Abstract
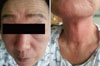
Eperisone hydrochloride is an antispasmodic drug, decreasing spasticity of skeletal muscle and alleviating stiffness, and as a consequence, controlling pain. It is preferably prescribed with other analgesics, beneficially less decreasing alertness compared with other antispasmodics. Its fatal drug adverse reactions were rarely reported. A 70 year-old female with hives, swollen face, hoarse voice, and near fainting admitted via emergency department. She suffered from the series of the fatal symptoms after administration of the pills, prescribed for her neck pain. Two months before, she had experienced hives on similar medications. At presentation, she revealed hypoxemia and hypotension, and treated with epinephrine, glucocorticoids and antihistamines. Among the medicines she took, eperisone hydrochloride was proven as the causative medicine and others were excluded in oral provocation tests. The positive result in intradermal test with eperisone hydrochloride suggested immediate-type hypersensitivity reaction. We report a case of anaphylaxis to eperisone hydrochloride, one of the widely prescribed medicines in clinical practice, previously without awareness of drug adverse reaction.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Inoue S, Bian K, Okamura T, Okunishi H, Toda N. Mechanisms of action of eperisone on isolated dog saphenous arteries and veins. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1989; 50:271–282.

2. Iwase S, Mano T, Saito M, Ishida G. Effect of a centrally-acting muscle relaxant, eperisone hydrochloride, on muscle sympathetic nerve activity in humans. Funct Neurol. 1992; 7:459–470.
3. Matsunaga M, Uemura Y, Yonemoto Y, Kanai K, Etoh H, Tanaka S, et al. Long-lasting muscle relaxant activity of eperisone hydrochloride after percutaneous administration in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1997; 73:215–220.

4. Ochiai T, Ishida R. Pharmacological studies on 6-amino-2-fluoromethyl-3-(O-tolyl)-4(3H)-quinazolinone (afloqualone), a new centrally acting muscle relaxant. (II) Effects on the spinal reflex potential and the rigidity. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1982; 32:427–438.

5. Kim YK. Drug allergy update. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 20:855–865.
6. Lee AY. Drug allergy update. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002; 22:669–676.
7. Brockow K, Romano A, Blanca M, Ring J, Pichler W, Demoly P. General considerations for skin test procedures in the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity. Allergy. 2002; 57:45–51.

8. Suzuki Y, Ra C. Analysis of the mechanism for the development of allergic skin inflammation and the application for its treatment: aspirin modulation of IgE-dependent mast cell activation: role of aspirin-induced exacerbation of immediate allergy. J Pharmacol Sci. 2009; 110:237–244.

9. Choonhakarn C. Non-pigmenting fixed drug eruption: a new case due to eperisone hydrochloride. Br J Dermatol. 2001; 144:1288–1289.

10. Ueno T, Kawana S. A case of eperisone hydrochloride (myonal): induced drug eruption leading to erythema and angioedema. Arerugi. 2007; 56:709–713.
11. Demitsu T, Tomita Y. Fixed drug eruption due to afloqualone: the first reported case. J Dermatol. 1998; 25:136.

12. Ribi C, Vermeulen C, Hauser C. Anaphylactic reactions to tolperisone (Mydocalm). Swiss Med Wkly. 2003; 133:369–371.
13. Hur GY, Hwang EK, Moon JY, Ye YM, Shim JJ, Park HS, et al. Oral muscle relaxant may induce immediate allergic reactions. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:863–865.

14. Cho YJ. Update on the diagnosis of drug allergy. Korean J Med. 2009; 76:282–290.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download