Abstract
Purpose
This study was done to identify prevalence of, and factors influencing metabolic syndrome among long-term care facility patients with schizophrenia.
Methods
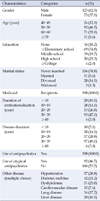
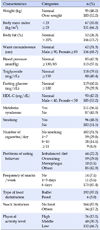
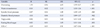
A cross-sectional survey was conducted using a 20-item questionnaire. Clinical data for blood triglyceride, HDL-cholesterol, and fasting blood sugar were collected from medical records. Body weight, body fat, body mass index, blood pressure, height, and abdominal circumference were measured. Data for 198 participants were analyzed using t-test, x2 test and logistic regression.
Results
Prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 56.1%. The number of persons who overate was significantly higher in the metabolic syndrome group than in the normal group (p<.001). Factors influencing metabolic syndrome were hyperphagia (p<.001), abdominal circumference (p<.001), systolic blood pressure (p=.040), blood triglyceride (p<.001), fasting blood sugar (p=.015), and HDL-cholesterol (p<.001).
Figures and Tables
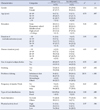
Table 3
Comparison of Demographic Characteristics and Lifestyle Factors between MS and No MS Group (N=198)
References
1. Lambert TJ, Velakoulis D, Pantelis C. Medical comorbidity in schizophrenia. Med J Aust. 2003; 178(9):S67.
2. Meyer JM. The metabolic syndrome and schizophrenia: clinical research update. Psychiatr Times. 2007; 24(2):29.
3. Meyer JM, Pandina G, Bossie CA, Turkoz I, Greenspan A. Effects of switching from olanzapine to risperidone on the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in overweight or obese patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder: analysis of a multicenter, rater-blinded, open-label study. Clin Ther. 2005; 27(12):1930–1941. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.12.005.

4. Roh J, Cho YS, Cho AH. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in inpatients with schizophrenia. Korean J Biol Psychiatry. 2011; 18(1):46–54.

5. DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991; 14(3):173–194.

6. Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009; 120(16):1640–1645. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644.

7. Lee S, Park HS, Kim SM, Kwon HS, Kim DY, Kim DJ, et al. Cutoff points of waist circumference for defining abdominal obesity in the Korean population. Korean J Obes. 2006; 15(1):1–9.

8. Nam YY, Kim CS, Ahn CW, Park KM, Ryu B, Kim CH. Clinical correlates of metabolic syndrome in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Korean J Psychopharmacol. 2006; 17(4):335–341.

9. Kang KD, Sea YH, Yoon BH. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in chronic schizophrenic inpatients. J Korean Soc Biol Psychiatry. 2012; 18(2):281–289.

10. Yun IS, Go HS, Lee SY. A study of quality of life and body image in schizophrenia patients with metabolic syndrome. Korean J Psychopharmacol. 2011; 22(4):208–213.

11. Ministry of Health & Welfare. Mental Health Guidelines [Internet]. 2013. 04. 1–516. cited 2015 November 10. Available from: http://www.mohw.go.kr/front_new/jb/sjb030301vw.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=03&MENU_ID=0320&CONT_SEQ=284396&page=1.

12. National Human Rights Commission of Korea. Forum for human rights promotion of mentally-ill people: focusing on residents' rights protection [Internet]. 2013. 11. 1–139. cited 2015 Nov 10. Available from: http://library.humanrights.go.kr/hermes/imgview/13-50.pdf.

13. Sicras-Mainar A, Navarro-Artieda R, Rejas-Gutiérrez J, Blanca-Tamayo M. Relationship between obesity and antipsychotic drug use in the adult population: a longitudinal, retrospective claim database study in primary care settings. J Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008; 4(1):219–226.

14. Lee JM. Foodservice systems of meal service programs for mental disorder care sites in Korea. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2001; 7(1):80–86.

15. Faulkner GE, Gorczynski PF, Cohn TA. Psychiatric illness and obesity: recognizing the "obesogenic" nature of an inpatient psychiatric setting. Psychiatr Serv. 2009; 60(4):538–541.

16. Jeon ES. A survey on the health status of mentally-ill patients in rural mental health care facility [master's thesis]. Daejeon: Daejeon University;2005. 49.

17. Lee K, Park J, Choi J, Park CG. Heart rate variability and metabolic syndrome in hospitalized patients with schizophrenia. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(6):788–794. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2011.41.6.788.

18. Heiskanen T, Niskanen L, Lyytikäinen R, Saarinen PI, Hintikka J. Metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003; 64(5):575–579.

19. Ellingrod VL, Taylor SF, Dalack G, Grove TB, Bly M, Brook RD, et al. Risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome in bipolar and schizophrenia subjects treated with antipsychotics: the role of folate pharmacogenetics. J Clin Psychopharmalcol. 2012; 32(2):261–265. DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e3182485888.

20. Boke O, Aker S, Sarisoy G, Saricicek EB, Sahin AR. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among inpatients with schizophrenia. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2008; 38(1):103–112. DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e3182485888.

21. Mitchell AJ, Vancampfort D, Sweers K, van Winkel R, Yu W, De Hert M. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and metabolic abnormalities in schizophrenia and related disorders-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr Bull. 2013; 39(2):306–318. DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbr148.

22. Connolly M, Kelly C. Lifestyle and physical health in schizophrenia. Adv Psychiatr Treat. 2005; 11(2):125–132. DOI: 10.1192/apt.11.2.125.

23. Lee HY, Choi JE. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among outpatients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Korean J Schizophr Res. 2012; 15:39–45.

24. Lee NY, Kim SH, Chung JD, Kim EY, Yu HY, Sung KH, et al. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korean patients with schizophrenia receiving a monotherapy with aripiprazole, olanzapine or risperidone. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011; 35(5):1273–1278. DOI: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2011.03.022.

25. Kim SH, Kim K, Kwak MH, Kim HJ, Kim HS, Han KH. The contribution of abdominal obesity and dyslipidemia to metabolic syndrome in psychiatric patients. Korean J Intern Med. 2010; 25(2):168–173. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.2.168.
26. Yoo JS, Jeong JI, Park CG, Kang SW, Ahn JA. Impact of life style characteristics on prevalence risk of metabolic syndrome. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2009; 39(4):594–601. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.59.
27. Park E, Choi SJ, Lee HY. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome and related risk factors based on the KNHANES V 2010. J Agric Med Community Health. 2013; 38(1):1–13.

28. Cho SH, Choi MJ, Jeong MH. Metabolic syndrome risk factors related to severity of coronary artery diseases in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2012; 18(1):171–181.

29. Na DW, Jeong E, Noh EK, Chung JS, Chok CH, Park J. Dietary Factors and metabolic syndrome in middle-aged men. J Agric Med Community Health. 2010; 35(4):383–394.
30. Park BS, Lim SO, Bae SW. A meta-analysis on the variables related with quality of life among persons with severe mental illness. Ment Health Soc Work. 2013; 41(3):63–92.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download