Abstract
Objectives
The neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) level following non cardiac surgery is useful for predicting acute kidney damage. However, there is insufficient conclusive evidence as to whether NGAL can be used to predict subclinical AKI following non-cardiac surgery.
Methods
We measured serum NGAL and creatinine levels in 41 patients following non-cardiac surgery, and the increase of these variables was used to predict acute decreases in kidney function.
Results
The study included a total of 41 patients. The mean age was 64.65 ± 17.09 years. The serum creatinine concentration was increased 12 hours after surgery. The mean SD serum NGAL decreased after 4hours after surgery and continued to decrease after 12 hours after surgery. The incidence of subclinical AKI determined by the 4 hour serum NGAL level was 10(24.4%), and the incidence of serum creatinine elevation was 0(0.0%). The incidence of subclinical AKI determined by the 12 hour serum NGAL level was 4(9.8%), and the incidence of subclinical AKI determined by serum creatinine was 4(9.8%). The elevation of NGAL was more rapid than the serum creatinine 4 hours after surgery
REFERENCES
1.Khwaja A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012. 2:1–138.
2.Brown JR., Kramer RS., MacKenzie TA., Coca SG., Sint K., Parikh CR. Determinants of acute kidney injury duration after cardiac surgery: an externally validated tool. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012. 93:570–6.

3.Rosner MH., Portilla D., Okusa MD. Cardiac surgery as a cause of acute kidney injury: pathogenesis and potential therapies. J Intensive Care Med. 2008. 23:3–18.
4.Lassnigg A., Schmidlin D., Mouhieddine M., Bachmann LM., Druml W., Bauer P, et al. Minimal changes of serum creatinine predict prognosis in patients after cardiothoracic surgery: a prospective cohort study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. 15:1597–605.

5.Waikar SS., Bonventre JV. Creatinine kinetics and the definition of acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. 20:672–9.

6.Bellomo R., Ronco C., Kellum JA., Mehta RL., Palevsky P. Acute Dialysis Quality workgroup. Acute renal failure - definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care. 2004. 8:R204–12.
7.Haase M., Kellum JA., Ronco C. Subclinical AKI--an emerging syndrome with important consequences. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012. 8:735–9.

8.Mishra J., Ma Q., Prada A., Mitsnefes M., Zahedi K., Yang J, et al. Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003. 14:2534–43.

9.Mishra J., Dent C., Tarabishi R., Mitsnefes MM., Ma Q., Kelly C, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomakers for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet. 2005. 365:1231–8.
10.Bellomo R., Chapman M., Finfer S., Hickling K., Myburgh J. Low-dose dopamine in patients with early renal dysfunction: a placebo-controlled randomized trial. Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society (ANZICS) Clinical Trials Group. Lancet. 2000. 356:2139–43.
11.Bolignano D., Lacquaniti A., Coppolino G., Donato V., Campo S., Fazio MR, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and progression of chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. 4:337–44.

12.Bellomo R., Ronco C., Kellum JA., Mehta RL., Palevsky P. Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative workgroup. Acute renal failure-definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care. 2004. 8:R204–12.
13.Morgan DJ., Ho KM. A comparison of nonoliguric and oliguric severe acute kidney injury according to the risk injury failure loss end-stage (RIFLE) criteria. Nephron Clin Pract. 2010. 115:c59–65.

14.De Santo LS., Romano G., Galdieri N., Buonocore M., Bancone C., De Simone V, et al. 4IFLE criteria for acute kidney injury in valvular surgery. J Heart Valve Dis. 2012. 19:139–47.
16.Moore E., Bellomo R., Nichol A. Biomarkers of acute kidney injury in anesthesia, intensive care and major surgery: from the bench to clinical research to clinical practice. Minerva Anestesiol. 2010. 76:425–40.
17.Lee EH., Baek SH., Chin JH., Choi DK., Son HJ., Kim WJ, et al. Preoperative hypoalbuminemia is a major risk factor for acute kidney injury following off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery. Intensive Care Med. 2012. 38:1478–86.

18.Swaminathan M., Phillips-Bute BG., Conlon PJ., Smith PK., Newman MF., Stafford-Smith M. The association of lowest hematocrit during cardiopulmonary bypass with acute renal injury after coronary artery bypass surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003. 76:784–91.

19.Moguel-González B., Wasung-de-Lay M., Tella-Vega P., iquelme-Mc-Loughlin C., Villa AR., Madero M, et al. Acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery. Rev Invest Clin. 2013. 65:467–75.
20.Haase M., Bellomo R., Devarajan P., Schlattmann P., Haase-Fielitz A. NGAL Meta-analysis Investigator Group. Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009. 54:1012–24.
Fig. 1.
Change in serum NGAL and serum creatinine after the operations with mean and standard error. (A) Serum creatinine (B) NGAL, neutrophil geletinase-associated lipocalin.
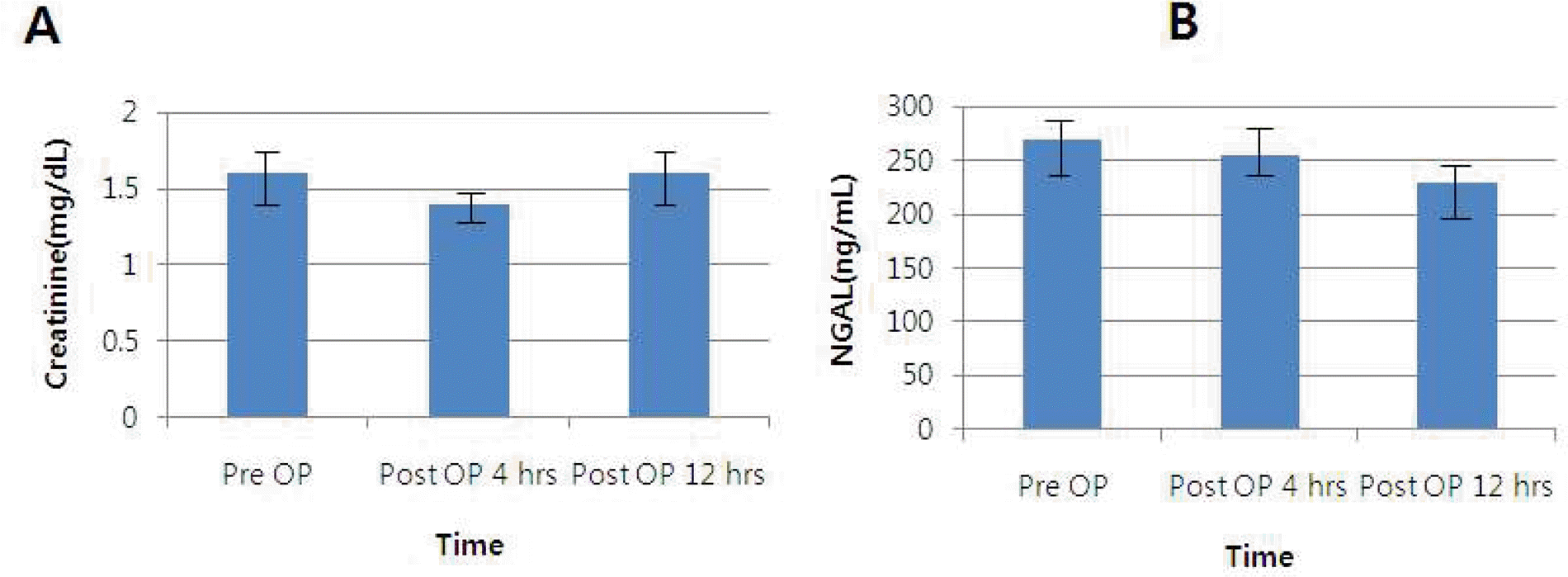
Fig. 2.
Incidence of subclinical AKI with NGAL and AKI with serum creatinine after the OP. OP : operation; NGAL : neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; AKI : acute kidney injury; CV : coefficient of variation
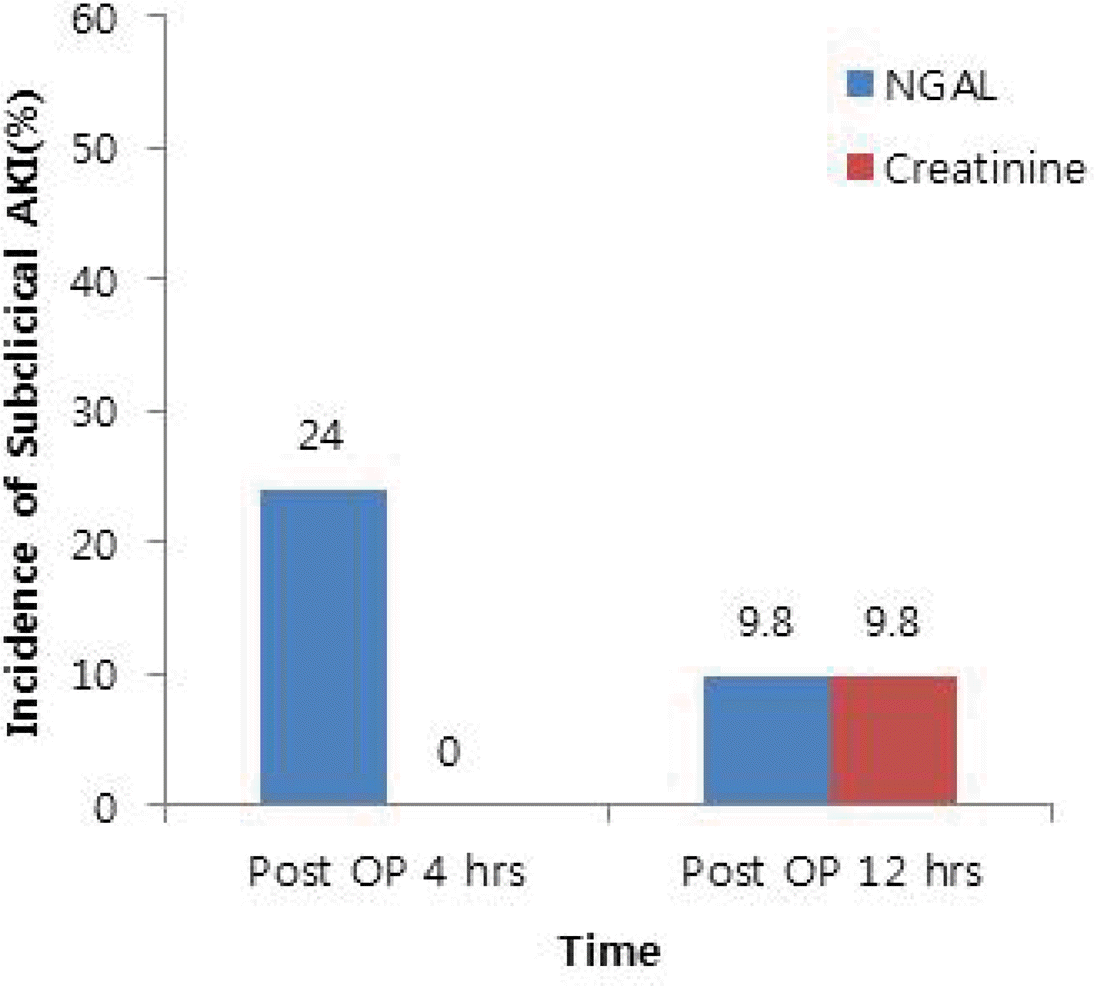
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients
Table 2.
Serum NGAL, creatinine on 4, 12 hours after the operations and the incidence of subclinical acute kidney injury as judged by sesrum NGAL.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download