Abstract
Accurate D antigen blood typing is needed owing to the clinical importance of the Rh blood group. We describe a female infant who was suspected to suffer from Rh incompatible hemolytic disease of the newborn, and who showed a strong positive direct antiglobin test (DAT) result and false red blood cell (RBC) agglutination in D typing. Using chloroquine dissociation of IgG, we confirmed that the antibodies coating her RBCs were of anti-D type. D typing with 0.8% RBC suspensions in saline using saline gel cards showed 2+ RBC agglutinations. After increasing the incubation time of dissociation by chloroquine for up to 4 hr, the dissociated RBCs began to show agglutination in both the tube technique (2+) and the gel card technique (4+) for D typing, although the DAT rest was still positive. Therefore, in order to prevent mistyping as a false-negative D blood group, whenever the D blood typing of a patient with a strong positive DAT rest does not show RBC agglutination, retesting of the D blood typing is recommended by using saline-suspended RBCs or dissociated RBCs.
Figures and Tables
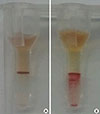
Fig. 1
Red blood cell (RBC) agglutination in the column agglutination test (CAT) for determining Rh(D) type. (A) CAT after 4 hr of chloroquine dissociation (4+). (B) CAT of RBC suspension in 0.8% normal saline before chloroquine dissociation (2+).
References
1. Roback JD, Brenda JG, editors. Technical manual. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;2011. p. 400.
2. Roback JD, Brenda JG, editors. Technical manual. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;2011. p. 637.
3. Roback JD, Brenda JG, editors. Technical manual. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;2011. p. 406–407.
4. Hwang YS. Haplotype frequencies of Rh gene loci in Koreans. Korean J Blood Transfus. 1996; 7:233–240.
5. Han KS, Park KU, editors. Transfusion medicine. 4th ed. Seoul: Korea Medical Publishing Co.;2014. p. 102.
6. Roback JD, Brenda JG, editors. Technical manual. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;2011. p. 891–892.
9. Han KS, Park KU, editors. Transfusion medicine. 4th ed. Seoul: Korea Medical Publishing Co.;2014. p. 193–194.
10. Roback JD, Brenda JG, editors. Technical manual. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;2011. p. 500–501.
11. Lee SH, Oh YC, Kim KH, Han KS, Han BY, Kim SI. IgG elution method using glycine acid EDTA -comparison to chloroquine method-. Korean J Blood Transfus. 1993; 4:61–66.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download