Abstract
Spontaneous pneumomediastinum is an uncommon disease that is defined as the presence of free air in the mediastinum in the absence of any obvious precipitating cause. This condition occurs as a rare complication of acute exacerbation of asthma. Classic symptoms include retrosternal chest pain, dyspnea and cough, but are not specific. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum complicated by asthma is usually self-limiting and well controlled with conservative management, but this condition can be potentially life threatening. We report a case of 18-year-old woman with asthma who presented with spontaneous pneumomediastinum. The patient was treated conservatively with oxygen and steroid therapy, and her clinical conditions were improved. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum disappeared.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Chest X-ray findings on admission. (A) A posteroanterior view of chest X-ray shows linear air density extended vertically from the internal side of left clavicle into the neck (arrow). (B) A lateral view of chest X-ray shows no obvious air density.
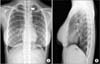
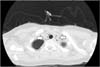
Fig. 2
Chest computed tomography (CT) findings on admission. An axial CT image shows diffuse pneumomediastinum around neck, esophagus, aorta and trachea (arrow).
References
1. Chalumeau M, Le Clainche L, Sayeg N, Sannier N, Michel JL, Marianowski R, et al. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2001; 31:67–75.
2. Macia I, Moya J, Ramos R, Morera R, Escobar I, Saumench J, et al. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: 41 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2007; 31:1110–1114.
3. Yang DJ, Choi EG, Lee M, Lee YM, Kwon SJ, Son JW, et al. A case of spontaneous pneumomediastinum caused by asthma exacerbation after H1N1 influenza vaccination. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:226–229.
4. Son JI, Kim HS, Choi JH, Lee EJ, Choi CW, Kim YH, et al. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema complicated by acute exacerbation of asthma. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:307–310.
5. Faruqi S, Varma R, Greenstone MA, Kastelik JA. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: a rare complication of bronchial asthma. J Asthma. 2009; 46:969–971.
6. Khalid MS, Ahmad N, Moin S, El-Faedy O, Gaffney P. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: a rare complication of acute asthma. Ir J Med Sci. 2008; 177:393–396.
7. Ameh V, Jenner R, Jilani N, Bradbury A. Spontaneous pneumopericardium, pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema: unusual complications of asthma in a 2-year-old boy. Emerg Med J. 2006; 23:466–467.
8. Kim SA, Lim JH, Oh JY, Park GM, Kim WK. A case of spontaneous pneumomediastinum during an acute asthma attack. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 26:310–313.
9. Egbagbe EE, Elusoji SO. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema associated with asthma exacerbation. J Pak Med Assoc. 2006; 56:287–289.
10. Hamman L. Spontaneous mediastinal emphysema. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1939; 64:1–21.
11. Macklin MT, Macklin CC. Malignant interstitial emphysema of the lungs and mediastinum as an important occult complication in many respiratory diseases and other conditions: an interpretation of the clinical literature in the light of laboratory experiment. Medicine. 1944; 23:281–358.
12. Kelly S, Hughes S, Nixon S, Paterson-Brown S. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum (Hamman's syndrome). Surgeon. 2010; 8:63–66.
13. Perna V, Vilà E, Guelbenzu JJ, Amat I. Pneumomediastinum: is this really a benign entity? When it can be considered as spontaneous? Our experience in 47 adult patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010; 37:573–575.
14. Caceres M, Ali SZ, Braud R, Weiman D, Garrett HE Jr. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: a comparative study and review of the literature. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008; 86:962–966.
15. Moon HJ. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: clinical experience of 24 patients in two medical center. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010; 43:663–668.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download