Abstract
Objectives
Patients with schizophrenia often have a concrete thinking or an impairment in abstract thinking, but there has been a limitation in quantitatively measuring this cognitive function. The aim of the current study was to investigate a deficit in abstract thinking in patients with schizophrenia using the theme identification task.
Methods
Twenty subjects with schizophrenia and 20 healthy volunteers participated in the behavioral study for theme identification. The visual stimuli were composed of a series of pictures, which contained positive or negative emotional situations. Three words, indicating a main theme of the picture, a theme-related item and a theme-unrelated item, respectively, were presented in the bottom of the pictures, and participants had to select a theme.
Results
The patient group selected theme words at significantly lower rate in both emotional conditions than the control group (positive, p=0.002; negative, p=0.001). Especially, in the negative condition, the patient group more selected theme-unrelated items than the control group (p=0.001). The rates of theme identification were inversely correlated with scores of the Social Anhedonia Scale (positive, r=-0.440, p=0.007; negative, r=-0.366, p=0.028).
Conclusion
Patients with schizophrenia exhibited an impairment in abstract thinking, and it was remarkable in the negative condition. The ability to think abstractly was associated with the severity of social anhedonia. The impairment of abstract thinking may become one of the reasons for poor social functioning in socially anhedonic patients.
REFERENCES
1). Sadock BJ, Sacock VA. Synopsis of Psychiatry; Tenth edition: 273.
2). Kim IJ, Shin MS. Assessment of concrete and abstract thinking of child-psychiatric children with the draw-a-person test and kedi-wisc similarity test. Kor J Child Adolescent Psychiatry. 1999; 10:186–194.
3). Kuperberg G, Heckers S. Schizophrenia and cognitive function. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000; 10:205–210.

4). Sharma T, Antonova L. Cognitive function in schizophrenia Deficits, functional consequences, and future treatment. Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2003; 26:25–40.
5). Peuskens J, Demily C, Thibaut F. Treatment of cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Clin Ther. 2005; 27:S25–S37.

6). Kim CK, Choe BM, Ha MY, Kim SH, Seo JM. Comparisons of Symptoms and Neurocogntive functions in Schizophrenic Patients Divided by Social Functioning. J Kor Neuropsychiatric Association. 2002; 41:1020–1029.
7). Lysaker PH, Bryson GJ, Davis LW, Bell MD. Relationship of impaired processing speed and flexibility of abstract thought to improvements in work performance over time in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2005; 75:211–218.

8). Schmittmann VD, Visser I, Raijmakers MEJ. Multiple learning modes in the development of performance on a rule-based category-learning task. Neuropsychologia. 2006; 44:2079–2091.

9). Harrow M, Adler D. Abstract and concrete thinking in schizophrenia during the prechronic phases. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1974; 31:27–33.

10). Flavell JH. Thinking and social behavior in schizophrenia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 1956; 52:208–211.
11). Kaland N, Smith L, Mortensen EL. Brief Report: Cognitive Flexibility and Focused Attention in Children and Adolescents with Asperger Syndrome or High-Functioning Autism as Measured on the Computerized Version of the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test. J Autism Dev Disorder. 2008; 38:1161–1165.

12). Gorham. Use of the proverbs test for differentiating schizophrenics from normals. J Consult Psychol. 1956; 20:435–440.
13). Nahor, Vannicelli. The influence of instructional set on schizophrenic vs. organic concreteness. Confin Psychiatr. 1976; 19:89–95.
14). Kiang M, Light GA, Prugh J, Coulson S, Braff DL, Kutas M. Cognitive, neurophysiological, and functional correlates of proverb interpretation abnormalities in schizophrenia. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2007; 13:653–663.

15). Christian GK, Travis HT, Warren BB, Collen MB. Facial emotion recognition in schizophrenia: intensity effects and error pattern. Am J Psychiatry. 2003; 160:1768–1774.
16). Manoabc QR, Brownabc GG. Emotion-cognition interactions in schizophrenia: Implicit and explicit effects of facial expression. Neuropsychologia. 2010; 48:997–1002.

17). Blanchard JJ, Mueser KT, Bellack AS. Anhedonia, Positive and Negative Affect, and Social Functioning in Schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1998; 24:413–424.

18). Chapman LJ, Chapman JP, Roulin ML. Scales for physical and social anhedonia. J Abnorm Psychol. 1976; 85:374–382.

19). Kay SR, Flazbein A, Opler LA. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1987; 13:261–276.

20). Albert, Wolfe, Lafleche. Differences in abstraction ability with age. Psychol Aging. 1990; 5:94–100.
21). Citron FMM, Weekes BS, Ferstl EC. Effects of valence and arousal on written word recognition: Time course and ERP correlates. Neurosci Lett. 2013; 15:90–95.

22). Quintana J, Lee J, Marcus M, Kee K, Wong T, Yerevanian A. Brain dysfunctions during facial discrimination in schizophrenia: Selective association to affect decoding. Psychiatry Res. 2011; 191:44–50.

23). Vercarmmen A, Morris R, Green MJ, Lenroot R, Kulkarni J, Carr VJ, et al. Reduced neural activity of the prefrontal cognitive control circuitry during response inhibition to negative words in people with schizophrenia. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012; 37:379–388.

24). Kohler CG, Turner TH, Bilker WB, Brensinger CM, Siegel SJ, Kanes SJ, et al. Facial emotion recognition in schizophrenia: intensity effects and error pattern. Am J Psychiatry. 2003; 160:1768–1774.

25). van't Wout M, van Dijke A, Aleman A, Kessels RPC, Pijpers W, Kahn RS. Fearful faces in schizophrenia: the relationship between patient characteristics and facial affect recognition. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2007; 195:758–764.
26). Bruce N. Carpenter. Relationship of scales of schizophrenia proneness and premorbid adjustment to thinking deficits in schizophrenia. J Clin Psychol. 1983; 39:311–314.
27). Kwapil T. Social anhedonia as a predictor of the development of schizophrenia-spectrum disorders. J Abnorm Psychol. 1998; 107:558–565.

28). O'Reilly P, Harrison K. The Gorham Proverbs Test. Dis Nerv Syst. 1960; 21:382–385.
29). Wechsler D. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Manual. Psychological Corp. 1955.
30). Corrigan. Social cue perception and intelligence in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 1994; 13:73–79. S.
Fig. 2.
Selection rate of related versus unrelated words in the wrong trials on the theme identification task. ∗ : p<0.01. SPR : schizophrenia.
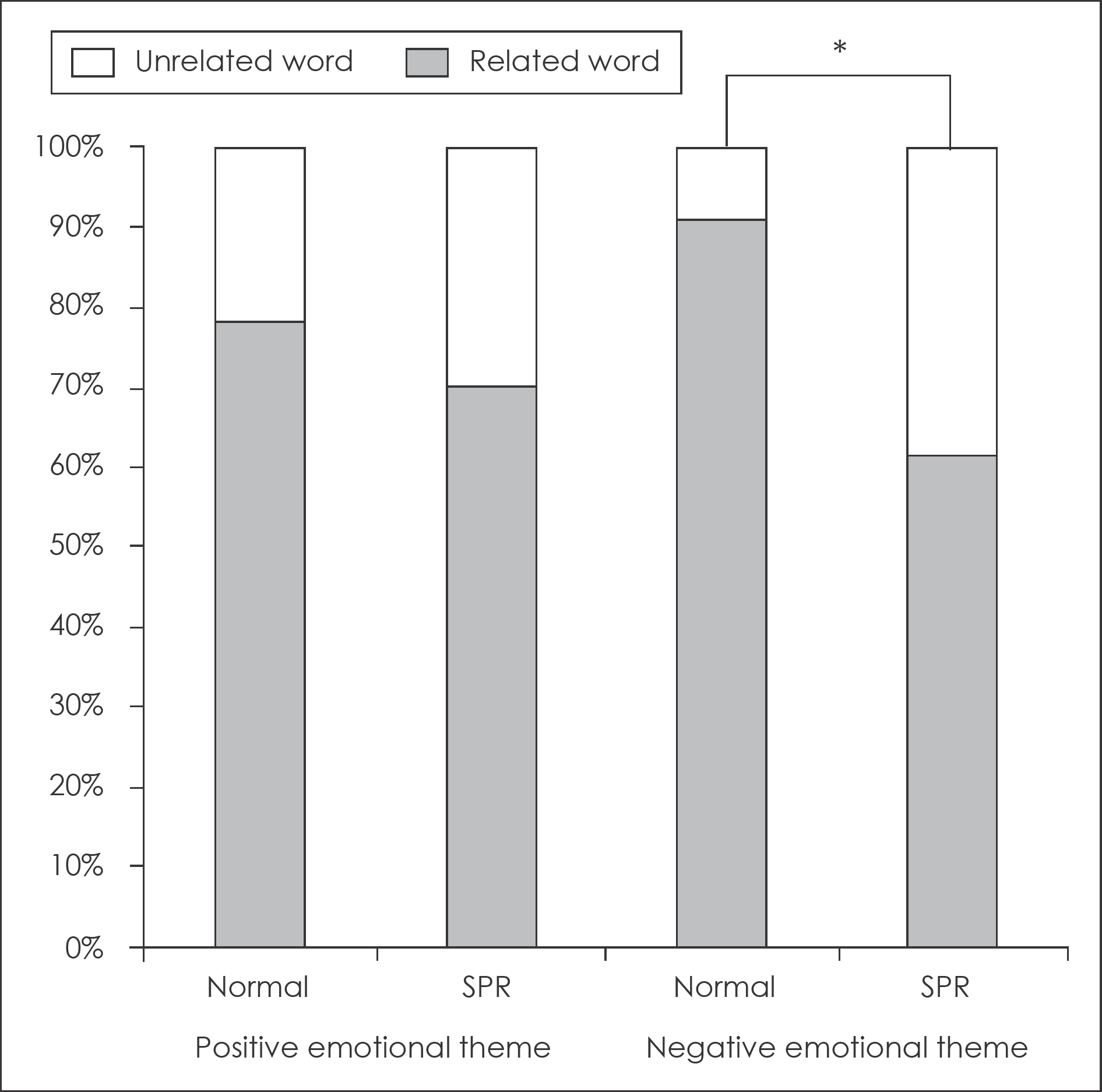
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the subjects
| Characteristic | Normal (N=20) | Schizophrenia (N=20) | p-value∗ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male/Female | 9/11 | 10/10 | 0.752 |
| Age (years) | 32.6±8.1 | 31.7±7.50 | 0.733 |
| Education (years) | 15.8±1.6 | 13.2±2.40 | <0.001 |
| P-AS | 12.6±5.9 | 19.4±9.40 | 0.019 |
| S-AS | 07.6±4.1 | 15.9±6.80 | <0.001 |
| Duration of illness (years) | 6.3 ±5.70 | ||
| PANSS_positive | 18.7±7.40 | ||
| PANSS_negative | 17.8±6.00 | ||
| PANSS_general | 38.5±11.7 | ||
| PANSS_total | 74.9±23.5 |
Table 2.
Behavioral responses in the theme identification task
Table 3.
Behavioral responses in the emotion recognition task
∗ : by ANCOVA (covariate : education) for mean number of response and independent sample t-test for response time, Values are mean±SD. SPR : schizophrenia. Positive_RT : Mean response time during the emotion recognition task with positive picture, Negative_RT : Mean response time during the emotion recognition task with negative picture




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download