Abstract
Purpose
Mycoplasma pneumonia (MP) is a major cause of community-acquired pneumonia in children and young adults. We aimed to investigate the factors that may influence on the clinical manifestations of MP in children.
Methods
A total of 109 admitted children from October 2011 to February 2012 were prospectively enrolled with physical examination and laboratory tests (complete blood count, C-reactive protein [CRP], and particle agglutinin assay). The diagnosis of MP was made when there was an infiltration on the chest X-ray and the particle agglutination test was once over 1:640 or showed 4-fold increase in serial tests. They were grouped by age, fever duration after treatment, presence of pleural effusion and wheezing.
Results
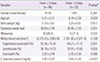
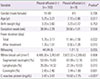
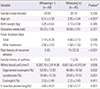
Preschool children showed shorter duration of fever (P=0.001), more wheezing (P<0.001), lower segmented neutrophil (P<0.001), and lower CRP levels (P=0.004) compared to schoolchildren. Prolonged fever (>3 days) and pleural effusion were developed in children with higher CRP (P=0.018 and P=0.007). Wheezing has been developed in children with younger age (P=0.007).
Figures and Tables
References
1. Atkinson TP, Balish MF, Waites KB. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, pathogenesis and laboratory detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008; 32:956–973.

2. Lee KY. Pediatric respiratory infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008; 6:509–521.
3. Kim JW, Seo HK, Yoo EG, Park SJ, Yoon SH, Jung HY, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children, from 1979 to 2006-a meta-analysis. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:315–323.

4. Lee SH, Noh SM, Lee KY, Lee HS, Hong JH, Lee MH, et al. Clinico-epidemiologic Study of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia (1993 through 2003). Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48:154–157.
5. Youn YS, Lee KY, Hwang JY, Rhim JW, Kang JH, Lee JS, et al. Difference of clinical features in childhood Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. BMC Pediatr. 2010; 10:48.

6. Hong SJ. The role of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:59–61.

7. Hong JY, Nah SY, Nam SG, Choi EH, Park JY, Lee HJ. Occurrence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Seoul, Korea, from 1986 to 1995. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1997; 40:607–613.
8. Nagayama Y, Sakurai N, Yamamoto K, Honda A, Makuta M, Suzuki R. Isolation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae from children with lower-respiratory-tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1988; 157:911–917.

9. Defilippi A, Silvestri M, Tacchella A, Giacchino R, Melioli G, Di Marco E, et al. Epidemiology and clinical features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in children. Respir Med. 2008; 102:1762–1768.

10. Kim KW, Kim KE. Mycoplasma and chlamydia infection in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:277–282.

11. Youn YS, Lee KY. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2012; 55:42–47.
12. Xia Y, Wu CK, Tang YY, Cao J. Differences in the clinical features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia among children of different ages. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2013; 15:179–182.
13. Lieberman D, Lieberman D, Printz S, Ben-Yaakov M, Lazarovich Z, Ohana B, et al. Atypical pathogen infection in adults with acute exacerbation of bronchial asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 167:406–410.

14. Esposito S, Blasi F, Arosio C, Fioravanti L, Fagetti L, Droghetti R, et al. Importance of acute Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae infections in children with wheezing. Eur Respir J. 2000; 16:1142–1146.

15. Kim KW, Lee BC, Lee KE, Kim ES, Song TW, Park MY, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced production of proasthmatic mediators in airway epithelium. Korean J Pediatr. 2006; 49:977–982.

16. Yang J, Hooper WC, Phillips DJ, Talkington DF. Cytokines in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004; 15:157–168.

17. Lazaar AL, Panettieri RA Jr. Airway smooth muscle: a modulator of airway remodeling in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 116:488–495.

18. Lee CG, Link H, Baluk P, Homer RJ, Chapoval S, Bhandari V, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces remodeling and enhances TH2-mediated sensitization and inflammation in the lung. Nat Med. 2004; 10:1095–1103.

19. Kim JT. Laboratory diagnosis of Mycoplasma infection. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2006; 16:23–25.
20. Waites KB. New concepts of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2003; 36:267–278.
21. Chan PW, Lum LC, Ngeow YF, Yasim MY. Mycoplasma Pneumoniae infection in Malaysian children admitted with community acquired pneumonia. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2001; 32:397–401.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download