Abstract
Background
In diabetic patients, both glucose and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) concentrations are frequently measured to monitor glycemic control. We examined the analytical performance of the recently developed, automated, ADAMS bridge system (Arkray, Inc., Japan) consisting of the ADAMS glucose GA-1171 and the ADAMS HbA1c HA-8180 analyzers, which allows the consecutive measurement of glucose and HbA1c concentrations.
Methods
We evaluated precision, linearity, carry-over, effects of hematocrit, and turnaround time. Method comparison was conducted between GA-1171 and UniCel DxC 800 (Beckman Coulter, Inc., USA) and Synchron CX3 Delta (Beckman Coulter) for glucose, and between HA-8180 and HLC-723 G8 (Tosoh Bioscience, Inc., Japan) for HbA1c measurements.
Results
Total precision (% CV) in measuring high and low level controls was 1.11% and 1.21% for glucose using GA-1171, and 0.86% and 1.3% for HbA1c using HA-8180, respectively. In the linearity test, R2 was 0.9997, 0.9991 and 0.9973 when measuring plasma glucose (58-532 mg/dL), whole blood glucose (74-401 mg/dL), and HbA1c concentrations (4.7-14.7%), respectively. Good correlation was observed between GA-1171 and DxC 800 (r=0.9987), and between HA-8180 and HLC-723 G8 (r=0.9980). Carry-over effect was less than 0.5% for glucose and HbA1c. Turnaround time was reduced from 7 min (CX3 Delta) and 1.43 min (HLC-723 G8) to 2.16 min (GA-1171) and 1.54 min (HA-8180), respectively, when whole blood glucose and HbA1c concentrations were measured consecutively by the ADAMS bridge system.
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Linearity curves of measured value vs. expected value for the measurement of glucose and HbA1c concentrations. (A) Plasma glucose concentration measured by GA-1171. (B) Whole blood glucose concentration measured by GA-1171. (C) HbA1c concentration measured by HA-8180. |
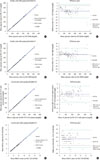 | Fig. 2Method comparison between different analyzers for the measurement of glucose and HbA1c concentrations. Scattered plots (-1) and difference plots (-2) are shown for each method comparison. (A) CX3 Delta vs. GA-1171 (measurement of plasma glucose concentration). (B) DxC 800 vs. GA-1171 (measurement of plasma glucose concentration). (C) GA-1171 vs. GA-1171 (measurement of whole blood vs. plasma glucose concentrations). (D) HLC-723 G8 vs. HA-8180 (measurement of HbA1c concentration). |
References
1. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2008; 3:Suppl 1. S55–S60.
2. Choi YJ, Kim HC, Kim HM, Park SW, Kim J, Kim DJ. Prevalence and management of diabetes in Korean adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1998-2005. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:2016–2020.
3. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI document EP5-A2. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; approved guideline-second edition. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2004.
4. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI document EP6-A. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: a statistical approach; approved guideline. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2003.
5. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI document EP9-A2. Method comparison and bias estimation using patient samples; approved guideline. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;2002.
6. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2012. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:Suppl 1. S11–S63.
7. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2545–2559.

8. Sacks DB, Arnold M, Bakris GL, Bruns DE, Horvath AR, Kirkman MS, et al. Guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:e61–e99.

9. Lim J, Kim JM, Koo SH, Kwon KC. Evaluation of the performance of ARKRAY ADAMS HA-8180 HbA1c analyzer. Lab Med Online. 2012; 2:126–130.

10. Weykamp C, Lenters-Westra E, van der Vuurst H, Slingerland R, Siebelder C, Visser-Dekkers W. Evaluation of the Menarini/ARKRAY ADAMS A1c HA-8180V analyser for HbA1c. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011; 49:647–651.

11. Choi Q, Han M, Chang HE, Song SH, Park KU, Song J. Performance evaluation of the ADAMS A1c HA-8180 analyzer for HbA1c. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2012; 34:25–30.
12. ISO. ISO 15197. In vitro diagnostic test system - Requirements for blood-glucose monitoring systems for self-testing in managing diabetes mellitus. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization;2003.
13. Park HD, Kim HJ, Kim MS, Lee SY, Kim JW. Evaluation of Hemoglobin A1c on the Cobas Integra 800 Immunoassay and Tosoh HLC-723 G8 HPLC analyzer. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2009; 31:239–246.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download