Abstract
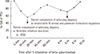
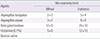
Galactosidase is generated from Aspergillus oryzae, which is widely used for antidiarrhea medicine to infants. Antibiotics and digestives were reported as a causative allergen inducing occupational asthma. Galatosidase-induced occupational asthma has not been reported yet. A forty-year-old female has suffered from rhinorrhea, sneezing, and nasal obstruction 1 year after handling galactosidase at obstetric and pediatric hospital, and then dyspnea appeared later. Skin prick test with inhalent allergens, beta-galactosidase, and Aspergillus oryzae showed strong positive reaction to beta-galactosidase only. Immunoinhibition test with beta-galactosidase and A. oryzae revealed inhibition to beta-galactosidase only. Bronchial provocation test with beta-galactosidase showed the dual asthmatic response. With these results, we confirmed that the patient has beta-galactosidase-induced occupational asthma and rhinitis.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Korean Society of Allergy and Immunology. Occupational asthma. Korean Society of Allergy and Immunology. Asthma and allergic disease. 2nd ed. Seoul: Yeo Moon Gak;2012. p. 286–293.
2. Oh JH, Park SW, Lee GT, Kim KU, Jeoung SW, Uh ST, et al. A case of occupational asthma induced by 7-Aminocephalosporanic acid (7-ACA). Korean J Allergy. 1997; 17:586–591.
3. Vera C, Guerrero C, Conejeros R, Illanes A. Synthesis of galacto-oligosaccharides by β-galactosidase from Aspergillus oryzae using partially dissolved and supersaturated solution of lactose. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2012; 50:188–194.

4. Kim SM, Kim KS, Kim MK. A case of anaphylaxis to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Korean J Med. 2011; 80:365–369.
5. Knuf C, Nielsen J. Aspergilli: systems biology and industrial applications. Biotechnol J. 2012; 7:1147–1155.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download