Abstract
Background
The heavy-light chain (HLC) quantitative test can identify and quantify the heavy and light chains of each immunoglobulin class. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of the HLC quantitative test.
Methods
To evaluate the effectiveness of the HLC quantitative test, a systemic review of the literature, using Ovid-MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane library, and eight domestic databases including KoreaMed, was performed until October 10, 2013. We included five cohort studies and one diagnostic evaluation study in the final evaluation. Two reviewers independently assessed the quality of the included studies and extracted data from the studies. The quality of the studies was assessed according to the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) tool.
Results
A correlation between the HLC quantitative test and previous assays was evaluated in one study, which enrolled patients with increased monoclonal IgA. The correlation coefficient was reported as 0.94 in this study. The clinical significance of the quantitative HLC test to predict a prognosis was also reported in five cohort studies. The survival rate in patients with higher HLC ratio was significantly lower and the increased IgA κ/λ ratio or IgM κ/λ ratio was significantly correlated with higher survival rate in patients with monoclonal gammaglobulinemia.
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Publications selected for the evaluation of the heavy-light chain quantitative test, according to the literature search strategy. |
Table 1
Ovid-MEDLINE, Ovid-EMBASE search strategy
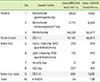
Table 2
Levels of evidence

Table 3
Grades of recommendations

Table 4
Literature selected for the evaluation of the heavy-light chain quantitative test

References
1. Hwang Y, Chung WS, Hong KS. Evaluation of the screening tests for the diagnosis of plasma cell neoplasm. Lab Med Online. 2012; 2:80–86.

2. Jung S, Kim M, Lim J, Kim Y, Han K, Min CK, et al. Serum free light chains for diagnosis and follow-up of multiple myeloma. Korean J Lab Med. 2008; 28:169–173.

3. Bradwell AR, Carr-Smith HD, Mead GP, Tang LX, Showell PJ, Drayson MT, et al. Highly sensitive, automated immunoassay for immunoglobulin free light chains in serum and urine. Clin Chem. 2001; 47:673–680.

4. Durie BG, Harousseau JL, Miguel JS, Bladé J, Barlogie B, Anderson K, et al. International uniform response criteria for multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2006; 20:1467–1473.

5. Bradwell AR, Harding SJ, Fourrier NJ, Wallis GL, Drayson MT, Carr-Smith HD, et al. Assessment of monoclonal gammopathies by nephelometric measurement of individual immunoglobulin kappa/lambda ratios. Clin Chem. 2009; 55:1646–1655.

6. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. SIGN 50: a guideline developer's handbook. Updated on March 2004. http://www.sign.ac.uk/pdf/sign50annexc.pdf.
7. Wolff F, Debaugnies F, Rozen L, Willems D, Brohet F, Brauner J, et al. Assessment of the diagnostic performances of IgA heavy and light chain pairs in patients with IgA monoclonal gammopathy. Clin Biochem. 2013; 46:79–84.

8. Bradwell A, Harding S, Fourrier N, Mathiot C, Attal M, Moreau P, et al. Prognostic utility of intact immunoglobulin Ig'κ/Ig'λ ratios in multiple myeloma patients. Leukemia. 2013; 27:202–207.

9. Ludwig H, Milosavljevic D, Zojer N, Faint JM, Bradwell A, Hübl W, et al. Immunoglobulin heavy/light chain ratios improve paraprotein detection and monitoring, identify residual disease and correlate with survival in multiple myeloma patients. Leukemia. 2013; 27:213–219.

10. Katzmann JA, Clark R, Kyle RA, Larson DR, Therneau TM, Melton LJ 3rd, et al. Suppression of uninvolved immunoglobulins defined by heavy/light chain pair suppression is a risk factor for progression of MGUS. Leukemia. 2013; 27:208–212.

11. Koulieris E, Panayiotidis P, Harding SJ, Kafasi N, Maltezas D, Bartzis V, et al. Ratio of involved/uninvolved immunoglobulin quantification by Hevylite™assay: clinical and prognostic impact in multiple myeloma. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2012; 1:9.

12. Tovar N, Fernández de, Elena M, Cibeira MT, Aróstegui JI, Rosiñol L, et al. Prognostic impact of serum immunoglobulin heavy/light chain ratio in patients with multiple myeloma in complete remission after autologous stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012; 18:1076–1079.

13. McPherson RA, Massey HD. Henry's clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods. In : McPherson RA, Pincus MR, editors. Laboratory evaluation of immunoglobulin function and humoral immunity. 21th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;2007. p. 835–848.
14. Haemato-oncology Task Force of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of multiple myeloma 2013. Updated on 2010. http://www.bcshguidelines.com/documents/MYELOMA_GUIDELINE_updated_29_aug_RG_jzw_(3).pdf.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download