Abstract
Objectives
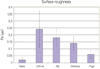
The purpose of this experiment was to evaluate four different polishing systems of their polishability and polishing time.
Materials and Methods
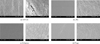
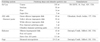
4 mm diameter and 2 mm thickness Teflon mold was made. Z-250 (3M ESPE) hybrid composite resin was slightly overfilled and pressed with slide glass and cured with Optilux 501 for 40 sec each side. Then the surface roughness (glass pressed: control group) was measured with profilometer. One surface of the specimen was roughened by #320 grit sand paper and polished with one of the following polishing systems; Sof-Lex (3M ESPE), Jiffy (Ultradent), Enhance (Dentsply/Caulk), or Pogo (Dentsply/Caulk). The surface roughness and the total polishing time were measured. The results were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Yap AU, Yap SH, Teo CK, Ng JJ. Finishing/polishing of composite and compomer restoratives: effectiveness of one-step systems. Oper Dent. 2004. 29:275–279.
2. Aykent F, Yondem I, Ozyesil AG, Gunal SK, Avunduk MC, Ozkan S. Effect of different finishing techniques for restorative materials on surface roughness and bacterial adhesion. J Prosthet Dent. 2010. 103:221–227.

3. Bollen CM, Lambrechts P, Quirynen M. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: a review of the literature. Dent Mater. 1997. 13:258–269.

4. Choi MS, Lee YK, Lim BS, Rhee SH, Yang HC. Changes in surface characteristics of dental resin composites after polishing. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2005. 16:347–353.

5. Neme AL, Frazier KB, Roeder LB, Debner TL. Effect of prophylactic polishing protocols on the surface roughness of esthetic restorative materials. Oper Dent. 2002. 27:50–58.
6. Stoddard JW, Johnson GH. An evaluation of polishing agents for composite resins. J Prosthet Dent. 1991. 65:491–495.

7. Chung KH. Effects of finishing and polishing procedures on the surface texture of resin composites. Dent Mater. 1994. 10:325–330.

8. Korkmaz Y, Ozel E, Attar N, Aksoy G. The influence of one-step polishing systems on the surface roughness and microhardness of nanocomposites. Oper Dent. 2008. 33:44–50.

10. Türkün LS, Türkün M. The effect of one-step polishing system on the surface roughness of three esthetic resin composite materials. Oper Dent. 2004. 29:203–211.
11. Lee JY, Shin DH. Surface roughness of universal composites after polishing procedures. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2003. 28:369–377.

12. van Noort R, Davis LG. The surface finish of composite resin restorative materials. Br Dent J. 1984. 157:360–364.

13. Da Costa J, Ferracane J, Paravina RD, Mazur RF, Roeder L. The effect of different polishing systems on surface roughness and gloss of various resin composites. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2007. 19:214–224. discussion 225-216.

14. Quirynen M, Bollen CM, Papaioannou W, Van Eldere J, van Steenberghe D. The influence of titanium abutment surface roughness on plaque accumulation and gingivitis: short-term observations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1996. 11:169–178.
15. Jones CS, Billington RW, Pearson GJ. The in vivo perception of roughness of restorations. Br Dent J. 2004. 196:42–45. discussion 31.

16. Fruits TJ, Miranda FJ, Coury TL. Effects of equivalent abrasive grit sizes utilizing differing polishing motions on selected restorative materials. Quintessence Int. 1996. 27:279–285.
17. St-Georges AJ, Bolla M, Fortin D, Muller-Bolla M, Thompson JY, Stamatiades PJ. Surface finish produced on three resin composites by new polishing systems. Oper Dent. 2005. 30:593–597.
18. Almeida GS, Poskus LT, Guimaräes JG, da Silva EM. The effect of mouthrinses on salivary sorption, solubility and surface degradation of a nanofilled and a hybrid resin composite. Oper Dent. 2010. 35:105–111.

19. Heintze SD, Forjanic M, Ohmiti K, Rousson V. Surface deterioration of dental materials after simulated tooth-brushing in relation to brushing time and load. Dent Mater. 2010. 26:306–319.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download