Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1

Fig. 2

Fig. 3

Table 1

*P-values were determined by using the paired t-test; †rho data were determined by Spearman's correlation with a P-value of <0.001; ‡Allowable difference range extrapolated from Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act/College of American Pathologists (CLIA/CAP) participant surveys.
Abbreviations: WBC, white blood cell count; RBC, red blood cell count; Hgb, hemoglobin; Hct, hematocrit; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; MCH, mean corpuscular hemoglobin; MCHC, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration; RDW, red cell distribution width; PLT, platelet; PDW, platelet distribution width; MPV, MPV, mean platelet volume.
Table 2

*P-values were determined by using the paired t-test; †rho data were determined by Spearman's correlation with a P-value <0.001; ‡Allowable difference range extrapolated from Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act/College of American Pathologists (CLIA/CAP) participant surveys.
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; GGT, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; T-BIL, total bilirubin; D-BIL, direct bilirubin; CHOL, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; PI, inorganic phosphorus; CK, creatine kinase; LD, lactate dehydrogenase; UIBC, unsaturated iron-binding capacity; PL, phospholipid; CRP, C-reactive protein; TIBC, total iron-binding capacity; T3, triiodothyronine; FT4, free thyroxine; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Table 3
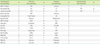
Abbreviations: WBC, white blood cell count; RBC, red blood cell count; Hgb, hemoglobin; Hct, hematocrit; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; MCHC, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration; RDW, red cell distribution width; PLT, platelet; PDW, platelet distribution width; MPV, mean platelet volume; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; GGT, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; T-BIL, total bilirubin; D-BIL, direct bilirubin; CHOL, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; PI, inorganic phosphorus; CK, creatine kinase; LD, lactate dehydrogenase; UIBC, unsaturated iron-binding capacity; CK-MB, creatine kinase myocardial band isoenzyme; PL, phospholipid; CRP, C-reactive protein; TIBC, total iron-binding capacity; T3, triiodothyronine; FT4, free thyroxine; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Table 4
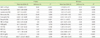
Table 5

*P-value for difference of the result between Day 0 (t=0 hr) and Day 3 (t=72±2 hr); †P-value for difference of the result between Day 3 (t=72±2 hr) and Day 7 (t=168±2 hr); ‡P-value for difference of the result between Day 0 (t=0 hr) and Day 7 (t=168±2 hr).
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; GGT, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; T-BIL, total bilirubin; D-BIL, direct bilirubin; TG, triglyceride; CHOL, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; PI, inorganic phosphorus; CK, creatine kinase; LD, lactate dehydrogenase; UIBC, unsaturated iron-binding capacity; CK-MB, creatine kinase myocardial band isoenzyme; PL, phospholipid; CRP, C-reactive protein; TIBC, total iron-binding capacity; sodium; T3, triiodothyronine; FT4, free thyroxine; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Table 6

*P-value for difference of the result between day 0 (t=0 hr) and day 3 (t=72±2 hr); †P-value for difference of the result between day 3 (t=72±2 hr) and day 7 (t=168±2 hr); ‡P-value for difference of the result between day 0 (t=0 hr) and day 7 (t=168±2 hr).
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; GGT, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; T-BIL, total bilirubin; D-BIL, direct bilirubin; CHOL, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; PI, inorganic phosphorus; CK, creatine kinase; LD, lactate dehydrogenase; UIBC, unsaturated iron-binding capacity; CK-MB, creatine kinase myocardial band isoenzyme; PL, phospholipid; CRP, C-reactive protein; TIBC, total iron-binding capacity; sodium; T3, triiodothyronine; FT4, free thyroxine; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download