Abstract
Objectives
Schizophrenia patients have deficits of prediction and learning related to dopaminergic dysfunction. It is hypothesized that there would be different characteristics in associative learning of reward approach and loss aversion between controls and patients.
Methods
Participants were 23 healthy participants and 20 out-patients fulfilling criteria for schizophrenia according DSM-IV-TR. Using a monetary incentive contingency reversal task, successful learning rates, numbers of trials and errors till learning, numbers of trials of maintaining learning, response times were measured. Characteristics of learning were compared between controls and patients.
Results
Physical anhedonia and PANSS negative symptom scores correlated with the number of trials while loss aversion was maintained. Overall correct response rates were decreased in patient group, particularly during reward approach learning. Patients required more trials and errors to learn reward approach than controls. There were no significant differences in learning performance and reaction times between groups during loss avoidance learning.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
The mean rates and standard errors of successful learning in healthy controls and patients with schizophrenia. Rates of Successful Learning were divided into two dimensions and analyzed by rmANOVA. A : While reversal Learning, there were no significances (Within-group : F<0, df=1, p=0.99. Between-group F=3.95, df=1, p=0.05). B : Overall correct response rates were significant in between-group effects (F=5.58, df=1, p=0.02) but not in within-group effects (F=2.18, df=1, p=0.15). Independent T-test was using for post hoc analysis of between-group effect. Specifically, during reward phase, controls showed higher successful learning rate than control did (t=2.73, df=41, p=0.001). *: p<0.05. R to L : Reward to Loss, L to R : Loss to Reward
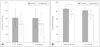
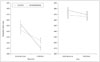
Fig. 2
The median and inter-quartile range of the numbers of trials and errors needed for initiating learning and trials maintained of reward and loss contingency in healthy controls and patients with schizophrenia. *: Between-group analysis using Mann-Whitney test revealed that the patient group needed more trials and errors to learn reward contingency (Z=-2.07, p=0.04). A : Within-group effects were analyzed by Wilcoxon-signed rank test. In the control group, significantly lesser numbers of trials and errors were needed to learn reward contingency than loss contingency (Z=-2.56, p=0.01). There were no significant within-group difference in the patient group. B : There were no between-group and within-group effects in analysis of numbers of maintained trials during reward and loss contingencies.

Fig. 3
The estimated marginal means and standard errors of the reaction times during the initiation and maintenance of reward and loss learning in healthy controls and patients with schizophrenia. Mixed model ANOVA was performed with a mean reaction time of correct response (453.40 ms) was used as covariates. During reward learning, within-group learning phase effect [F(1, 40)=6.39, p=0.02] and interaction between learning phase and groups were statistically significant [F(1, 40)=6.20, p=0.02].
References
1. Strauss GP, Frank MJ, Waltz JA, Kasanova Z, Herbener ES, Gold JM. Deficits in positive reinforcement learning and uncertainty-driven exploration are associated with distinct aspects of negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. 69:424–431.

3. Waltz JA, Frank MJ, Robinson BM, Gold JM. Selective reinforcement learning deficits in schizophrenia support predictions fromcomputational models of striatal-cortical dysfunction. Biol Psychiatry. 2007. 62:756–764.

4. Prentice KJ, Gold JM, Buchanan RW. The Wisconsin Card Sorting impairment in schizophrenia is evident in the first four trials. Schizophr Res. 2008. 106:81–87.

5. Kapur S. Psychosis as a state of aberrant salience: a framework linking biology, phenomenology, and pharmacology in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2003. 160:13–23.

6. Frank MJ. Schizophrenia: a computational reinforcement learning perspective. Schizophr Bull. 2008. 34:1008–1011.

7. Gard DE, Kring AM, Gard MG, Horan WP, Green MF. Anhedonia in schizophrenia: distinctions between anticipatory and consummatory pleasure. Schizophr Res. 2007. 93:253–260.

8. Gold JM, Waltz JA, Prentice KJ, Morris SE, Heerey EA. Reward processing in schizophrenia: a deficit in the representation of value. Schizophr Bull. 2008. 34:835–847.

9. Wächter T, Lungu OV, Liu T, Willingham DT, Ashe J. Differential effect of reward and punishment on procedural learning. J Neurosci. 2009. 29:436–443.

10. Association AP. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV-TR. 2000. Washington: American Psychiatric Publishing.
11. Raven J, Court J, Raven J. Raven-Matrizen-test standard progressive matrices. 1988. Weinheim: Test Gesellschaft.
12. Chapman LJ, Chapman JP, Raulin ML. Scales for physical and social anhedonia. J Abnorm Psychol. 1976. 85:374.

13. Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1988. 54:1063.

14. Min BB, Oh HS, Lee JY. Temperament and Character Inventory(TCI) Manual. 2007. Seoul: Maumsarang.
15. Yi JS, Ahn YM, Shin HK, An SK, Joo YH, Kim SH, et al. Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2001. 40:1090–1105.
16. van der Gaag M, Hoffman T, Remijsen M, Hijman R, de Haan L, van Meijel B, et al. The five-factor model of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale II: a ten-fold cross-validation of a revised model. Schizophr Res. 2006. 85:280–287.

17. Blanchard JJ, Mueser KT, Bellack AS. Anhedonia, positive and negative affect, and social functioning in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1998. 24:413–424.

18. Waltz JA, Gold JM. Probabilistic reversal learning impairments in schizophrenia: further evidence of orbitofrontal dysfunction. Schizophr Res. 2007. 93:296–303.

19. Lee Y, Kim YT, Seo E, Park O, Jeong SH, Kim SH, et al. Dissociation of emotional decision-making from cognitive decision-making in chronic schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2007. 152:113–120.

20. Danion JM, Gokalsing E, Robert P, Massin-Krauss M, Bacon E. Defective relationship between subjective experience and behavior in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2001. 158:2064–2066.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download