Abstract
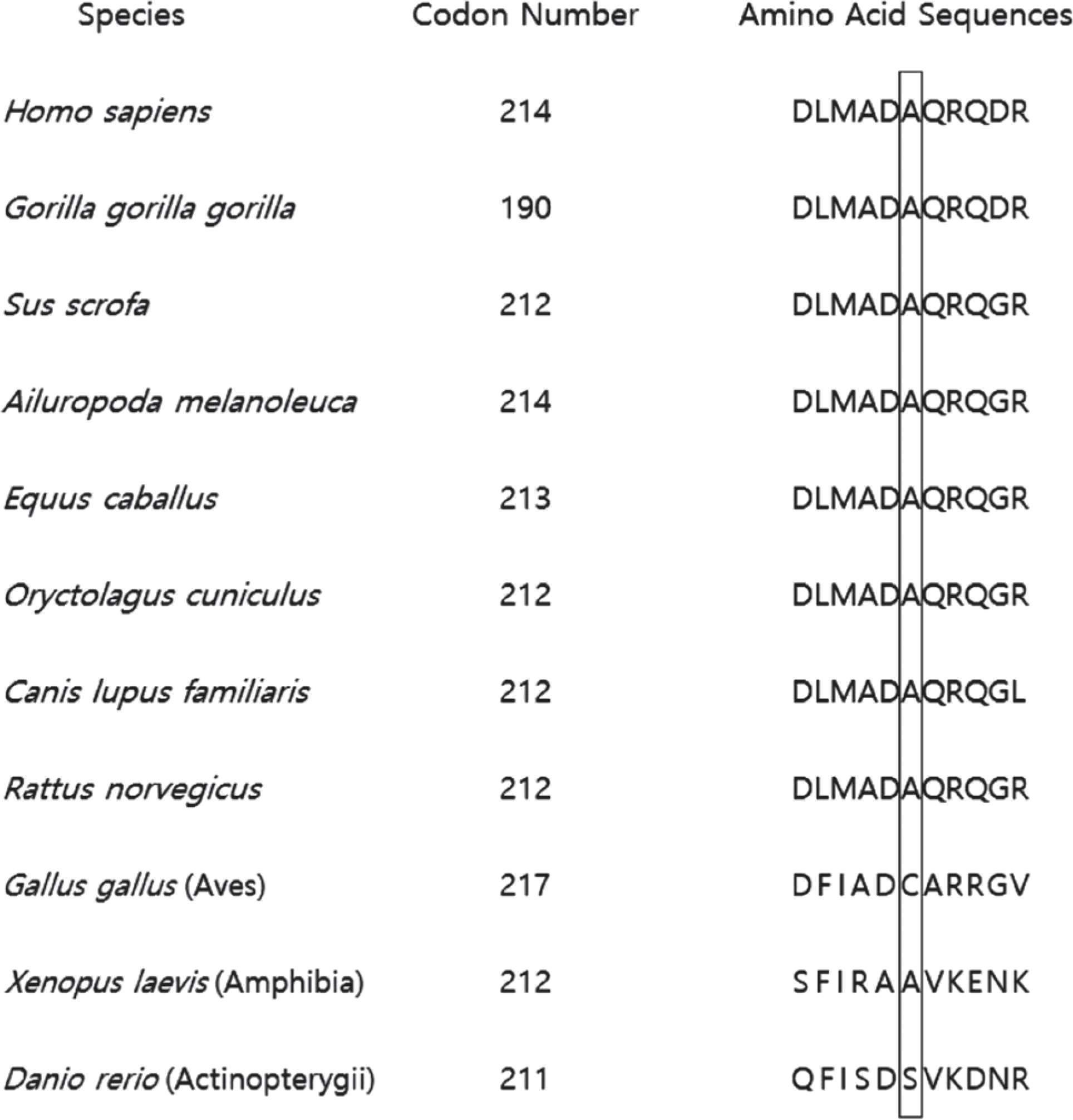
Metachromatic leukodystrophy is an inherited lysosomal storage disorder caused by the deficiency of arylsulfatase A activity. The patient in this study, a 5-yr-old girl, presented with progressive psychomotor regression. An MRI image of her brain showed bilateral symmetrical demyelination. The arylsulfatase A activity in her leukocytes was decreased to 8.0 nmol/hr/mg protein (reference range, 25-80 nmol/hr/mg protein). Mutation analysis of ARSA, using PCR and direct sequencing, showed two heterozygote pathogenic variations of c.449C>T (p.Pro150Leu) and c.640G>A (p.Ala214Thr). In summary, we report a Korean patient with an early juvenile form of metachromatic leukodystrophy, who was diagnosed based on her clinical symptoms as well as by using biochemical, radiological, and molecular genetic investigations.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Gieselmann V, Krageloh-Mann I. Metachromatic leukodystrophy–an update. Neuropediatrics. 2010; 41:1–6.
2. Biff A, Cesani M, Fumagalli F, Del Carro U, Baldoli C, Canale S, et al. Metachromatic leukodystrophy - mutation analysis provides further evidence of genotype-phenotype correlation. Clin Genet. 2008; 74:349–57.
3. van Rappard DF, Boelens JJ, Wolf NI. Metachromatic leukodystrophy: disease spectrum and approaches for treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 29:261–73.

4. Cesani M, Lorioli L, Grossi S, Amico G, Fumagalli F, Spiga I, et al. Mutation update of ARSA and PSAP genes causing metachromatic leukodystrophy. Hum Mutat. 2016; 37:16–27.
5. Gieselmann V. Metachromatic leukodystrophy: genetics, pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Acta Paediatr. 2008; 97:15–21.

6. Regis S, Corsolini F, Stroppiano M, Cusano R, Filocamo M. Contribution of arylsulfatase A mutations located on the same allele to enzyme activity reduction and metachromatic leukodystrophy severity. Hum Genet. 2002; 110:351–5.

7. Han M, Jun SH, Lee YJ, Eun BL, Lee SJ, Seong MW, et al. Biochemical and genetic analysis of seven Korean individuals with suspected metachromatic leukodystrophy. Ann Lab Med. 2015; 35:458–62.

8. Kang DH, Lee DH, Hong YH, Lee ST, Jeon BR, Lee YK, et al. Identifcation of a novel splicing mutation in the ARSA gene in a patient with late-infantile form of metachromatic leukodystrophy. Korean J Lab Med. 2010; 30:516–20.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download