Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to test the effects of a forgiveness therapy program to improve self-esteem, anger and forgiveness in people who abuse alcohol.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group pre-posttest design was employed. Participants were 38 people who abuse alcohol and who agreed to participate in this study. They were assigned to the experimental group in Alcoholics Anonymous meetings of J hospital(n=19) and the control group in Alcoholics Anonymous meetings of B hospital(n=19). The eight session program was provided once a week for 8 weeks. The data were analyzed using percentage, χ2-test, Kolmogorov - Smirnov test, and t-test with SPSS 21.0 program.
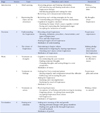
Figures and Tables
References
1. Lee HK, Lee BH. The epidemiology of alcohol use disorders. J Korean Diabetes. 2012; 13(2):69–75. DOI: 10.4093/jkd.2012.13.2.69.

2. Kwon SM. Contemporary abnormal psychology. 2nd ed. Seoul: Hakjisa;2014. p. 521.
3. Cho MJ, Shin SJ, Shin SY, Kim JS, Chon SB, Kim MJ, et al. The epidemiological survey of mental disorders in Korea. Ministry of Health and Welfare of Academic Research Service Business Report. Seoul National University College of Medicine;2011. December.
4. Yun MS. The current situation and developmental direction of Korean addiction service delivery system. Ment Health Soc Work. 2010; 35:234–266.
5. Kim SJ. Group activity center for rehabilitation of alcoholism. 1st ed. Seoul: Hyunmoonsa;2003. p. 685.
6. Kim YH. The effectiveness of alcoholics forgiveness research group program. Proceedings of the 2006 Korea academy of mental health social work. In : Korea academy of mental health social work 2006 Spring Conference; 2006 May; Seoul, Korea. Seoul (Korea): Korea Academy of Mental Health Social Work;2006. p. 424. 123-55.
7. Coyle CT, Enright RD. Forgiveness intervention with postabortion men. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1997; 65(6):1042–1046. DOI: 10.1037/0022-006x.65.6.1042.

8. Lin WF, Mack D, Enright RD, Krahn D, Baskin TW. Effects of forgiveness therapy on anger, mood, and vulnerability to substance use among inpatient substance-dependent clients. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2004; 72(6):1114–1121. DOI: 10.1037/0022-006x.72.6.1114.

9. Kang OG, Gee SW, Kim KJ, Kim KS, Kim DJ, Kim SG, et al. Addiction psychiatry. 1st ed. Seoul: ML communications;2009. p. 420.
10. Kim GS, Park KK, Oh DY. Effect of anger management on alcoholism. J Clin Res: Seoul Natl Hosp. 1998; 12:29–53.
11. Enright RD. Forgiveness heals: forgiveness is choice. 1st ed.
KM Chae
. Seoul: Hakjisa;2004. p. 347.
12. Enright RD, Richard FP. Helping clients forgive: an empirical guide for resolving anger and restoring hope. 1st ed.
GY Bang
. Seoul: Sigmapress;2011. p. 425.
13. Wade NG, Hoyt WT, Kidwell JE, Worthington EL. Efficacy of psychotherapeutic interventions to promote forgiveness: a meta-analysis. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2014; 82(1):154–170. DOI: 10.1037/a0035268.

14. Webb JR, Robinson EA, Brower KJ. Mental health, not social support, mediates the forgiveness-alcohol outcome relationship. Psychol Addict Behav. 2011; 25(3):462–473. DOI: 10.1037/a0022502.

15. Kim KK. Forgiveness counseling program. 2nd ed. Seoul: Hakjisa;2012. p. 278.
16. Kim HK, Lee M. Effectiveness of forgiveness therapy on resilience, self-esteem, and spirituality of female spouses of alcoholics. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2014; 44(3):237–247. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2014.44.3.237.

17. Park YR, Hyun MH. The effect of forgiveness therapy on the negative affects and subjective well-being of adult-child. Korean J Youth Stud. 2012; 19(2):275–297.
18. Shin SH. Effects of forgiveness program on anger, self-esteem in male patient group with alcohol dependence. In : Proceedings of the 2011 Korean psychological association annual conference; 2011 August 25-27; Jeonju, Korea. Jeonju (Korea): Korean Psychological Association;2011. p. 353. Psychologist's Roles and Tasks in an Aging Society.
19. Fitzgibbons RP. The cognitive and emotive uses of forgiveness in the treatment of anger. Psychotherapy: Theory, Research, Practice, Training. 1986; 23(4):629–633.

20. Rosenberg M. Society and the adolescent self-image. Soc Forces. 1965; 44(2):255. DOI: 10.2307/2575639.

21. Jon BJ. Self-esteem: a test of its measurability. Yonsei Nonchong. 1974; 11:107–130.
22. Spielberger CD, Krasner S, Solomon EP. The experience, expression, and control of anger. Individ Differ Stress Health Psychol. 1988; 89–108. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3824-9_5.

23. Chon KK, Hahn DW, Lee CH, Speilberger CD. Korean adaptation of the state-trait anger expression inventory: anger and blood pressure. Korean J Health Psychol. 1997; 2(1):60–78.
24. Oh YH. Development and validation of the Korean forgiveness scale-short form. Korean J Health Psychol. 2011; 16(4):799–813. DOI: 10.17315/kjhp.2011.16.4.010.

25. Enright RD. Counselling within the forgiveness triad: on forgiving, receiving forgiveness, and self-forgiveness. Couns Values. 1996; 40(2):107–126. DOI: 10.1002/j.2161-007x.1996.tb00844.x.

26. Kim KS. Development of education program for forgiveness [dissertation]. Seoul: Seoul National University;1999. 163.
27. Park HR. Effective analysis of the forgiveness counseling program in family relations [master's thesis]. Daejeon: Hannam University;2009. 36–45.
28. Baskin TW, Enright RD. Intervention studies on forgiveness: a meta-analysis. J Couns Dev. 2004; 82(1):79–90. DOI: 10.1002/j.1556-6678.2004.tb00288.x.

29. Kang JH, Park JH. Development of a forgiveness program and evaluation of its effectiveness for female victims of domestic violence. Korean J Couns. 2014; 15(6):2245–2267. DOI: 10.15703/kjc.15.6.201412.2245.

30. Sharkin BS. The measurement and treatment of client anger in counseling. J Couns Dev. 1988; 66(8):361–365. DOI: 10.1002/j.1556-6676.1988.tb00887.x.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download