Abstract
Eosinophilic cholecystitis (EC) is a rare form of acute cholecystitis, of which diagnosis is based on classical symptoms of cholecystitis with a presence of >90% eosinophilic infiltration within the gall bladder. EC rarely manifests in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome (IHES). Here, we report two cases of EC with IHES. One is a 57-year-old male who presented with acute right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain, jaundice and fever. The initial peripheral blood eosinophil count was 2,070/mm3, and further elevated to 12,590/mm3. Acute acalculous cholecystitis with cholangitis was confirmed by computed tomography (CT). He improved with endocopic nasobiliary drainage and antibiotic therapy. The other is a 64-year-old female who presented with acute RUQ pain. She also complained of dyspnea and tingling sensation of both hands and feet. The initial peripheral blood eosinophil count was 10,400/mm3. Abdominal CT revealed findings suggestive of acute acalculous cholecystitis. She improved with systemic glucocorticosteroid therapy. No other causes of hypereosinophilia were found in either patients. Thus, cholecystectomy may not be mandatory for the treatment of EC with IHES.
Figures and Tables
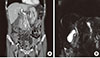
Fig. 1
(A) Abdominal computed tomography shows diffuse wall thickening and mild dilatation of gall bladder and common bile duct which is compatible with acute cholangitis and cholecystitis. (B) Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography shows normal passage of bile. There is not any filling defect in gall bladder and bile duct by stone or mass. (C) Esophagogastroduodenoscopic biopsy shows diffuse eosinophilic infiltration (>50/high power field) in the stomach (H&E, ×400).

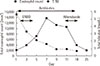
Fig. 2
Clinical course of the patients. Total bilirubin (T. Bil) level (●) was gradually recoverd after endoscopic nasobiliary drainage (ENBD) insertion. Total peripheral eosinophil count (■) was also recovered from hospital day 8.
References
1. Fox H, Mainwaring AR. Eosinophilic infiltration of the gallbladder. Gastroenterology. 1972; 63:1049–1052.

2. Kerstein MD, Sheahan DG, Gudjonsson B, Lewis J. Eosinophilic cholecystitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1976; 66:349–352.
4. Felman RH, Sutherland DB, Conklin JL, Mitros FA. Eosinophilic cholecystitis, appendiceal inflammation, pericarditis, and cephalosporin-associated eosinophilia. Dig Dis Sci. 1994; 39:418–422.

5. Kim YM, Lee DY, Lee JS. A case of eosinophilic cholecystitis associated with eosinophilic cholangitis and pancreatitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2000; 35:664–670.
6. Shakov R, Simoni G, Villacin A, Baddoura W. Eosinophilic cholecystitis, with a review of the literature. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2007; 37:182–185.
7. Chusid MJ, Dale DC, West BC, Wolff SM. The hypereosinophilic syndrome: analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1975; 54:1–27.
9. Tefferi A, Patnaik MM, Pardanani A. Eosinophilia: secondary, clonal and idiopathic. Br J Haematol. 2006; 133:468–492.

10. Choi DC. Eosinophilia. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:237–245.
11. Yeom SS, Kim HH, Kim JC, Hur YH, Koh YS, Cho CK, et al. Peripheral eosinophilia - is it a predictable factor associated with eosinophilic cholecystitis? Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2012; 16:65–69.

12. Rosengart TK, Rotterdam H, Ranson JH. Eosinophilic cholangitis: a self-limited cause of extrahepatic biliary obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990; 85:582–585.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download