Abstract
Objectives
Medical students sometimes do not receive proper feedback from their instructors. This study evaluated a newly developed automated and personalized real-time feedback system intended to address this issue.
Methods
Third- and fourth-year medical students participated in quizzes focusing on 17 learning objectives and a five-scale survey that queried their prior knowledge related to blood transfusions. Immediately after completing the quizzes, the students received automated and personalized, real-time feedback and were instructed to take part in self-directed learning. This activity was followed by a final quiz. After completion of the final quiz, the students responded to the five-scale survey that probed the usefulness of and satisfaction with the automated, personalized, real-time feedback system.
Results
Eighty students took part in this study. The third-year group had a higher score for prior knowledge and also on the first quiz (P= 0.008, P= 0.046, respectively). There was no significant difference in final quiz scores between the third- and fourth-year groups (P= 0.633). The scores for usefulness of and satisfaction with the automated, real-time feedback system were 4.45 and 4.34, and 4.55 and 4.40 in the third- and fourth-year students, respectively.
Go to : 
References
1. Branch WT, Jr. , Paranjape A. Feedback and reflection: teaching methods for clinical settings. Acad Med. 2002; 77:1185–8.
2. Hewson MG, Little ML. Giving feedback in medical education: verification of recommended techniques. J Gen Intern Med. 1998; 13:111–6.
3. van de Ridder JM, Stokking KM, McGaghie WC, ten Cate OT. What is feedback in clinical education? Med Educ. 2008; 42:189–97.

5. Garra G, Wackett A, Thode H. Feasibility and reliability of a multisource feedback tool for emergency medicine residents. J Grad Med Educ. 2011; 3:356–60.

6. Gil DH, Heins M, Jones PB. Perceptions of medical school faculty members and students on clinical clerkship feedback. J Med Educ. 1984; 59:856–64.

7. Burr SA, Brodier E, Wilkinson S. Delivery and use of individualised feedback in large class medical teaching. BMC Med Educ. 2013; 13:63.

8. Halkoaho A, Matveinen M, Leinonen V, Luoto K, Keränen T. Education of research ethics for clinical investigators with Moodle tool. BMC Med Ethics. 2013; 14:53.

9. Gormley GJ, Collins K, Boohan M, Bickle IC, Stevenson M. Is there a place for e-learning in clinical skills? A survey of undergraduate medical students' experiences and attitudes. Med Teach. 2009; 31:e6–12.

10. Kim KJ, Han J, Park Ie B, Kee C. Medical education in Korea: the e-learning consortium. Med Teach. 2009; 31:e397–401.

11. Lee SP, Su HK, Lee SD. Effects of computer-based immediate feedback on foreign language listening comprehension and test-associated anxiety. Percept Mot Skills. 2012; 114:995–1006.

12. Fox S, Reid WA, Evans P. Web-based feedback of medical student assessment results. Med Educ. 2003; 37:1036–7.

13. Barnett S, Jones SC, Caton T, Iverson D, Bennett S, Robinson L. Implementing a virtual community of practice for family physician training: a mixed-methods case study. J Med Internet Res. 2014; 16:e83.

14. Saidinejad M, Zorc J. Mobile and web-based education: delivering emergency department discharge and aftercare instructions. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014; 30:211–6.
15. Kuhbeck F, Engelhardt S, Sarikas A. Online TED.com – a novel web-based audience response system for higher education. A pilot study to evaluate user acceptance. GMS Z Med Ausbild. 2014; 31:Doc5.
16. Sampaio-Maia B, Maia JS, Leitᾶo S, Amaral M, Vieira-Marques P. Wiki as a tool for Microbiology teaching, learning and assessment. Eur J Dent Educ. 2014; 18:91–7.

17. Seluakumaran K, Jusof FF, Ismail R, Husain R. Integrating an open-source course management system (Moodle) into the teaching of a first-year medical physiology course: a case study. Adv Physiol Educ. 2011; 35:369–77.

18. Sparacia G, Cannizzaro F, D'Alessandro DM, D'Alessandro MP, Caruso G, Lagalla R. Initial experiences in radiology e-learning. Radiogra phics. 2007; 27:573–81.

Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.The quiz, feedback, and final exam provided to the students in this study. The quiz, feedback, and final exam were hosted on the website, which was developed by the author on the Moodle platform. When students clicked on the quiz question number (A), the quiz question appeared on the screen (B). After completing the quizzes, the students could view feedback that varied depending on quiz score (C), view the activated feedback, and perform self-directed learning guided by the feedback (D). After completion of the self-directed learning, students were permitted to take the final exam. |
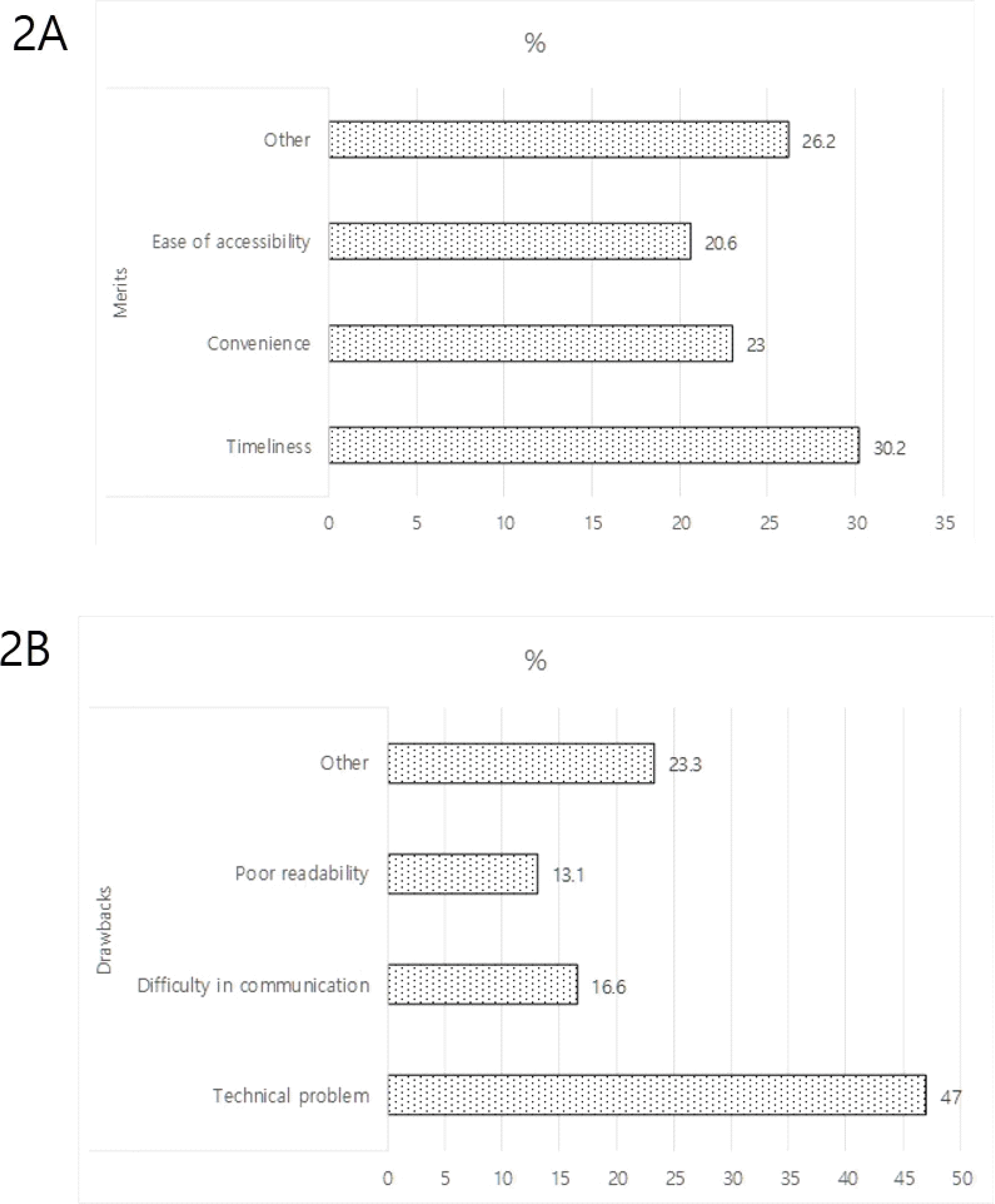 | Fig. 2.Subjective opinions from students about the merits and drawbacks of the automated, real-time feedback system. Some highly ranked opinions are listed, and more opinions are included in the “Other” category. |
Table 1.
Mean, standard deviation (SD), and t-test results of third- and fourth-year medical students on a survey of prior knowledge, usefulness, and satisfaction conducted using Moodle
Table 2.
Scores between third-year and fourth-year medical students
| Category | Mean (SD) | T-test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Third year (n=40) | Fourth year (n=40) | ||
| Quiz | 85.57 (10.26) | 89.66 (7.51) | P = 0.046 |
| Final quiz | 96.02 (4.56) | 95.53 (4.74) | P = 0.633 |
Table 3.
The degrees of satisfaction with and usefulness of a computer-assisted, automated, real-time feedback system amongst medical students




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download