Abstract
Methods
Selected from an elderly welfare center in an agricultural district located in N City. Thirty seven elders were selected in the experimental group and 38 in the control group, and all the subjects aged over 65. Collected data were statistically analyzed by SPSS/PC 12.0 Win. Detailed data analysis methods were Chi-square, Fisher's exact test, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, t-test, Mann-Whitney u-test, paired t-test, and Wilcoxon's rank sum test.
Results
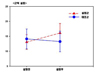
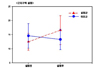
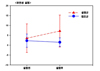
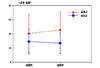
The first hypothesis "The experimental group who had the aerobic exercise therapy will have greater development in lower leg muscular strength compared to the control group" was supported (t=8.95, p<.001). The second hypothesis "Aerobic exercise therapy participants will show greater development in lower leg endurance" was supported (t=6.12, p<.001). The third hypothesis "Aerobic exercise therapy participants will show greater development in flexibility" was supported (U=49.00, p<.001). The forth hypothesis "Aerobic exercise therapy participants will show greater development in balance" was supported (U=322.00, p<.001).
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Aerobic Exercise Therapy

E1=Before experimenting the experimental group muscular strength, endurance, pliability and balanced characteristic measurement;
C1=Before experimenting the control group muscular strength, endurance, pliability and balanced characteristic measurement;
X1-X20=Aerobic exercise therapy (10 wk, 20 round);
E2=After experimenting the experimental group muscular strength, endurance, pliability and balanced characteristic measurement;
C2=After experimenting the control group muscular strength, endurance, pliability and balanced characteristic measurement.
References
1. Cho SB. Effects of the regular exercise program on the physical fitness of 60's for age. Korean J Phys Educ. 1995; 34(2):277–285.
2. Cho SY, Kim JJ. A study on health promotion needs assessment of the rural elderly in korea. J Korea Community Health Nurs Acad Soc. 1996; 10(2):146–161.
3. Choi JH, Moon JS, Song JY. The effects of tai chi exercise on physiologic, psychological functions, and falls among fall-prone elderly. J Rheumatol Health. 2003; 10(1):62–76.
4. Choi SK. The study of the effects of silverobic exercise program on physical functions and powerlessness in elderly women. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;2002. Unpublished master's thesis.
5. Han SS, Kim KB, Kim WO, Won JS, Hyun KS. The Effects of a Health Promotion Program for Elderly. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2005; 35(6):1054–1061.

6. Jang NS. The effect of regular participation in the exercise program on their physical fitness and mental health in the elderly. Korean J Growth Dev. 2008; 16(2):215–223.
7. Jun MY. Dance movement affects in physiology and psychological variable of the elderly woman. Seoul: Seoul National University;1996. Unpublished master's thesis.
8. Jeon MY, Choi MY. Dance movement affects in physiology and psychological variable of the elderly woman. J Nurs Acad Soc. 1996; 26(4):833–852.
9. Jeon MY, Choi MA, Choi YL. Effect of korean traditional dance movement training on balance, gait and leg strength in home bound elderly women. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2000; 30(3):647–658.

10. Jung DS, Kim KH. The assessment of activity fitness age in elderly men. 2001 International Congress on Growth and Development. 2001. p. 18–26.
11. Kauffman TL. Strength training effect in young and aged women. 2nd ed. Illinois: Human Kinetics Publishers;1985.
12. Kim DH. Effect of exercise prescription program on adult's knowledge related to health, attitudes, behaviors, and serum lipoprotein values. J Korean Soc Health Educ Promot. 2001; 16(1):127–135.
13. Kim HJ. The effect which the muscular power reinforcement motion of reaches in quality of life of muscular power, muscular endurance, daily life function in the facility elderly. Seoul: Seoul Catholicism University;1994. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
14. Kim JH. The effect of aerobic rhythmical exercise program on physical fitness, self-efficacy and quality of life in elderly. J Korea Community Health Nurs Acad Soc. 1999; 14(1):12–25.
15. Kim KS. The effects of with aroma therapy on the body composition in middle aged women. Korean J Sport Sci. 2003; 14(1):9–17.
16. Kim MJ. The rhythm motion program development for the body balance of in the elderly. Korean J Res Gerontol. 1997; 6:3–18.
17. Kim SB. Sports and health. Seoul: Naeha Publishing Company;1998.
18. Kirkendall DR. Measurement & evaluation for physical educators. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1987; 66:223–226.
19. Korea statistical Information Service. 2005 report on the Elderly statistics, 2007. 2007. Retrieved August 2, 2007. from http://www.Kosis.go.kr.
20. Lee ES. The effect of integrated exercising prescription program for old people in their 60s and 70s on their physical strength, heart and lung function, physical and blood components. Seoul: Chung-an University Department of Physical Education;2006. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
21. Lee EY, Lim RY, Park HY. Nursing medical research and statistical analysis. Vol 3. Seoul: Soomoonsa Publishing Company;1998.
22. Lee SJ. An application effect of rhythmic movement program for the health promotion in the elderly. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2000; 30(3):776–790.

23. Park JS, Oh YJ. The effects of a health promotion program in rural elderly on health promotion life style and health status. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2005; 35(5):943–954.
24. Rider RA, Daly J. Effects of flexibility training on enhancing spinal mobility in order women. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 1991; 31(2):213–217.
25. Shephard RJ. Geriatric benefits of exercise as on adult. J Gerontol. 1988; 43(4):M86–M90.
26. Shin YH, Choi YH. The effect which reaches in pliability in elderly women. J Nurs Acad Soc. 1997; 26(2):372–386.
27. Simmons V, Hasen PD. Effectiveness of water exercise on postural mobility in the elderly. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1996; 51(5):M233–M238.
28. Song R, Jun KJ, No YJ, Kim CG. The motive reinforcement program affects in healthy act, the heart and soul tube diseased dangerous vip and functional health condition of the old age woman. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2001; 31(5):858–870.
29. Won CW, Kim BS, Choi HL. The effect of tai chi (9 basic forms) on the equilibrium in the aged: A controlled trial. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2001; 22(5):324–333.




 ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print







 XML Download
XML Download