Abstract
We report a rare case of a 71-year-old male patient who had suffered from long-lasting neurogenic shock for 13 weeks after cervical spinal cord injury (SCI) caused by a bicycle accident. The neurogenic shock was resolved dramatically 2 weeks after the administration of alpha-1-adrenergic agonist, midodrine hydrochloride. In usual cases, neurogenic shock tends to improve between 2 and 6 weeks after SCI; however, in a few cases, the shock lasts for several months. In our case, spinal shock lasted for 13 weeks and exhibited very sensitive decline of blood pressure for even a slight decrease of dopamine despite recovered bulbospongiosus reflex. Three days after midodrine hydrochloride was added, hypotension improved dramatically. We discuss our rare case with pertinent literatures.
Go to : 
Although the duration of neurogenic spinal shock varies, spinal shock generally begins to improve within approximately 2 to 6 weeks.2) In a few cases, however, neurogenic shock can unusually last for several more months. Early recovery of spinal shock will be important in the prognosis of a patient with spinal cord injury (SCI). Yet, the exact cause of maintained neurogenic shock after SCI still remains unclear, and there are only several options that can be suggested for possible treatments. We report a 71-year-old male patient with sustained spinal shock for 13 weeks after acute SCI. In addition, we report an attempted treatment option of stopping dopamine infusion for 2 weeks after initial response to midodrine hydrochloride.
Go to : 
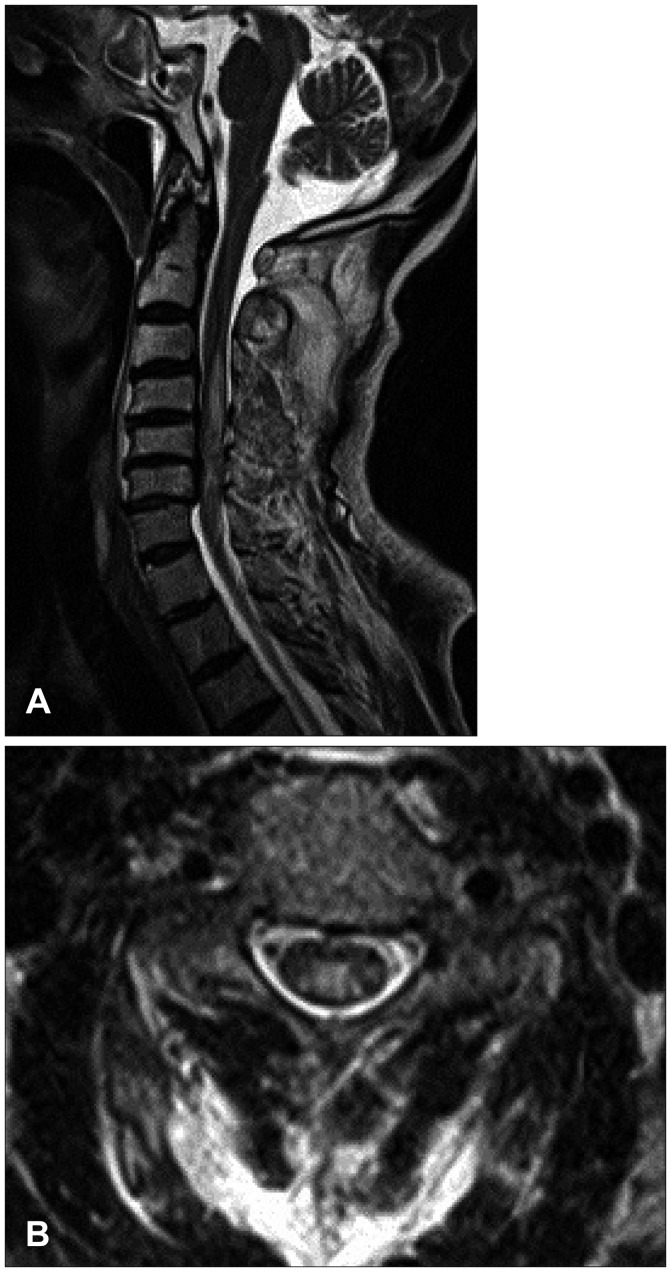
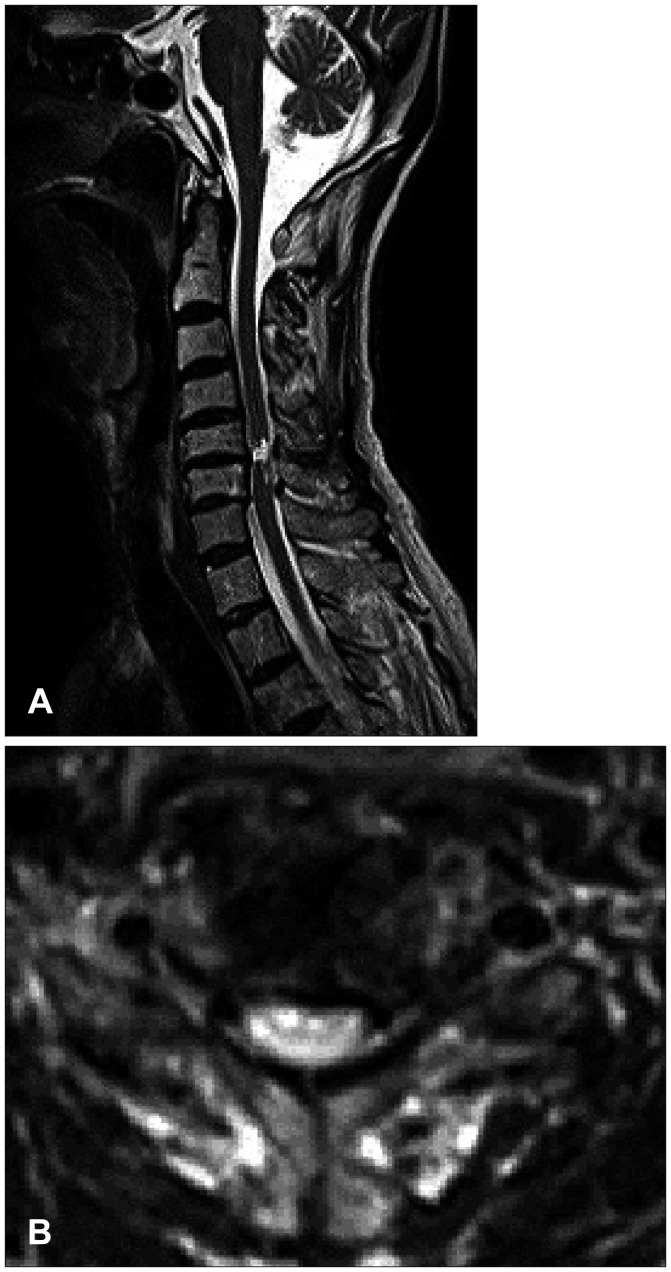
The 71-year-old male presented quadriparesis and drowsiness caused by a bicycle accident a day ago. He was healthy with unremarkable medical history before admission. Initial vital sign was low blood pressure (systolic blood pressure 60 mm Hg, pulse rate 96/min). Initial neurological examinations showed drowsy mentality, quadriparesis (both upper limbs grade 3 and complete paraplegia), anesthesia below T4 dermatome, urinary retention, and decreased anal sphincter tone. According to the American Spinal Injury Association (ASIA) impairment scale, the neurological severity of a SCI was class B. The patient suddenly developed severe bradycardia (below 45/min), hypotension (systolic blood pressure 45 mm Hg), and respiratory difficulty while waiting for additional tests. We immediately administered intravenous bolus atropine and crystalloids, continuously infused dopamine, and performed endotracheal intubation. Electrocardiography and laboratory data were all within normal limits. Initial T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the cervical spine showed high signal intensity with diffuse spinal cord edema at C3 to C7 level accompanied with multilevel spondylosis (Figure 1). Small epidural hematoma along the left frontal convexity and skull fracture on the left frontal area were also noted through the computed tomography of the brain. Conservative treatment was maintained at the intensive care unit with continuous dopamine infusion to achieve blood pressure of 120/80 mm Hg and pulse rate of 60/min. Consciousness was fully improved after the vital signs were restored. The 4-week hospital course was complicated by pneumonia and paralytic ileus, resulting in maintained endotracheal intubation and ventilator support. Despite thigh-high compression stocking, adequate hydration, increased salt intake, and gradual changes in position, hypotension after spinal shock was not resolved. There was no sign of fever found, and laboratory data or blood culture was normal. We tried to lower the rate of dopamine infusion (12-15 µg/kg/min), but reverted to the original regimen of continuous infusion at the rate of 15 µg/kg/min under blood pressure and central venous pressure monitoring since even a slight change of rolling posture caused a notable drop in blood pressure and triggered dizziness. Eight weeks after admission, the weakness of distal upper limb and sensory functions slightly improved and bulbospongiosus reflex was positive. The follow-up ASIA impairment scale was class C. The follow-up MRI at week 8 showed a focal severe myelomalatic change between C5 and C6 level (Figure 2). Although bulbospongiosus reflex was restored, hypotension did not improve. Additional pseudoephedrine (180 mg per day) was administered for 2 weeks; however, it was not effective enough to prevent orthostatic hypotension. Thus, we added midodrine hydrochloride (7.5 mg/day). From day 3 of adding midodrine hydrochloride, blood pressure was maintained at 120/80 mm Hg despite a gradual decrease of dopamine. We decreased dopamine dosage by 1 µg/kg/min per day for 2 weeks since we started to add midodrine hydrochloride. The hemodynamic state of the patient remained stable, and the patient did not complain of dizziness. Six months later, he was died of pneumonia.
Go to : 
A drop in blood pressure related to an acute cervical SCI causes severe hypotension and bradycardia, also known as neurogenic shock or spinal shock. Neurogenic shock is one of the manifestation of autonomic nervous system dysfunction observed following SCI as a result of the imbalance of autonomic control, with an intact parasympathetic influence via the vagal nerve and a loss of sympathetic tone because of the disruption in supraspinal control.48) Damage between T1 and T4 may shut down sympathetic nerve innervated to visceral organs, but a sympathetic nerve will act on heart to increase pulse rate and heart contractility to compensate low blood pressure. However, a patient in our case had every sympathetic nerves shut off due to cervical SCI which resulted in vessel distention and blood pooling without any means of compensation. This made it more difficult to treat hypotension. According to the literature, severe hypotension was noted up to 6 weeks after SCI.2) The incidence rate of neurogenic shock caused by cervical SCI was reported as 19.3% while the incidence rates of neurogenic shock in thoracic SCI and lumbar SCI were 7.0% and 3.0% respectively.246) As of treatment, it is recommended that the minimum mean arterial blood pressure be maintained at 85 mm Hg with a correction of bradycardia and hypotension to avoid spinal cord ischemia.4) If hemodynamic instability with low central venous pressure persists despite loading crystalloid and colloid volumes, the high dose of vasopressors such as norepinephrine, dobutamine, and dopamine will be needed. Additionally, the combination of pharmacologic agents such as fludrocortisone, ephedrine, and midodrine with non-pharmacologic interventions such as exercise programs, indoor temperature control, and the usage of elastic stocking or abdominal binder will be required in order to achieve successful treatment of spinal shock.348) Fludrocortisone is a potent mineralocorticoid with little glucocorticoid activity that retains sodium and fluid which cause increased blood pressure, electrolyte imbalance, weight gain, or edema so that it can aggravate the overall condition of patients with congestive heart failure.36) Midodrine, on the other hand, is a prodrug which is metabolized into desglymidodrine and can be easily absorbed (93%) so that it functions restrictively on gastrointestinal vasculature.69) Furthermore, midodrine causes less frequent and severe alpha-adrenergic effect than ephedrine or other sympathomimetic agents. Frequent adverse effects include scalp paresthesia (18.3%), piloerection (13.4%), dysuria (13.4%), pruritus (12.2%), supine hypertension, and chills and pain which are quite mild and easily controlled by lowering the dosage.510) Midodrine has been used for patients with SCI and orthostatic hypotension because it directly raises the blood pressure by constricting arterioles and veins and increases peripheral vascular resistance.6) In addition, the supersensitivity of vascular alpha-adrenoceptors in patients with SCI reinforces the pharmacologic effect of midodrine. Barber et al.1) reported two cases of successfully treated orthostatic hypotension by midodrine that had been refractory to classic treatment interventions. The other report by Mukand et al.6) showed that a single individual with C6 tetraplegia who had severe orthostatic hypotension unresponsive to various treatment options experienced excellent results with midodrine for 4 weeks. In double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of midodrine for exercise performance enhancement in tetraplegia study, Nieshoff et al.7) demonstrated that midodrine enhances exercise performance in some patients with SCI, similar to other clinical populations with cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction. In our case, the treatment with peripheral selective alpha-1-adrenergic agonist (midodrine, 7.5 mg daily) was given in order to resolve spinal shock.3) Both objective and subjective conditions were favorable since the addition of midodrine without any side effects. The patient showed better hemodynamic recovery from spinal shock 2 weeks after the additional administration of midodrine.
Go to : 
References
1. Barber DB, Rogers SJ, Fredrickson MD, Able AC. Midodrine hydrochloride and the treatment of orthostatic hypotension in tetraplegia: two cases and a review of the literature. Spinal Cord. 2000; 38:109–111. PMID: 10762185.

2. Casha S, Christie S. A systematic review of intensive cardiopulmonary management after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2011; 28:1479–1495. PMID: 20030558.

3. Freeman R. Clinical practice. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:615–624. PMID: 18256396.
4. Hagen EM, Faerestrand S, Hoff JM, Rekand T, Gronning M. Cardiovascular and urological dysfunction in spinal cord injury. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2011; (191):71–78. PMID: 21711260.

5. McTavish D, Goa KL. Midodrine. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in orthostatic hypotension and secondary hypotensive disorders. Drugs. 1989; 38:757–777. PMID: 2480881.
6. Mukand J, Karlin L, Barrs K, Lublin P. Midodrine for the management of orthostatic hypotension in patients with spinal cord injury: a case report. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 82:694–696. PMID: 11346851.

7. Nieshoff EC, Birk TJ, Birk CA, Hinderer SR, Yavuzer G. Double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial of midodrine for exercise performance enhancement in tetraplegia: a pilot study. J Spinal Cord Med. 2004; 27:219–225. PMID: 15478524.
8. Teasell RW, Arnold JM, Krassioukov A, Delaney GA. Cardiovascular consequences of loss of supraspinal control of the sympathetic nervous system after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000; 81:506–516. PMID: 10768544.

9. Thulesius O, Gjöres JE, Berlin E. Vasoconstrictor effect of midodrine, ST 1059, noradrenaline, etilefrine and dihydroergotamine on isolated human veins. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979; 16:423–424. PMID: 93544.

10. Wright RA, Kaufmann HC, Perera R, Opfer-Gehrking TL, McElligott MA, Sheng KN, et al. A double-blind, dose-response study of midodrine in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. Neurology. 1998; 51:120–124. PMID: 9674789.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download