Abstract
Background
This study was conducted to evaluate the significance of serum eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels in children with allergic diseases and non-allergic inflammatory diseases, and to assess the relationships between serum ECP levels and inflammatory parameters.
Methods
In this study, we included 146 children with allergic diseases, 76 children with non-allergic inflammatory diseases, and 25 control subjects. Serum concentrations of ECP, hs-CRP, total IgE, and allergen-specific IgE were measured.
Results
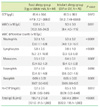
Serum ECP levels (77.5±88.2 µg/L) of patients with allergic diseases were significantly higher than those of the patients with non-allergic inflammatory diseases (42.2±58.8 µg/L) and control subjects (12.7±4.2 µg/L) (P<0.001, respectively). The serum ECP levels in patients with non-allergic inflammatory diseases were also significantly higher than those in the controls (42.2±58.8 vs. 12.7±4.2 µg/L; P<0.001). The hs-CRP levels were significantly higher in patients with allergic diseases than in the controls (0.4±0.9 vs. 0.1±0.2 mg/dL; P<0.05). No significant relationship was observed between serum ECP and hs-CRP levels in the allergic patients (r=0.09, P>0.05).
Conclusions
Measurement of serum ECP and hs-CRP concentrations can be helpful in the clinical evaluation and monitoring of patients with allergic diseases. No significant correlation was observed between serum ECP and hs-CRP levels in allergic patients, thereby suggesting that elevated levels of ECP do not necessarily reflect the degree of systemic inflammation in allergic diseases.
Figures and Tables
Table 2
ECP, WBC, hs-CRP, and total IgE levels in the patient and control groups
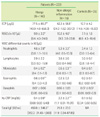
Data are expressed as mean±SD (median: range).
*P<0.05, allergy group vs. control; †P<0.05, non-allergic inflammation group vs. control; ‡P<0.05, allergy group vs. non-allergic inflammation group.
Abbreviations: ECP, eosinophil cationic protein; WBC, white blood cell; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; NA, not applicable.
Table 3
Correlation coefficients of serum ECP and hs-CRP levels versus other variables in allergy, non-allergic inflammation, and control groups
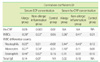
Table 4
hs-CRP concentrations on the basis of upper and lower 10 percentile of ECP levels in allergy and non-allergic inflammation group

References
1. Gleich GJ, Adolphson CR. The eosinophilic leukocyte: structure and function. Adv Immunol. 1986. 39:177–253.

2. Hogan SP, Rosenberg HF, Moqbel R, Phipps S, Foster PS, Lacy P, et al. Eosinophils: biological properties and role in health and disease. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008. 38:709–750.

3. Venge P, Byström J, Carlson M, Hâkansson L, Karawacjzyk M, Peterson C, et al. Eosinophil cationic protein (ECP): molecular and biological properties and the use of ECP as a marker of eosinophil activation in disease. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999. 29:1172–1186.

4. Koh GC, Shek LP, Kee J, Wee A, Ng V, Koh D. Saliva and serum eosinophil cationic protein in asthmatic children and adolescents with and without allergic sensitization. J Asthma. 2010. 47:61–65.

5. Koh GC, Shek LP, Goh DY, Van Bever H, Koh DS. Eosinophil cationic protein: is it useful in asthma? A systematic review. Respir Med. 2007. 101:696–705.

6. Wolthers OD. Eosinophil granule proteins in the assessment of airway inflammation in pediatric bronchial asthma. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2003. 14:248–254.

7. Fujita M, Ueki S, Ito W, Chiba T, Takeda M, Saito N, et al. C-reactive protein levels in the serum of asthmatic patients. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007. 99:48–53.

8. Olafsdottir IS, Gislason T, Thjodleifsson B, Olafsson I, Gislason D, Jögi R, et al. C reactive protein levels are increased in non-allergic but not allergic asthma: a multicentre epidemiological study. Thorax. 2005. 60:451–454.

9. Zietkowski Z, Tomasiak-Lozowska MM, Skiepko R, Mroczko B, Szmitkowski M, Bodzenta-Lukaszyk A. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein in the exhaled breath condensate and serum in stable and unstable asthma. Respir Med. 2009. 103:379–385.

10. Tolan RW Jr. Fever of unknown origin: a diagnostic approach to this vexing problem. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2010. 49:207–213.

11. Fitch PS, Brown V, Schock BC, Taylor R, Ennis M, Shields MD. Serum eosinophil cationic protein (ECP): reference values in healthy nonatopic children. Allergy. 1999. 54:1199–1203.

12. Nye L, Merrett TG, Landon J, White RJ. A detailed investigation of circulating IgE levels in a normal population. Clin Allergy. 1975. 5:13–24.

13. Pastorello EA, Incorvaia C, Ortolani C, Bonini S, Canonica GW, Romagnani S, et al. Studies on the relationship between the level of specific IgE antibodies and the clinical expression of allergy: I. Definition of levels distinguishing patients with symptomatic from patients with asymptomatic allergy to common aeroallergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995. 96:580–587.

14. Silva AC, Levy L, Trindade JC, Mendonca P, Silva C, Lopes AI. Faecal and serum levels of eosinophil cationic protein in a healthy paediatric population. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2007. 67:757–766.

15. Lönnkvist K, Hellman C, Lundahl J, Halldén G, Hedlin G. Eosinophil markers in blood, serum, and urine for monitoring the clinical course in childhood asthma: impact of budesonide treatment and withdrawal. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. 107:812–817.

16. Prehn A, Seger RA, Faber J, Torresani T, Molinari L, Gerber A, et al. The relationship of serum-eosinophil cationic protein and eosinophil count to disease activity in children with bronchial asthma. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 1998. 9:197–203.

17. Nielsen LP, Bjerke T, Christensen MB, Skamling M, Peterson CG, Mygind N, et al. Eosinophil markers in seasonal allergic rhinitis. Intranasal fluticasone propionate inhibits local and systemic increases during the pollen season. Allergy. 1998. 53:778–785.
18. Lorenzo GD, Mansueto P, Melluso M, Candore G, Cigna D, Pellitteri ME, et al. Blood eosinophils and serum eosinophil cationic protein in patients with acute and chronic urticaria. Mediators Inflamm. 1996. 5:113–115.

19. Murat-Susić S, Lipozencić J, Zizić V, Husar K, Marinović B. Serum eosinophil cationic protein in children with atopic dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 2006. 45:1156–1160.

20. Zietkowski Z, Skiepko R, Tomasiak-Lozowska MM, Mroczko B, Szmitkowski M, Bodzenta-Lukaszyk A. Changes in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in serum and exhaled breath condensate after intensive exercise in patients with allergic asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010. 153:75–85.

21. Sahoo RC, Acharya PR, Noushad TH, Anand R, Acharya VK, Sahu KR. A study of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in bronchial asthma. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2009. 51:213–216.
22. Cetinkaya F, Cakir M. Serum ECP and total IgE levels in children with acute laryngotracheobronchitis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2005. 69:493–496.

23. Chen CJ, Hung MC, Kuo KL, Chung JL, Wu KG, Hwang BT, et al. The role of eosinophil cationic protein in patients with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. J Chin Med Assoc. 2008. 71:37–39.

24. Chu YT, Chiang W, Wang TN, Hung CH, Jong YJ, Wu JR. Changes in serum eotaxin and eosinophil cationic protein levels, and eosinophil count during treatment of childhood asthma. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2007. 40:162–167.
25. Abu-Ghazaleh RI, Dunnette SL, Loegering DA, Checkel JL, Kita H, Thomas LL, et al. Eosinophil granule proteins in peripheral blood granulocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1992. 52:611–618.

26. Monteseirín J, Vega A, Chacón P, Camacho MJ, El Bekay R, Asturias JA, et al. Neutrophils as a novel source of eosinophil cationic protein in IgE-mediated processes. J Immunol. 2007. 179:2634–2641.

27. Chen ST, Sun HL, Lu KH, Lue KH, Chou MC. Correlation of immunoglobulin E, eosinophil cationic protein, and eosinophil count with the severity of childhood perennial allergic rhinitis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2006. 39:212–218.
28. Sugai T, Sakiyama Y, Matumoto S. Eosinophil cationic protein in peripheral blood of pediatric patients with allergic diseases. Clin Exp Allergy. 1992. 22:275–281.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download