Abstract
Pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP) is a group of genetic disorders in which the kidneys fail to respond to parathyroid hormone. Genetic defects in the GNAS complex locus lead to reduced Gsα (alpha-subunit of the heterotrimeric stimulatory G protein) activity in PHP type Ia patients. These patients exhibit characteristics of Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (AHO) and hypocalcemia, increased parathyroid hormone, and resistance to other Gsα protein-coupled hormones. AHO has a wide range of manifestations such as short stature, obesity, round face, subcutaneous ossification, and bone shortening in the hands and feet. In this study, we present the case of a 47-yr-old woman who was diagnosed with PHP type Ia with AHO. She showed tetany, dizziness, irritability to light, decreased visual acuity, cognitive impairment, and motor dysfunction. Direct sequencing identified a heterozygous missense mutation in exon 6 (c.466G>A, p.Asp156Asn) in GNAS1. To our knowledge, this case is the first report in Korea of PHP type Ia caused by a heterozygous missense mutation in exon 6 (c.466G>A, p.Asp156Asn) in GNAS1.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
The patient had small hands and feet with significantly short digits (A, B). X-ray reveals shortening of metatarsal bones in the feet (C) and metacarpal bones and phalanges in the hands (D).
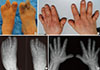
Fig. 2
The brain CT scan of the patient of Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy with pseudohypoparathyroidism establishes extensive calcifications in the bilateral dense cerebellum (A) and basal ganglia (B).
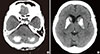
Fig. 3
Direct sequencing of GNAS1 exon 6 region in the affected patient. A heterozygous G>A substitution at nucleotide position 466 converts an aspartate (GAT) to asparagine (AAT), designated as D156N.
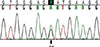
Table 1
Results of biochemical tests performed on the patient
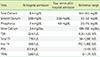
Table 2
List of primers

Table 3
Clinical findings and molecular profile of Korean pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia patients in previously published studies

| Patient No. | Age at Dx | Sex | Characteristics | Base change | Amino acid change | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 yr, 2 mo | F | Pain in both legs, subcutaneous calcification | c.94A > T | p.K32X | [3, 5] |
| 2 | 7 yr, 1 mo | M | Seizures | c.344_345 insT | p.V117RfsX23 | [3, 5] |
| 3 | 12 yr | M | Hypocalcemic seizure | c565_568 del | p.Asp189_Tyr190 | [4] |
| delinsMetfsX14 | ||||||
| 4 | - | M | Asymptomatic | c.569_570 del | p.Tyr190CysfsX19 | [4] |
| 5 | 9 yr, 5 mo | F | Hypocalcemic seizure | c.348_349 insC | p.Val117fsX23 | [4] |
| 6 | 2 yr, 11 mo | F | Subcutaneous calcification | c.348_349 insC | p.Val117fsX23 | [4] |
| 7 | - | M | Asymptomatic | c.348_349 insC | p.Val117fsX23 | [4] |
| 8 | 13 yr, 10 mo | M | Hypocalcemic seizure | c659+1G > A | Splicing mutation | [4] |
| 9 | 6 yr, 1 mo | F | Brachydactyly, subcutaneous calcification | c85C > T | p.Q29X | [5] |
| 10 | 28 yr, 6 mo | M | Subcutaneous calcification, seizures | Exon 1-13 large deletion | [5] | |
| 11 | 9 yr | M | Subcutaneous calcification, short stature, round face, brachydactyly | c637C > T | p.Gln213 | [6] |
References
1. Nakamura Y, Matsumoto T, Tamakoshi A, Kawamura T, Seino Y, Kasuga M, et al. Prevalence of idiopathic hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism in Japan. J Epidemiol. 2000; 10:29–33.

2. John TP, Harald J. Disorders of the parathyroid gland and calcium homeostasis. In : Longo DL, Harrison TR, editors. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 18th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2012. p. 3117–3118.
3. Park CH, Park HD, Lee SY, Kim JW, Sohn YB, Park SW, et al. Clinical, biochemical, and genetic analysis of Korean patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2010; 40:261–266.
4. Jin HY, Lee BH, Choi JH, Kim GH, Kim JK, Lee JH, et al. Clinical characterization and identification of two novel mutations of the GNAS gene in patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism and pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2011; 75:207–213.

5. Cho SY, Yoon YA, Ki CS, Huh HJ, Yoo HW, Lee BH, et al. Clinical characterization and molecular classification of 12 Korean patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism and pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2013; 121:539–545.

6. Lee YS, Kim HK, Kim HR, Lee JY, Choi JW, Bae EJ, et al. Identification of a novel mutation in a patient with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia. Korean J Pediatr. 2014; 57:240–244.

7. Levine MA. An update on the clinical and molecular characteristics of pseudohypoparathyroidism. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012; 19:443–451.

8. Goto M, Mizunashi K, Kimura N, Furukawa Y. Decreased sensitivity of distal nephron and collecting duct to parathyroid hormone in pseudohypoparathyroidism type I. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001; 12:1965–1970.

9. Ahrens W, Hiort O, Staedt P, Kirschner T, Marschke C, Kruse K. Analysis of the GNAS1 gene in Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:4630–4634.
10. Linglart A, Carel JC, Garabédian M, Lé T, Mallet E, Kottler ML. GNAS1 lesions in pseudohypoparathyroidism Ia and Ic: genotype phenotype relationship and evidence of the maternal transmission of the hormonal resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:189–197.

11. Lim SG, Kim DP, Hong HP, Kim MC, Ko YG. Idiopathic hypoparathyroidism combined with extensive intracranial calcification: a case report. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2005; 16:383–386.
12. Eşel Ertuğrul, Bayram Fahri, Çatakoğlu Özgül, Candemir Zuhal, Turan M Tayfun, Kılıç Canan. Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy and dementia: a case report. Klinik Psikofarmakol Bülteni. 2001; 11:183–186.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download