Abstract
Fat embolism syndrome is a serious complication that can occur after trauma or operation of the limbs. Clinical criteria are used for the diagnosis of fat embolism syndrome and sometimes radiologic findings are helpful. Fat embolism syndrome is known to occur less frequently in children than in adults, but there is an increased risk in children with connective tissue disease. However, there are only a few reported cases of fat embolism syndrome in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis which is the most common connective tissue disease in children. We report a case of fat embolism syndrome diagnosed in a 13-year-old boy with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, which was treated with corticosteroid.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Initial chest computed tomographic scan shows ground-glass opacities at the left lower lobe (arrows).
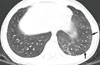
Fig. 2
(A) Chest radiograph obtained 2 days after admission revealed bilateral diffuse haziness. (B) Follow-up chest computed tomographic scans obtained on the same day demonstrate multiple small nodules (arrows) and diffuse ground-glass opacities in both lungs.
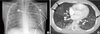
Fig. 3
Fundus exam shows multiple white patches in the right fundus with an embolic infarct at the macula.

Fig. 4
Ten days later, nodular and ground-glass opacities on chest computed tomography were completely resolved.
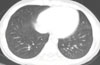
Table 1
Gurd's diagnostic criteria of fat embolism

Fat embolism syndrome=1 major+4 minor+fat macroglobulinemia.
Reproduced from Gurd and Wilson. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1974;56B:408-16, with permission of the British Editorial Society of Bone and Joint Surgery.7)
Table 2
Fat embolism index

Fat embolism syndrome=5 or more score.
Reproduced from Schonfeld et al. Ann Intern Med 1983;99:438-43, with permission of American College of Physicians.2)
References
2. Schonfeld SA, Ploysongsang Y, DiLisio R, Crissman JD, Miller E, Hammerschmidt DE, et al. Fat embolism prophylaxis with corticosteroids. A prospective study in high-risk patients. Ann Intern Med. 1983. 99:438–443.
3. Gossling HR, Pellegrini VD Jr. Fat embolism syndrome: a review of the pathophysiology and physiological basis of treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982. 165:68–82.
4. Drummond DS, Salter RB, Boone J. Fat embolism in children: its frequency and relationships to collagen disease. Can Med Assoc J. 1969. 101:200–203.
8. Talbot M, Schemitsch EH. Fat embolism syndrome: history, definition, epidemiology. Injury. 2006. 37:Suppl 4. S3–S7.

9. Malagari K, Economopoulos N, Stoupis C, Daniil Z, Papiris S, Muller NL, et al. High-resolution CT findings in mild pulmonary fat embolism. Chest. 2003. 123:1196–1201.

10. Lindeque BG, Schoeman HS, Dommisse GF, Boeyens MC, Vlok AL. Fat embolism and the fat embolism syndrome. A double-blind therapeutic study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987. 69:128–131.

11. Kubota T, Ebina T, Tonosaki M, Ishihara H, Matsuki A. Rapid improvement of respiratory symptoms associated with fat embolism by high-dose methylpredonisolone: a case report. J Anesth. 2003. 17:186–189.

12. Rabinovich CE. Pulmonary complications of childhood rheumatic disease. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2012. 13:29–36.

13. Athreya BH, Doughty RA, Bookspan M, Schumacher HR, Sewell EM, Chatten J. Pulmonary manifestations of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. A report of eight cases and review. Clin Chest Med. 1980. 1:361–374.
14. Moon JM, So JI, Kim YK, Ryoo JH, Heo T, Seo JJ, et al. Post-traumatic cerebral fat embolism. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2001. 12:170–175.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download