Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study is to investigate the variables besides symptom that influence the family burden in the primary caregivers of remitted schizophrenic outpatients, and to evaluate the impact of changeable or unchangeable variables by clinical practice on the family burden.
Methods
A total 105 remitted schizophrenic outpatients and 105 their primary caregivers were participated in the psychiatric outpatient clinic of the university hospital. Socio-demographic characteristics (age, sex, education, income, marital status, religion), clinical variables (duration of illness, age of onset), patients' symptom (korean version of the positive and negative syndrome scale), patients' social function (korean version of the social functioning scale), patients' insight (self-appraisal of illness questionnaire), patients' attitude toward medication (drug attitude inventory), family perceived social support (multidimensional scale of perceived social support), family attitude toward patient (family attitude scale) were gathered from subjects.
Results
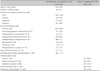
Total score of family burden scale (0–144) of the primary caregivers of remitted schizophrenic outpatients was 71.3 (SD 20.7) and mean score per item was 1.9. Unchangeable six variables by clinical practice (relation with patient, patients' education, age of onset, duration of illness, parent age, parent income) explain 17%, and changeable four variables (family attitude toward patient, family perceived social support, patients' social function, patients' insight) explain 72% of family burden. Four areas such as interpersonal communication, independence-performance, independence-competence, occupation/ employment explain family burden significantly in the seven areas of the social functioning scale.
Figures and Tables
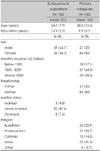
Table 1
Socio-demographic characteristics of the schizophrenic outpatients and their primary caregivers
References
1. Lefley HP. Family burden and family stigma in major mental illness. Am Psychol. 1989; 44:556–560.

2. Kreisman DE, Joy VD. Family response to the mental illness of a relative: A review of the literature. Schizophr Bull. 1974; 1:34–57.

3. Bateson G, Jackson DD, Haley J, Weakland J. Toward a therapy of schizophrenia. Behav Sci. 1956; 1:251–264.
4. Lidz T, Cornelison AR, Fleck S, Terry D. The intrafamilial environment of schizophrenic patients: II. Marital schism and marital skew. Am J Psychiatry. 1957; 114:241–248.

5. Bowen M. The family as the unit of study and treatment. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 1961; 31:40–60.
6. Singer MT, Wynne LC. Thought disorder and family relations of schizophrenics: IV. Result and implication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1965; 12:201–212.

7. Hatfield AB. The family as a partner in the treatment of mental illness. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1979; 30:338–340.
8. Gibbons J, Horn S, Powell J, Gibbons J. Schizophrenic patients and their families. A survey in a psychiatric service based on a DGH Unit. Br J Psychiatry. 1984; 144:70–77.

9. Stein L, Test M. Training in community living: One year evaluation. Am J Psychiatry. 1976; 133:917–918.
10. Hoenig J, Hamilton MW. The schizophrenic patient in the community and his effect on the household. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 1966; 12:165–176.

11. Platt S. Measuring the burden of psychiatric illness on the family: An evaluation of some rating scales. Psychol Med. 1985; 15:383–393.

12. Kim CK, Seo JM, Lee GZ, Kim JW, Kim GJ, Byun WT. Family burden of schizophrenics in the primary caregivers and siblings. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2000; 39:113–127.
13. Provencher HL, Mueser KT. Positive and negative symptom behaviors and caregiver burden in the relatives of persons with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 1997; 26:71–80.

14. Schene AH, Van Wijngaarden B, Koeter MW. Family caregiving in schizophrenia: Domains and distress. Schizophr Bull. 1998; 24:609–618.

15. Wolthaus J, Dingemans P, Schene A, Linszen D, Wiersma D, Van Den, et al. Caregiver burden in recent-onset schizophrenia and spectrum disorders: the influence of symptoms and personality traits. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2002; 190:241–247.

16. Dyck DG, Short R, Vitaliano PP. Predictors of burden and infectious illness in schizophrenia caregivers. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1999; 61:411–419.

17. Grandón P, Jenaro C, Lemos S. Primary caregivers of schizophrenia outpatients: Burden and predictor variables. Psychiatry Res. 2008; 158:335–343.

18. Webb C, Pfeiffer M, Mueser KT, Gladis M, Mensch E, DeGirolamo J, et al. Burden and well-being of caregivers for the severely mentally ill: the role of coping style and social support. Schizophr Res. 1998; 34:169–180.
19. Roick C, Heider D, Toumi M, Angermeyer MC. The impact of caregivers’ characteristics, patients’ conditions and regional differences on family burden in schizophrenia: a longitudinal analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2006; 114:363–374.

20. Lowyck B, De Hert M, Peeters E, Wampers M, Gilis P, Peuskens J. A study of the family burden of 150 family members of schizophrenic patients. Eur Psychiatry. 2004; 19:395–401.

21. Jones SL, Roth D, Jones PK. Effect of demographic and behavioral variables on burden of caregivers of chronic mentally ill persons. Psychiatr Serv. 1995; 46:141–145.

22. Baronet AM. Factors associated with caregiver burden in mental illness: a critical review of the research literature. Clin Psychol Rev. 1999; 19:819–841.

23. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. DSM-IV-TR. 4th ed. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association;2000.
24. Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1987; 13:261–276.

25. Yi JS, Ahn YM, Shin HK, An SK, Joo YH, Kim SH, et al. Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the positive and negative syndrome scale. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2001; 40:1090–1105.
26. Birchwood M, Smith J, Cochrane R, Wetton S, Copestake S. The social functioning scale. The development and validation of a new scale of social adjustment for use in family intervention programmes with schizophrenic patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1990; 157:853–859.

27. Kim CK, Lee JA. Development of the Korean version of the social functioning scale in the schizophrenics: A study on the reliability and validity. Korean J Biol Psychiatry. 2009; 16:76–111.
28. Kim CK, Cho JS, Seo JM, Kim YK, Kim HC, Kim HS, et al. A preliminary study for the development of the family burden scale of the schizophrenics. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1999; 38:539–553.
29. Kavanagh DJ, O’Halloran P, Manicavasagar V, Clark D, Piatkowska O, Tennant C, et al. The family attitude scale: Reliability and validity of a new scale for measuring the emotional climate of families. Psychiatry Res. 1997; 70:185–195.

30. Dahlem NW, Zimet GD, Walker RR. The multidimensional scale of perceived social support: A confirmation study. J Clin Psychol. 1991; 47:756–761.

31. Hogan TP, Awad AG, Eastwood MR. A self-report scale predictive of drug compliance in schizophrenics: Reliability and discriminative validity. Psychol Med. 1983; 13:177–183.

32. Marks KA, Fastenau PS, Lysaker PH, Bond GR. Self-appraisal of illness questionnaire (SAIQ): Relationship to researcher-rated insight and neuropsychological function in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2000; 45:203–211.

33. Magliano L, Fiorillo A, Malangone C, Marasco C, Guarneri M, Maj M. National mental health project working group. The effect of social network on burden and pessimism in relatives of patients with schizophrenia. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2003; 73:302–309.

34. Saunders JC. Families living with severe mental illness: a literature review. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2003; 24:175–198.

35. Rosenheck R, Cramer J, Jurgis G, Perlick D, Xu W, Thomas J, et al. Clinical and psychopharmacologic factors influencing family burden in refractory schizophrenia. The department of veterans affairs cooperative study group on clozapine in refractory schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000; 61:671–676.

36. Caqueo-Urízar A, Gutiérrez-Maldonado J. Burden of care in families of patients with schizophrenia. Qual Life Res. 2006; 15:719–724.

37. Magliano L, Fadden G, Economou M, Held T, Xavier M, Guarneri M, et al. Family burden and coping strategies in schizophrenia: 1-year follow-up data from the BIOMED I study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2000; 35:109–115.

38. Scazufca M, Kuipers E. Coping strategies in relatives of people with schizophrenia before and after psychiatric admission. Br J Psychiatry. 1999; 174:154–158.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download