Abstract
Purpose
This study was to identify health needs of the elderly at nursing homes by long-term care grade.
Methods
The health needs of 116 elders at two nursing homes in Seoul were measured with resident assessment protocols (RAPs), activities of daily living (ADL), and cognitive performance scale (CPS), and pain and depression were measured by resident assessment instrument (RAI).
Results
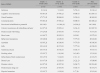
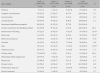
With regard to RAPs, 11 out of 18 items had different distribution in the 3 groups significantly. The 1st-grade elders had a higher percentage of 9 items than the 2nd- and 3rd-grade ones but the 3rd-grade ones had the highest health needs related with activity. The 2nd-grade elders had similar health needs to the 1st-grade ones. In terms of functional level, the 1st-grade elders had the highest percentage of CPS and ADL but the 3rd-grade ones had the highest score of pain and depression out of the 3 groups. The standardized assessment instrument to identify specific health needs by the 3 groups should be developed. Therefore, care plans to meet health needs of the 3 groups will be made.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Bjorkgren MA, Fries BE, Hakkinen U, Brommels M. Case-mix adjustment and efficiency measurement. Scand J Public Health. 2004; 32:464–471.

2. Burrows A, Morris JN, Simon S, Hirdes JP, Phillips C. Development of a minimum data set-based depression rating scale for use in nursing homes. Age Ageing. 2000; 29(2):165–172.

3. Choi HJ. A study of depression and cognitive function for the elderly use welfare facilities for the aged. J Korean Acad Public Health Nurs. 2006; 20(2):119–129.
4. Fries BE, Simon SE, Morris JN, Flodstrom C, Bookstein FL. Pain in US nursing homes: Validating a pain scale for the minimum data set. Gerontologist. 2001; 41(2):173–179.
5. Juh HS, Yvonne S. Advantages and disadvantages of using MDS data in nursing research. J Gerontol Nurs. 2009; 35(1):7–17.

6. June KJ, Lee JY, Yoon JL. Effects of case management using resident assessment instrument-home care (RAI-HC) in home health services for older people. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2009; 39(3):366–375.

7. Kang IO, Lee JS, Keun JH, Han EJ, Lee YK. A study of connectivity development for long-term care insurance approval tool and evaluation index. Seoul: National Health Insurance Corporation;2008.
8. Kim KB, Lee HK, Sok SH. Activities of daily living and nursing needs of the elderly in nursing home. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2009; 20(1):1–11.
9. Kim KH, Jung MH. Health needs of visiting health subjects evaluated by using RAI-MDS-HC 2.0. J Korean Soc Living Environ Syst. 2008; 15(1):102–111.
10. Kim EK. Care time of elderly in long-term care facilities. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2003; 9(3):353–364.
11. Kim MA, Kim HS, Kim EJ. Cognitive function and depression in the elderly. J Korean Gerontol Nurs. 2005; 7(2):176–184.
12. Kim HJ. The validity of RAI-MDS 2.0. Seoul: Seoul National University;2000. Unpublished master's thesis.
13. Kim HJ, Jun KJ, Kim HG, So AA, Lee KM, Kim EY, et al. Development of services delivery model for the elderly in the community. Seoul: Korean Health Industry Development Institute & Graduate School of Public Health, Seoul National University;2000.
14. Kim JS. Comparisons of health status and health care needs between institutionalized and community-living elders. Jeonju: Chonbuk National University;2007. Unpublished master's thesis.
15. Kim SM, Bae SS, Kim DH, June KJ, Kim CY, Yoon JL. A evaluation study of resident assessment instrument-minimum data aet-for the elderly patient at home in Korea. Geriatr Dis. 2000; 4(1):2–8.
16. Korea National Statistical Office. 2009 Statistics of aged. 2009. Retrieved September 30, 2009. from http://stat.mw.go.kr/.
17. Lee KO, Yim MR. A study of nursing service need for institutionalized elderly. Nurs Sci. 2002; 14(2):46–56.
18. Lee JH. The evaluation system of long-term care insurance: focusing on nursing. Seoul: 2008. 11. Paper presented at the International meeting of the Korean Gerontological Society on the Concerns of the aged society and longterm care insurance.
19. Lee JL. The relationship of functional status and resource utilization among elderly patients: Focused on care times among elderly patients in geriatric hospitals. Seoul: Yonsei University;2005. Unpublished master's thesis.
20. Lee JS, Han EJ, Keun JH, Kang IO. Study on the correlation between long-term care expense and standard utilization plan of long-term care. Seoul: National Health Insurance Corporation;2008.
21. Lee TW, Cho SY, Jang YK. Predictors of Nursing Service Need for Nursing Homes Residents. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2009; 39(1):95–106.

22. Morris JN, Fries BE, Mehr DR, Hawes C, Philips C, Mor V, et al. MDS cognitive performance scale. J Gerontol. 1994; 49(4):M174–M182.
23. Morris JN, Fries BE, Morris SA. Scaling ADLs within the MDS. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1999; 54(11):M546–M553.

24. Murray RB, Zentner JP. Nursing Concepts for Health Promotion. 3rd ed. Newjersy: Prentice-Hall;1985.
25. National Health Insurance Corporation [NHIC]. 2008 Long term care insurance statistical yearbook. 2009. Retrieved December, 27 2009. from http://www.nhic.or.kr/portal/site/main/menuitem.611d0884858d73f46e20bbb5b210101c.
26. Yoon JL. Discussion on the issue of long-term care insurance evaluation system. Seoul: 2008. 11. Paper presented at the International meeting of the Korean Gerontological Society on the Concerns of the aged society and long-term care insurance.
27. Yoo IY. Health problems and support from the health & welfare service in the elderly at home. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2004; 34(1):111–122.




 ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print







 XML Download
XML Download