Abstract
Roseomonas is a genus of pink-pigmented, oxidative, gram-negative coccobacilli and rarely causes opportunistic infection. We report a case of wound infection by Roseomonas species in a 53-yr-old man with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene sequencing was performed to confirm the infectious agent. The patient recovered without complication after ciprofloxacin treatment. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of Roseomonas infection reported in Korea.
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1(A) Gram staining of Roseomonas showing gram-negative coccobacilli in small chains (×1,000). (B) Roseomonas on blood agar showing non-hemolytic pink mucoid colonies after incubation for 24 hr. |
 | Fig. 2Phylogenic tree showing the relationship of the clinical isolate with other Roseomonas species constructed by the neighbor-joining method on the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequences. The scale bar represents 1% sequence distance. |
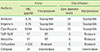
Table 1
Susceptibility of the clinical isolate to antimicrobial drugs
References
1. Rihs JD, Brenner DJ, Weaver RE, Steigerwalt AG, Hollis DG, Yu VL. Roseomonas: a new genus associated with bacteremia and other human infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1993; 31:3275–3283.

2. Han XY, Pham AS, Tarrand JJ, Rolston KV, Helsel LO, Levett PN. Bacteriologic characterization of 36 strains of Roseomonas species and proposal of Roseomonas mucosa sp nov and Roseomonas gilardii subsp rosea subsp nov. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003; 120:256–264.
3. Struthers M, Wong J, Janda JM. An initial appraisal of the clinical significance of Roseomonas species associated with human infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1996; 23:729–733.

4. Nahass RG, Wisneski R, Herman DJ, Hirsh E, Goldblatt K. Vertebral osteomyelitis due to Roseomonas species: case report and review of the evaluation of vertebral osteomyelitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1995; 21:1474–1476.

5. Dé I, Rolston KV, Han XY. Clinical significance of Roseomonas species isolated from catheter and blood samples: analysis of 36 cases in patients with cancer. Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 38:1579–1584.
6. Sandoe JA, Malnick H, Loudon KW. A case of peritonitis caused by Roseomonas gilardii in a patient undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1997; 35:2150–2152.

7. Furuhata K, Miyamoto H, Goto K, Kato Y, Hara M, Fukuyama M. Roseomonas stagni sp. nov.,isolated from pond water in Japan. J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2008; 54:167–171.
8. Zhang YQ, Yu LY, Wang D, Liu HY, Sun CH, Jiang W, et al. Roseomonas vinacea sp. nov., a Gram-negative coccobacillus isolated from a soil sample. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2008; 58:2070–2074.

9. Sung JY, Kwon KC, Park JW, Kim YS, Kim JM, Shin KS, et al. Dissemination of IMP-1 and OXA type ß-lactamase in carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Korean J Lab Med. 2008; 28:16–23.

10. Bard JD, Deville JG, Summanen PH, Lewinski MA. Roseomonas mucosa isolated from bloodstream of pediatric patient. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:3027–3029.

11. Srifuengfung S, Tharavichitkul P, Pumprueg S, Tribuddharat C. Roseomonas gilardii subsp rosea, a pink bacterium associated with bacteremia: the first case in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2007; 38:886–891.
12. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Twenty-forth informational supplement. Document M100-S23. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2014.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download