Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the predictors of health-related quality of life and to examine their effects in frail elderly.
Methods
This was a correlation study. The subjects were 680 frail elders aged over 65 who were receiving home care from one of 253 public health centers in 16 provinces, and data were collected from the 1st to 30th of April, 2008.
Results
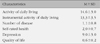
The mean health-related quality of life in the subjects was 6.0±2.0. The predictors identified in this study significantly explained 41.3% of health-related quality of life. Self-rated health was the most significant predictor of health-related quality of life. ADL and depression had an effect on health-related quality of life.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Chang SO, Park YJ, Youn JW. Study on relations of variables: Attributions of somatic symptoms, fatigue, chronic pain and depression in the elderly. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2003; 33(1):26–33.

2. Fried L, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman A, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, et al. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001; 56:M146–M157.

3. Kang EJ, Shin HS, Park HJ, Jo MW, Kim NY. A Valuation of Health Status Using EQ-5D. Korean J Health Econ Policy. 2006; 12(2):19–43.
4. Kee BS. A preliminary study for the standardization of geriatric depression scale short form-Korea Version. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1996; 35(2):298–307.
5. Kim HR. Health status among community elderly inKorea. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2003; 33(5):544–552.
6. Kim HR, Oh KS, Oh HO, Lee SO, Lee SJ, Kim JA, et al. Quality of Life in Low Income Korean Aged. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2008; 38(5):694–703.

7. Korean National Statistical Office. 2008 Statistics on older people. Korean National Statistical Office;2008. Retrieved January 28, 2009. from http://www.kostat.go.kr.
8. Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. Development of assessment tool for public long-term care system. 2004. Retrieved Feb. 2, 2009. from http://www.e-welfare.go.kr.
9. Lee FJ, Han CW. The relationship between the health-related quality of life and home care service needs in the elderly. J Welf Aged. 2005; 30:171–190.
10. Lee HJ, Chung YJ, Kim HJ, Seo HS, Lee HS, Shim KW, et al. Determinants of Self-assessed Health among Elderly Adults. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2002; 23(10):1210–1218.
11. Lee JK, Park HS. A Study on the Perceived Health Status, Depression and Activities of Daily Living for the Elderly in Urban Areas. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2006; 12(3):221–230.

12. Lee KJ, Lee HJ. Determinats of the Quality of Life in Three Elderly Cohorts. J Welf Aged. 2008; 41:159–182.
13. Meredith CM, James EG, Timothy AR, Kyriakos SM, Kenneth JO. Frailty and health related quality of life in older Mexican Americans. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2009; 7:70–88.

14. Ministry of Health and Welfare Affairs. The Forth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. 2008-a. Retrieved January 20, 2009. from http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr.
15. Ministry of Health and Welfare Affairs. Case Management for Frail Elderly. 2008-b. Retrieved January 20, 2009. from http://chc.hp.go.kr.
16. Moon MJ. A study on the instrumental activities of daily living and quality of life of elderly home residents. Korean J Rehabil Nurs. 2001; 4:46–57.
17. Park YR, Kwon HJ, Kim KH, Choi MH, Han SE. A study on relations between self-esteem, self efficacy and quality of life of the elderly. J Welf Aged. 2005; 29:237–258.
18. Puts M, Shekary N, Widdershoven G, Heldens J, Lips P, Deeg D. What does quality of life mean to older frail and non-frail community dwelling adults in the Netherlands? Qual Life Res. 2007; 16:263–277.
19. Scott WK, Macera CA, Cornman CB, Sharpe PA. Functional health status as a predictor of mortality in men and women over 65. J Clin Epidemiol. 1997; 50(3):291–296.

20. Shin KR, Byeon YS, Kang YH, Oak JW. A study on physical symptom, activity of daily living, and health-related quality of life in the community-dwelling older adults. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2008; 33(3):437–444.
21. Sun YD, Song HJ, Lee YH, Kim DJ. Study on development of health care services and coordinated system for frail elderly people. Seoul: Yaewon Publishing Company;2004.
22. The EuroQoL Group. EuroQoL-a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy. 1990; 16(3):199–208.
23. Yim ES, Lee KJ. Effect of physical ability, depression and social support on quality of life in low income elders living at home. J Korean Gerontol Nurs. 2003; 5:38–49.
24. Ware J, Kosinski M. Interpretation: Content and criterion-based in SF-36 physical mental health summary scale: A manual for users of version I. 2nd ed. Lincoln, RI: Quality Metric Incorporated;2001.
25. Won CW, Rho YG, Kim SY, Cho BR, Lee YS. The validity and reliability of Korean Activities of Daily Living (K-ADL) Scale. J Korean Geriatr Soc. 2002; 6(2):98–106.
26. Won CW, Rho YG, Sun WD, Lee YS. The validity and reliability of Korean Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (K-IADL) Scale. J Korean Geriatr Soc. 2002; 6(4):273–280.




 ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download