Abstract
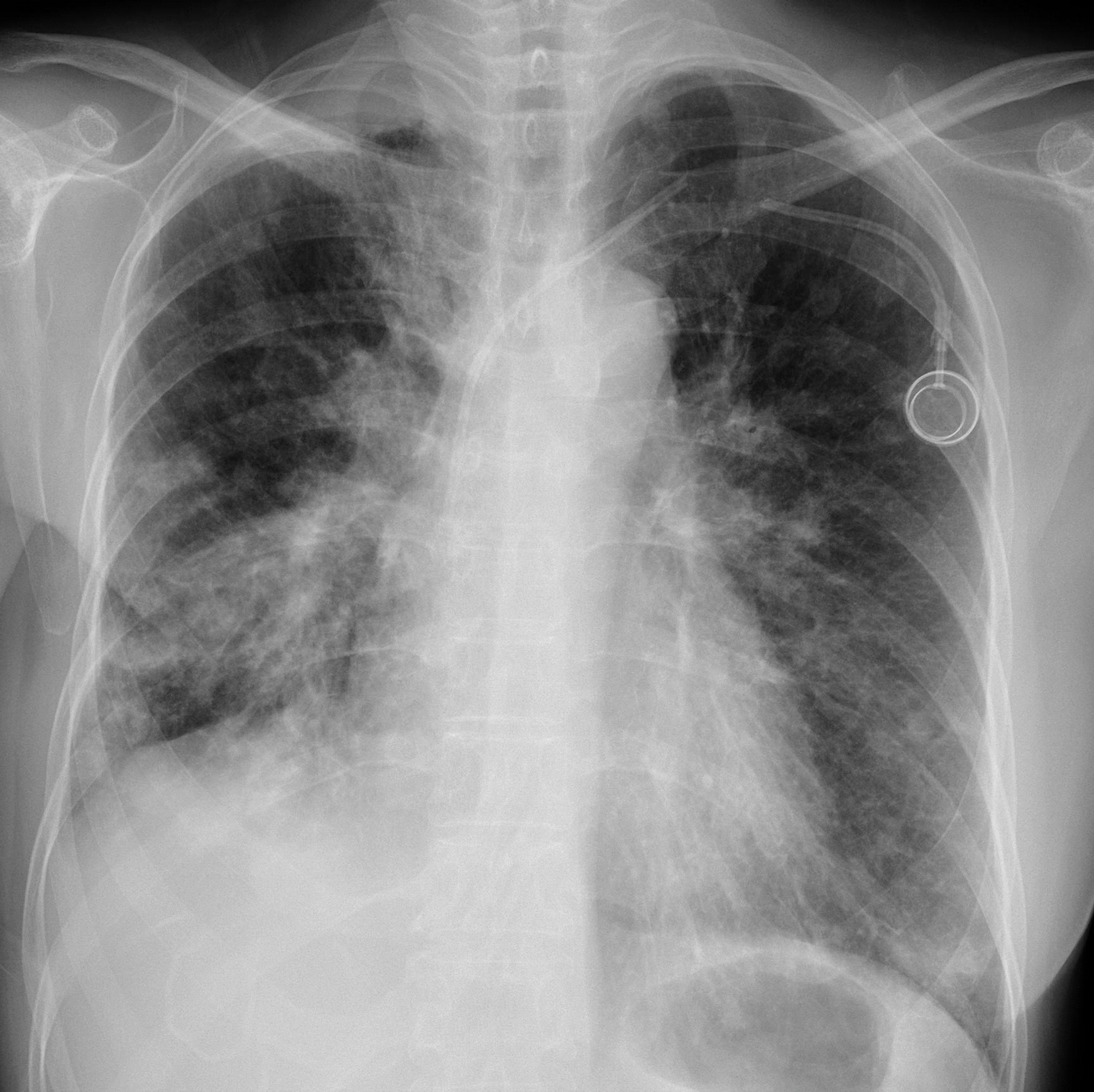
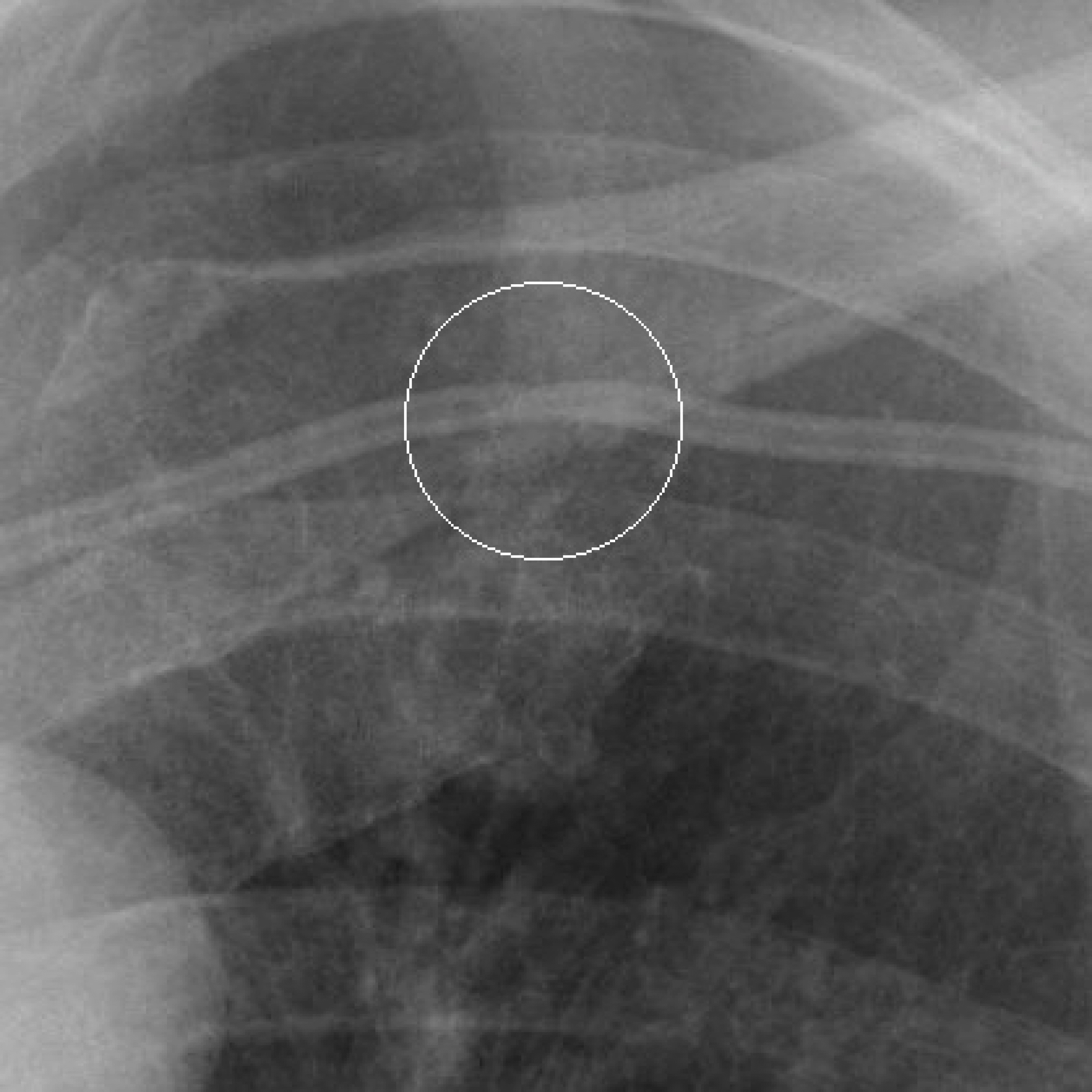
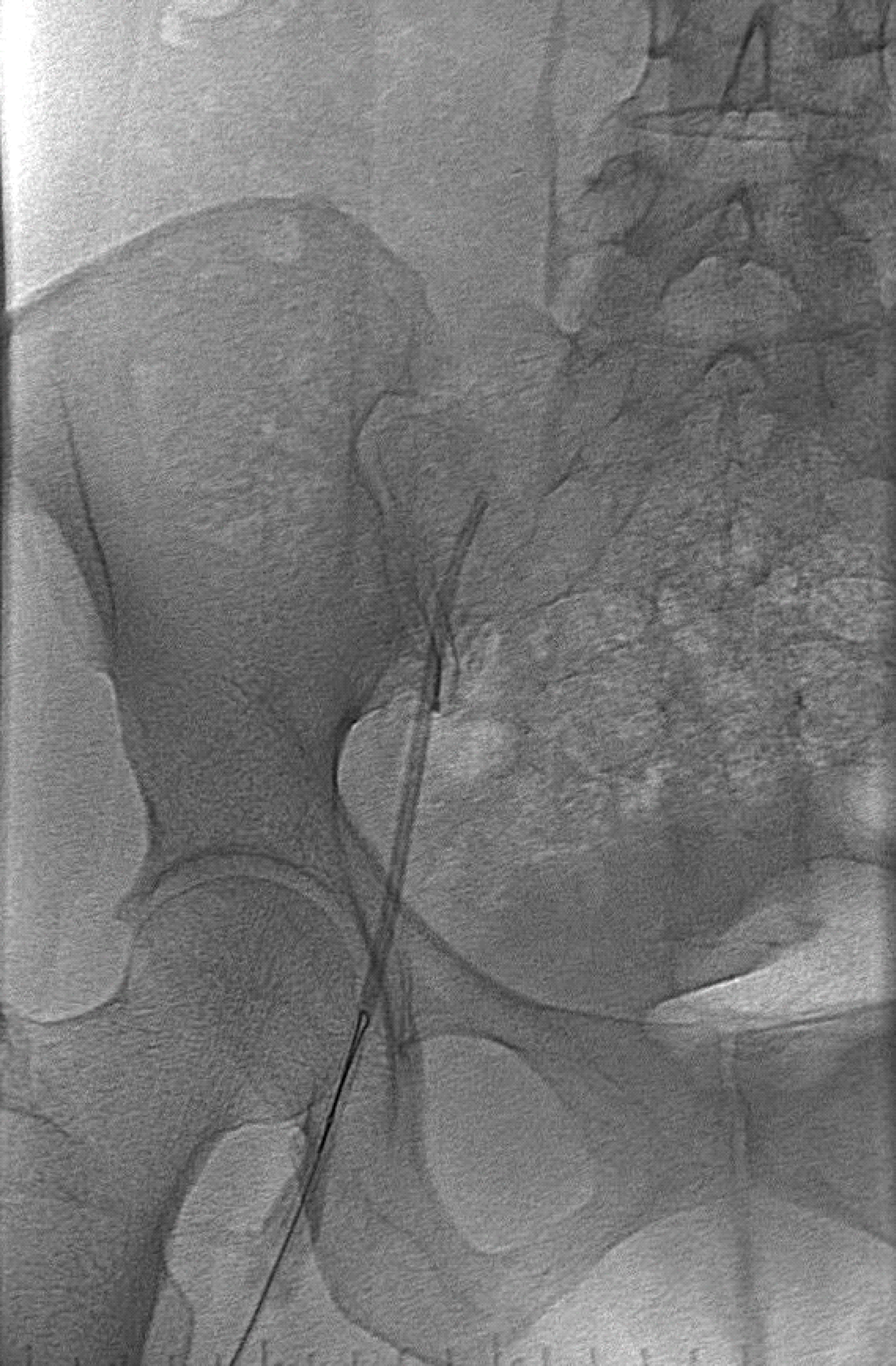
Totally implantable venous devices are used in medical care for parenteral nutrition, vascular access, administrating chemotherapeutic agents and so on. Although the large variety of catheter complications, catheter fracture is a rare but serious complication. The pinch off syndrome is caused by the compression of the catheter between the clavicle and first rib, and may lead to fracture and possible dislocation of the catheter. We report here the case history of a patient with metastatic breast cancer who developed a rare complication of subclavian catheter fracture as a consequence of pinch off syndrome.
Go to : 
References
1. Hinke DH, Zandt-Stastny DA, Goodman LR, Quebbeman EJ, Krzywda EA, Andris DA. Pinch-off syndrome: a complication of implantable subclavian venous access devices. Radiology. 1990; 177:353–6.

2. Osawa H, Hasegawa J, Yamakawa K, Matsunami N, Mikata S, Shimizu J, et al. Ultrasound-guided infraclavicular axillary vein puncture is effective to avoid pinch-off syndrome: a longterm follow-up study. Surg Today. 2013; 43:745–50.

3. Maisey NR, Sacks N, Johnston SR. Catheter fracture: a rare complication of totally implantable venous devices. Breast. 2003; 12:287–9.

4. Gowraiah V, Culham G, Chilvers MA, Yang CL. Embolization of a central venous catheter due to pinch-off syndrome. Acta Paediatr. 2013; 102:e49–50.

5. Fazeny-Dörner B, Wenzel C, Berzlanovich A, Sunder-Plassmann G, Greinix H, Marosi C, et al. Central venous catheter pinch-off and fracture: recognition, prevention and management. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003; 31:927–30.

6. Cho JB, Park IY, Sung KY, Baek JM, Lee JH, Lee DS. Pinch-off syndrome. J Korean Surg Soc. 2013; 85:139–44.

8. Mirza B, Vanek VW, Kupensky DT. Pinch-off syndrome: case report and collective review of the literature. Am Surg. 2004; 70:635–44.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download