Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to determine the prevalence of allergic rhinitis and nonallergic rhinitis, difference in symptoms between allergic rhinitis and nonallergic rhinitis, and the association between lung function and the degree of asthma control in children with asthma.
Methods
One hundred seventy patients who were followed-up for asthma treatment at the department of pediatrics of CHA Bundang Medical Center were enrolled in this study. We conducted the questionnaire regarding coexistence of rhinitis, childhood asthma control test (C-ACT), and the basic lung function test. The patients were classified as allergic rhinitis group and nonallergic rhinitis group according to the response to 11 common inhalation and food allergens, and assessed the degree of asthma control and the severity of rhinitis.
Results
One hundred thirty patients (73%) were found to have rhinitis. Of these, 79 patients (53%) had allergic rhinitis and 34 patients (20%) had nonallergic rhinitis. The allergic rhinitis group was older than the nonallergic rhinitis group or the nonrhinitis group (7.73±2.85 vs. 5.97±2.48 vs. 6.12±2.70, P<0.001). Nasal itching sense was more prevalent in the allergic-rhinitis group than in the nonallergic rhinitis group (3.23±1.90 vs. 2.44±1.56, P=0.036). There was an inverse correlation between the rhinitis and C-ACT (r= -0.329, P<0.05). Of note, nasal obstruction symptom was highly correlated with C-ACT (r=-0.334, P<0.001).
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
The relationship between nasal severity scores (total visual analog scale [VAS] score) and childhood asthma control test (C-ACT) (r=-0.329 and P<0.001).
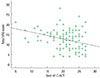
Table 2
Comparison of subjects with allergic rhinitis, nonallergic rhinitis, and nonrhinitis (n=170)
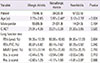
Values are presented as number (%) or mean±standard deviation. Analysis of variance testing with post hoc Scheffe analysis was used to assess differences between groups.
C-ACT, childhood asthma control test; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC, forced vital capacity; MMEF, maximum mid expiratory flow; Xrs5, reactance at 5 Hz; Rrs5, resistance at 5 Hz.
*Nonallergic rhinitis group versus allergic rhinitis group, P=0.008. †Nonrhinitis group versus allergic rhinitis group, P=0.004.
References
1. Miraglia Del Giudice M, Marseglia A, Leonardi S, La Rosa M, Salpietro C, Brunese FP, et al. Allergic rhinitis and quality of life in children. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2011; 24:4 Suppl. 25–28.

2. Westman M, Stjarne P, Asarnoj A, Kull I, van Hage M, Wickman M, et al. Natural course and comorbidities of allergic and nonallergic rhinitis in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:403–408.

3. Leynaert B, Neukirch F, Demoly P, Bousquet J. Epidemiologic evidence for asthma and rhinitis comorbidity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 106:5 Suppl. S201–S205.

4. Rusconi F, Galassi C, Corbo GM, Forastiere F, Biggeri A, Ciccone G, et al. Risk factors for early, persistent, and late-onset wheezing in young children. SIDRIA Collaborative Group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; 160(5 Pt 1):1617–1622.

5. Valovirta E, Pawankar R, et al. Survey on the impact of comorbid allergic rhinitis in patients with asthma. BMC Pulm Med. 2006; 6:Suppl 1. S3.

6. Ray NF, Baraniuk JN, Thamer M, Rinehart CS, Gergen PJ, Kaliner M, et al. Healthcare expenditures for sinusitis in 1996: contributions of asthma, rhinitis, and other airway disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 103(3 Pt 1):408–414.

7. Chawes BL, Bonnelykke K, Kreiner-Moller E, Bisgaard H. Children with allergic and nonallergic rhinitis have a similar risk of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:567–573.e1-8.

8. Lötvall J, Ekerljung L, Lundback B. Multi-symptom asthma is closely related to nasal blockage, rhinorrhea and symptoms of chronic rhinosinusitis-evidence from the West Sweden Asthma Study. Respir Res. 2010; 11:163.

9. Mølgaard E, Thomsen SF, Lund T, Pedersen L, Nolte H, Backer V. Differences between allergic and nonallergic rhinitis in a large sample of adolescents and adults. Allergy. 2007; 62:1033–1037.

10. Liu AH, Zeiger R, Sorkness C, Mahr T, Ostrom N, Burgess S, et al. Development and cross-sectional validation of the Childhood Asthma Control Test. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:817–825.

12. Manohar S, Selvakumaran R. Estimation of serum immunoglobulin E (IgE) level in allergic asthma and allergic rhinitis patients before and after treatment. Eur J Exp Bio. 2012; 2:2199–2205.
13. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; 63:Suppl 86. 8–160.
14. Seo HK, Chang SJ, Jung DW, Wee YS, Jee HM, Seo JY, et al. The quality control and acceptability of spirometry in preschool children. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:1267–1272.

15. Dencker M, Malmberg LP, Valind S, Thorsson O, Karlsson MK, Pelkonen A, et al. Reference values for respiratory system impedance by using impulse oscillometry in children aged 2-11 years. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2006; 26:247–250.

17. Greisner WA 3rd, Settipane RJ, Settipane GA. Co-existence of asthma and allergic rhinitis: a 23-year follow-up study of college students. Allergy Asthma Proc. 1998; 19:185–188.

18. Masuda S, Fujisawa T, Katsumata H, Atsuta J, Iguchi K. High prevalence and young onset of allergic rhinitis in children with bronchial asthma. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2008; 19:517–522.

19. de Groot EP, Duiverman EJ, Brand PL. Comorbidities of asthma during childhood: possibly important, yet poorly studied. Eur Respir J. 2010; 36:671–678.

21. Asher MI, Montefort S, Bjorksten B, Lai CK, Strachan DP, Weiland SK, et al. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006; 368:733–743.

22. Skoner DP. Allergic rhinitis: definition, epidemiology, pathophysiology, detection, and diagnosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:1 Suppl. S2–S8.

23. Hamouda S, Karila C, Connault T, Scheinmann P, de Blic J. Allergic rhinitis in children with asthma: a questionnaire-based study. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:761–766.

24. Van Cauwenberge P, Van Hoecke H. Management of allergic rhinitis. B-ENT. Suppl 1. 2005; 45–62.
25. Bousquet PJ, Combescure C, Neukirch F, Klossek JM, Mechin H, Daures JP, et al. Visual analog scales can assess the severity of rhinitis graded according to ARIA guidelines. Allergy. 2007; 62:367–372.

26. Mastin T. Recognizing and treating non-infectious rhinitis. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2003; 15:398–409.

27. Di Lorenzo G, Pacor ML, Amodio E, Leto-Barone MS, La Piana S, D'Alcamo A, et al. Differences and similarities between allergic and nonallergic rhinitis in a large sample of adult patients with rhinitis symptoms. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011; 155:263–270.

28. Vichyanond P, Suratannon C, Lertbunnaphong P, Jirapongsananuruk O, Visitsunthorn N. Clinical characteristics of children with non-allergic rhinitis vs with allergic rhinitis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2010; 28:270–274.
29. Taussig LM, Wright AL, Holberg CJ, Halonen M, Morgan WJ, Martinez FD. Tucson Children's Respiratory Study: 1980 to present. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:661–675.

30. Ciprandi G, Pistorio A, Tosca M, Cirillo I. Relationship between rhinitis duration and response to nasal decongestion test. Laryngoscope. 2008; 118:1139–1141.

31. Kurukulaaratchy RJ, Fenn M, Matthews S, Arshad SH. Characterisation of atopic and non-atopic wheeze in 10 year old children. Thorax. 2004; 59:563–568.

32. Yin J, Kemp AS, van Asperen PP. Pulmonary function in non-atopic and atopic childhood asthma. Acta Paediatr. 2007; 96:1088–1090.

33. Navarro A, Valero A, Julia B, Quirce S. Coexistence of asthma and allergic rhinitis in adult patients attending allergy clinics: ONEAIR study. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2008; 18:233–238.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download