Abstract
Purpose
This study was done to provide a basis for safer medical services by describing nurses' perception of patient safety culture and patient safety activities, and analyzing factors that affect patient safety management activities among nurses working in mental health hospitals.
Methods
The study participants included 208 nurses with three months or more experience and who worked in one of 14 mental health hospitals. The instruments were the Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture and Patient Safety Management Activities Scale. Collected data were analyzed using mean, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficient and Stepwise multiple regression with the SPSS/WIN 20.0 program.
Results
Perceptions of patient safety culture and patient safety management activities were positively correlated. Factors influencing patient safety management activities were communication and procedures, patient safety in the field, frequency of events reported and attitude of supervisor/manager. The explanatory power for patient safety management activities of these variables was 35.0%.
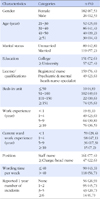
Figures and Tables
Table 3
Difference by General Characteristics on Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture and Patient Safety Activities (N=208)

References
1. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Improving value in health care: measuring quality. [Internet]. 2010. cited 2014 Nov 29. Available from: http://www.oecd.org/health/ministerial/46098506.pdf.
2. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Hospital survey on patient culture. [Internet]. 2004. cited 2014 May 29. Available from: http://www.ahrq.gov/professionals/quality-patient-safety/patientsafetyculture/hospital/resources/hospscanform.pdf.
3. Lee SI. Policy challenges for healthcare quality and patient safety. Health Policy Manag. 2013; (5):39–55.
4. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Hospital survey on patient culture: 2014 user comparative database report. [Internet]. 2014. cited 2014 Dec 1. Available from: http://www.ahrq.gov/professionals-patient-safety/patientsafetyculture/hospital/2014/hsops14pt1.pdf.
5. Go HS. Every sanatorium and mental hospital subject to govermental assessment, starting 2013. Health Korea News. [Internet]. 2012. 12. 03. cited 2014 May 29. Available from: http://www.hkn24.com/news/articleView.html?idxno=112354.
6. Park JH, Bae HA. Legal judgement about psychiatric patients injuries during admission of closed ward. Korean J Med Law. 2012; 20(2):219–246.
7. Jung IW, Yang S. Emotional reaction of psychiatric nurses and resident physicians toward suicidal behavior in psychiatric inpatients. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2011; 20(4):365–375.

8. Mills PD, DeRosier JM, Ballot BA, Shepherd M, Bagian JP. Inpatient suicide and suicide attempts in veterans affairs hospitals. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2008; 34(8):482–488.

9. Chung SH, Jho KH, Shin YM. Analysis of the risk factors and psychotropics' role in the falls of the dementic elderlies in a nursing home. J Korean Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001; 5(1):76–85.
10. An HJ, Kim EH, Chung YH, An JS, Cho WA, Park JH. A study about restraint use in care of patients with psychiatric disorders. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2013; 19(3):432–442.
11. Evans D, Wood J, Lambert L. Patient injury and physical restraint devices: a systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2003; 41(3):274–282.

12. Sullivan-Marx EM. Achieving restraint-free care of acutely confused older adults. J Gerontol Nurs. 2001; 27(4):56–61.

13. Yim JH, Kim HJ, Kim E, Park HS, Choi J. A study on fire protection plan hospital building through case studies. J Korean Inst Fire Sci Eng. 2004; (6):199–204.
14. Korea Institute for Healthcare Accreditation. Healthcare accreditation survey standard of mental hospital. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2012. p. 140.
15. Je WY. Hospital worker's perception of patient safety culture in a university hospital. [master's thesis]. Seoul: Sungkyunkwan University;2007. 69.
16. Lee GO. The study on nurse manager leadership and patient safety-related nursing activities. [master's thesis]. Seoul: Kyung Hee University;2009. 50.
17. Cho HW, Yang JH. relationship between perceived patient safety culture and patient safety management activities among health personnel. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2012; 19(1):35–45.

18. Lee HR. The role the Korean hospital association in korea's healthcare accreditation system. J Korean Med Assoc. 2012; 55(1):23–30.

19. Nam MH, Lim JH. The influences of the awareness of patient safety culture on safety care activities among nurse in small-medium sized general hospitals. J Digit Converg. 2013; 11(1):349–359.
20. Kim JE, Kang MA, An KE, Sung YH. A survey of nurses' perception of patient safety related to hospital culture and reports of medical errors. Clin Nurs Res. 2007; 13(3):169–179.
21. Kahn WA. Psychological conditions of personal engagement and disengagement at work. Acad Manag J. 1990; 33(4):692–724.

22. Nieva VF, Sorra J. Safety culture assessment: a tool for improving patient safety in healthcare organizations. Qual Saf Health Care. 2003; 12(2):ii17–ii23.

23. Cohen H, Tuohy N, Carroll R. The risk management professional and medication safety. J Healthc Risk Manag. 2009; 29(1):34–43.

24. Rogers AE, Hwang WT, Scott LD, Aiken LH, Dinges DE. The working hours of hospital staff nurses and patient safety. Health Aff (Millwood). 2004; 23(4):202–212.

25. Schubert M, Glass TR, Clarke SP, Aiken LH, Schaffert-Witvliet B, Sloane DM, et al. Rationing of nursing care and its relationship to patient outcomes: the Swiss extension of the international hospital outcomes study. Int J Qual Health Care. 2008; 20(4):227–237.

26. Choi KC. A study on fire safety management of social welfare facilities. J Korean Inst Fire Sci Eng. 2013; 27(1):1–7.

27. Aiken LH, Sloane DM, Bruyneel L, Van den Heede K, Griffiths P, Busse R, et al. Nurse staffing and education and hospital mortality in nine European countries: A retrospective observational study. Lancet. 2014; 383(9931):1824–1830.

28. Park J, Kim Y, Chung HK, Hisanaga N. Long working hours and subjective fatigue symptoms. Ind Health. 2001; (39):250–254.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download