Abstract
Purpose
This study was done to analyze the effects of tele-care case management services using secondary data.
Methods
A descriptive research design was utilized, and the participants were 134 medical aid beneficiaries who were in either the high-risk group or the preventive group. Case management services were delivered by 8 care managers. Data were analyzed using PAWS Statistics 17 through descriptive statistics and paired t-test.
Results
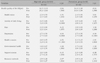
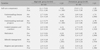
After the case management intervention, the participants' health quality of life, self-care competency, and reasonable medical care utilization increased significantly for the high-risk group. However there were no significant changes in the preventive group.
Conclusion
The results showed that the tele-care case management services were effective for high-risk medical aid beneficiaries. Further studies with controls for constitutional variables and a comparison group are required to validate the robustness of the effectiveness of the case management program in the present study.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Case Management Society of America. Definition of case management. 2002. Retrieved March 28, 2009. from http://www.cmsa.org.
2. Choi GC, Bae SI, Kim KH, Lee DH. Analysis of innovative outcomes and suggestions on 2007 Medical Aid Program. Seoul: National Health Insurance Corporation;2008.
3. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers;1988.
4. Dean K. Self-care components of lifestyles, the importance of gender, attitudes and the social situation. Soc Sci Med. 1989; 29(2):137–152.

5. Eunpyeong-gu. Year Book of Eonpyeong Statistics. Seoul: Eunpyeong-gu;2009.
6. Han MA, Ryu SY, Park J, Kang MG, Park JG, Kim KS. Health-related quality of life assessment by the EQQol-5D in some rural adults. J Prev Med Public Health. 2008; 41(3):173–180.
7. Kasl SV, Cobb S. Health behavior, illness behavior and sick role behavior. Arch Environ Health. 1966; 12:246–266.

8. Kim ES, Lee JR, Yoo WS, Lee YP, Lim SJ, Cho JH, et al. Case management for utilizing reasonable medical service of long-term hospitalized patients among medical aid beneficiaries. Seoul: Medical Aid Program Center;2009.
9. Kim ES, Ahn YH, Ko IS, Lee KO, Ko JS. Planning and development of guide for medical aid case management services. Seoul: Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Family Yonsei University · College of Nursing, Institute of Nursing Policy;2008.
10. Kim ES, Nam JJ, Kim MY, Ko IS, Lee DM, Kim KS, et al. Long-tern medical service use status of medical aid beneficiaries and it's improvements. Seoul: Yonsei University College of Nursing, Institute of Nursing Policy;2007.
11. Kim SM. Utilization changes of hypertension patients according to the medical aid program types. Incheon: Gachon University of Medicine and Science;2009. Unpublished master's thesis.
12. Kim YH. Case management of schizophrenic patients. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 1997; 6(2):298–306.
13. Kim HG. Development of case management model for the bed-ridden elderly at home and its evaluation: Focusing on RAI MDS-HC 2.0 application. Seoul: Chung-Ang University;2001. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
14. Lee IS, Kim SW. The factor influencing behavior of health care of medicaid recipients. Yonsei Soc Welf Rev. 2004; 11:66–99.
15. Lee IS, Kim DK, Um TY. The study of relationship between self-respect and quality of life and dedication effect of depression among the recipients of the medical security with a chronic disease. Korean J Soc Welf Res. 2007; 17:79–104.
16. Morales-Asencio JM, Gonzalo-Jimenez E, Martin-Santos FJ, Morilla-Herrera JC, Celdraan-Manas M, Millan Carrasco A, et al. Effectiveness of a nurse-led case management home care model in primary health care: A quasi-experimental, controlled, multi-centre study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2008; 8:193–206.

17. Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Family. Introduction for medical aid program in 2010. Seoul: Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Family;2009.
18. Oh JJ. Outcome of a pilot project on case management service for medical aid clients. J Korean Acad Public Health Nurs. 2010; 24(1):61–70.
19. Onder G, Liperoti R, Solidato M, Carpenter I, Steel K, Bernabei R, et al. Case management and risk of nursing home admission for older adults in home care: Results of the aged and home care study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007; 55:439–444.
20. Park HJ. The factors affecting the mental health of the recipients of the national basic livelihood security. Jeonju: Chonbuk National University;2003. Unpublished master's thesis.
21. Park KA. The related factors on medication adherence in elderly patients with hypertension or diabetes mellitus. Daegu: Kyungpookk National University;2010. Unpublished master's thesis.
22. Rhee WH. Developing a case management strategies program for Korean medical aid clients. Seoul: Hanyang University;2006. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
23. Riegel B, Carlson B, Kopp Z, LePetri B, Glaser D, Unger A. Effect of a standardized nurse case-management telephone intervention on resource use in patients with chronic heart failure. Arch Intern Med. 2002; 162:705–712.

24. Schraeder C, Fraser CW, Clark I, Long B, Shelton P, Waldschmidt V, et al. Evaluation of a primary care nurse case management intervention for chronically ill community dwelling older people. J Clin Nurs. 2008; 17:407–417.

25. Shin EY, Kim CH, Yoo WS, Kim HG, Kim CY. The effect of case management program for diabetic patients in Korean community. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2003; 14(4):559–567.
26. Shin HR, Lim SJ, Cho JH. Support and evaluation on case management of medical aid program. Seoul: Korea Human Resource Development Institute of Health and Welfare;2009.
27. Shin YS, Shin HW, Whang DG. Medical aid case management & its effects analysis I. Seoul: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2007.
28. So AY, Kim YM, Kim EY, Kim CY, Kim CH, Kim HG, et al. Effects of community-based case management program for clients with hypertension. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2008; 38(6):822–830.

29. Yang SO, Ahn SY, Yim ES, Kwon MS. The effects of customized home visiting health service in Gangwon-do: Focused on hypertension and DM clients. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2008; 19(1):88–100.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download