Abstract
Purpose
This study was conducted to identify factors which predict sleep in people who have alcoholism.
Methods
Data were collected from 171 people with alcoholism who live in Daegu, Kyungpook Province, in Korea. The collected data were analyzed using frequency, percentage, correlation and stepwise multiple regression analysis.
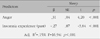
Figures and Tables
References
1. Bonnet MH, Arand DL. Insomnia, metabolic rate and sleep restoration. J Intern Med. 2003; 254:23–31.

2. Brower KJ, Hall JM. Effects of age and alcoholism on sleep: A controlled study. J Stud Alcohol. 2001; 62:335–343.

3. Brower KJ, Robinson EAR, Zucker RA. Epidemiology of insomnia an alcoholism in the general population. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000; 24:Suppl. 5. 43A.
4. Cho KH. A study on the factors affecting the relapse among alcoholics. Cheonan: Baekseok University;2006. Unpublished master's thesis.
5. Chon KK. Development of the Korean state-trait anger expression inventory (II). Korean J Rehabil Psychol. 1996; 3(1):53–69.
6. Deffenbacher JL, McNamara K, Stark RS, Sabadell PM. A comparison of cognitive-behavioral and process oriented group counseling for general anger reduction. Journal of Counseling and Development. 1990; 69:167–172.

7. Fuller J, Schaller-Ayers J. Health assessment: A nursing approach. Philadelphia: Lippincott;2000.
8. Han KW, Kim MJ, Kim SG, Byun WT. Study of conditioned stimuli provoking alcohol craving in the patients with alcohol dependence. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1996; 35(4):809–819.
9. Jang MH, Won JS. Association of anger and anger expression, social support, self-esteem, and depression in elderly. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2009; 18(3):259–268.
10. Jung HH. The effect of psychodynamic group psychotherapy for sleep-problems on depression, anxiety, and sleep quality. Seoul: Seoul University of Buddhism;2005. Unpublished master's thesis.
11. Junghanns K, Horbach R, Ehrenthal D, Blank S, Backhaus J. Chronic and high alcohol consumption has a negative impact on sleep and sleep associated consolidation of declarative memory. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009; 33(5):893–897.

12. Kim ES. Association between sleep disturbance and depression among patients with brain injury. Daegu: Keimyung University;2008. Unpublished master's thesis.
13. Kim HS. A study on the relapse factors of the alcoholics. Cheongju: Cheongju University;2007. Unpublished master's thesis.
14. Kim JY. Relationship between trait-anger and sleep disturbances in Korean adults aged 40-69 years. Ewha Womans University: Seoul;2004. Unpublished master's thesis.
15. Kim MY. A phenomenological study of the psychological state of Alcoholics inpatients. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 1995; 4(2):98–109.
16. Kim S. The effect of music therapy on anger control in patients with alcoholism. Gunpo: Hansei University;2007. Unpublished master's thesis.
17. Kwon MR. The difference of trait anger and anger expression among two types of alcoholics and nonalcoholics. Daegu: Daegu Catholic University;2005. Unpublished master's thesis.
18. Lim YR. The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy and structural equation modeling of the psychological risk factors for alcohol dependence. Seoul: Korea University;1999. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
19. Maisto SA, O'Farrel TJ, Connors GJ, Mckay JR, Pelcovits M. Alcoholics' attribution of factors affecting their relapse to drinking and reasons for terminating relapse episodes. Addict Behav. 1988; 13(1):79–82.

20. Mayo Clinic Staff (2009, February 20). Stress symptoms: Effects on your body, feeling and behavior. April 8, 2010. from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/stress-symptoms/SR00008_D.
21. Oh JJ, Song MS, Kim SM. Development and validation of Korean sleep scale A. J Korean Acad Nurs. 1998; 28(3):563–572.
22. Ryu HD. A study on relation between the quality of life and factors for recurrent stress of alcohol dependents. Iksan: Wonkwang University;2008. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
23. Schoenborn CA, Adams PF. Sleep duration as a correlate of smoking, alcohol use, leisure-time physical inactivity and obesity among adults: United States, 2004-2006. NCHS Health E-Stats. 2008; 1–10.
24. Skoloda TE, Alterman AI, Gottheil E. Sleep quality reported by drinking and nondrinking alcoholics. In : Gottheil EL, editor. Addiction research and treatment: Converging trends. Elmsford, NY: Pergamon;1979. p. 102–112.
25. Spielberger CD. Professional manual for the state-trait anger expression inventory (STAXI) (research ed.). Tampa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc;1988.
26. Tabachnick BG, Fidell IS. Using multi-variate statistics. New York: Harper Collins;1989.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download