R, Poussa T, Savilahti E. High intestinal IgA associates with reduced risk of IgE-associated allergic diseases. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010; 21(1 Pt 1):67–73.

11. Bottcher MF, Haggstrom P, Bjorksten B, Jenmalm MC. Total and allergen-specific immunoglobulin A levels in saliva in relation to the development of allergy in infants up to 2 years of age. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:1293–1298.
12. Lai A, van Furth R. Serum immunoglobulin levels in various skin diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974; 17:129–137.
13. Senol M, Ozerol E, Sasmaz S, Sahin K, Turan F, Soyturk D. Serum immunoglobulin and complement levels in atopic skin diseases. J Turgut Özal Med Cent. 1997; 4:47–49.
14. Hill PB, Moriello KA, DeBoer DJ. Concentrations of total serum IgE, IgA, and IgG in atopic and parasitized dogs. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1995; 44:105–113.

15. Pesonen M, Kallio MJ, Siimes MA, Savilahti E, Ranki A. Serum immunoglobulin A concentration in infancy, but not human milk immunoglobulin A, is associated with subsequent atopic manifestations in children and adolescents: a 20-year prospective follow-up study. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011; 41:688–696.

16. Ludvíksson BR, Eiríksson TH, Ardal B, Sigfusson A, Valdimarsson H. Correlation between serum immunoglobulin A concentrations and allergic manifestations in infants. J Pediatr. 1992; 121:23–27.

17. Lee JS, Kim TH, Cho GL, Jung JA, Kim JH. The classification between IgE and non-IgE mediated atopic dermatitis in Korean children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2005; 15:352–358.

18. International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee on Primary Immunodeficiencies. Notarangelo LD, Fischer A, Geha RS, Casanova JL, Chapel H, et al. Primary immunodeficiencies: 2009 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:1161–1178.

19. Wang N, Shen N, Vyse TJ, Anand V, Gunnarson I, Sturfelt G, et al. Selective IgA deficiency in autoimmune diseases. Mol Med. 2011; 17:1383–1396.

20. Varelzidis A, Wilson AB, Meara RH, Turk JL. Immunoglobulin levels in atopic eczema. Br Med J. 1966; 2:925–927.

21. Weemaes C, Klasen I, Goertz J, Beldhuis-Valkis M, Olafsson O, Haraldsson A. Development of immunoglobulin A in infancy and childhood. Scand J Immunol. 2003; 58:642–648.

22. Piirainen L, Pesola J, Pesola I, Komulainen J, Vaarala O. Breastfeeding stimulates total and cow's milk-specific salivary IgA in infants. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2009; 20:295–298.

23. Sandin A, Bjorksten B, Bottcher MF, Englund E, Jenmalm MC, Braback L. High salivary secretory IgA antibody levels are associated with less late-onset wheezing in IgE-sensitized infants. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011; 22:477–481.

24. Al-saimary IE, Bakr SS, Al-Hamdi KE. Serum immunoglobulin and complement component levels in patients with atopic dermatitis. Adv Biores. 2013; 4:111.
25. Fraser NG, Dick HM, Crichton WB. Immunoglobulins in dermatitis herpetiformis and various other skin diseases. Br J Dermatol. 1969; 81:89–95.

26. Hong CU. Pediatrics. 10th ed. Seoul: Mirae N;2012. p. 222.
27. Meites S, Buffone GJ. Pediatric clinical chemistry: reference (normal) values. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: AACC Press;1989.
28. Soldin SJ, Brugnara C, Hicks JM. Pediatric reference ranges. Washington, DC: AACC Press;1999.
29. Aksu G, Genel F, Koturoglu G, Kurugol Z, Kutukculer N. Serum immunoglobulin (IgG, IgM, IgA) and IgG subclass concentrations in healthy children: a study using nephelometric technique. Turk J Pediatr. 2006; 48:19–24.
30. Kardar G, Oraei M, Shahsavani M, Namdar Z, Kazemisefat G, Haghi Ashtiani M, et al. Reference Intervals for Serum Immunoglobulins IgG, IgA, IgM and Complements C3 and C4 in Iranian Healthy Children. Iran J Public Health. 2012; 41:59–63.
31. Sitcharungsi R, Ananworanich J, Vilaiyuk S, Apornpong T, Bunupuradah T, Pornvoranunt A, et al. Nephelometry determined serum immunoglobulin isotypes in healthy Thai children aged 2-15 years. Microbiol Immunol. 2012; 56:117–122.

32. Jolliff CR, Cost KM, Stivrins PC, Grossman PP, Nolte CR, Franco SM, et al. Reference intervals for serum IgG, IgA, IgM, C3, and C4 as determined by rate nephelometry. Clin Chem. 1982; 28:126–128.

33. Buckley RH, Dees SC, O'Fallon WM. Serum immunoglobulins. I. Levels in normal children and in uncomplicated childhood allergy. Pediatrics. 1968; 41:600–611.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download