Abstract
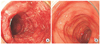
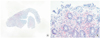
Oseltamivir has been used as a worldwide preparation for treatment of influenza A and B including H1N1. Gastrointestinal discomforts as like nausea, vomiting are commonly reported but acute hemorrhagic colitis is a very rare adverse effect. We report a case of a 17-year-old male who showed abdominal pain, diarrhea and hematochezia after the second administration of oseltamivir. Computed tomography revealed continuous, circumferential and edematous wall thickening involving ascending to descending colon with pericolic infiltration. Colonoscopic examination revealed diffuse mucosal edema, congestion and friability, suggesting hemorrhagic colitis. Histopathological examination showed ischemia and focal loss of the crypts. It also showed hyalinization and minimal inflammatory cell infiltration in the lamina propria, consistent with acute to subacute ischemic colitis. This report is the first case of oseltamivir-related ischemic colitis proved by both endoscopic examination and pathologic findings in the patient who had no risk factor of ischemic colitis in Korea.
Figures and Tables
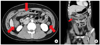 | Fig. 1Abdominal computed tomography. (A) In axial view, it shows circumferential and edematous wall thickening involving ascending to descending colon (arrows). (B) In coronal view, it shows continuous transverse wall thickening and pericolic infiltration (arrow). |
References
1. Jeong HJ. Influenza. The Korean Society of Infectious Diseases. Infectious diseases. 2nd ed. Seoul: Koonja;2014. p. 831–852.
2. Riley LW. The epidemiologic, clinical, and microbiologic features of hemorrhagic colitis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987; 41:383–407.
3. Matsushita M, Nishihara H, Nishiyama R, Kobayashi Y. Acute hemorrhagic colitis associated with oral administration of oseltamivir for the treatment of influenza A. J Infect Chemother. 2007; 13:267–269.
4. Ryu KH, Shim KN, Jung SA, Kim SE, Oh HJ, Song HJ, et al. Clinical features of ischemic colitis: a comparision with colonoscopic findings. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 33:145–151.
5. Lim YJ, Son HJ, Kang TW, Kim GC, Lee MS, Lee JH, et al. Clinical patterns and prognostic factors of ischemic colitis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 22:76–82.
6. Saegesser F, Loosli H, Robinson JW, Roenspies U. Ischemic diseases of the large intestine. Int Surg. 1981; 66:103–117.
7. Ina K, Kusugami K, Ohta M. Bacterial hemorrhagic enterocolitis. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:111–120.
8. Green BT, Tendler DA. Ischemic colitis: a clinical review. South Med J. 2005; 98:217–222.
9. Shim HJ, Cho SH, Lee JK, Ahn JS, Yang DH, Kim YK, et al. A case of extensive hemorrhagic colitis after docetaxel-based combination chemotherapy. Korean J Med. 2006; 70:207–212.
10. Khor TS, Fujita H, Nagata K, Shimizu M, Lauwers GY. Biopsy interpretation of colonic biopsies when inflammatory bowel disease is excluded. J Gastroenterol. 2012; 47:226–248.
11. Yoneda S, Kobayashi Y, Nunoi T, Takeda K, Matsumori A, Andoh M, et al. Acute hemorrhagic colitis induced by the neuraminidase inhibitor oseltamivir. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2006; 103:1270–1273.
12. Nakagawa Y, Nagai T, Okawara H, Nakashima H, Hisamatsu A, Shuto M, et al. Acute hemorrhagic colitis induced by the oral administration of oseltamivir used for influenza A treatment. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:Suppl 2 UCTN. E261.
13. Chen YH, Lai HJ. Acute hemorrhagic colitis after oral administration of oseltamivir for influenza. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:976.
14. Chung DW, Son HS, Park JH, Jung MK, Jeon SW, Cho CM, et al. Acute hemorrhagic colitis associated with the use of oseltamivir. Korean J Med. 2011; 80:Suppl 2. S87–S90.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download