Abstract
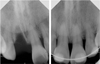
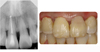
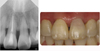
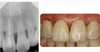
Coronal discoloration is a common sequela to traumatic injuries. In subluxation cases, although the injury is not strong enough to rupture the apical vessels, discoloration may appear by tearing thin walls or occluding small capillaries. In absence of infection pulpal regeneration can occur, and as a result discoloration may completely or partially subside. But judging pulpal status by coronal discoloration can be dangerous and it may lead to unnecessary treatment.
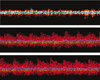
This case presents coronal discoloration and recovery following traumatic injury of maxillary anterior teeth. In diagnosing traumatized teeth routine cold tests or electric pulp tests are known to be unreliable, but with the aid of ultrasound doppler imaging, assessing pulp vitality of traumatized teeth can be more accurate.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Andreasen FM, Vestergaard Pedersen B. Prognosis of luxated permanent teeth: the development of pulp necrosis. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1985. 1(6):207–220.
2. Yu DC, Abd-Elmeguid A. Dental pulp neurophysiology: Part 2. Current diagnostic tests to assess pulp vitality. J Can Dent Assoc. 2009. 75(2):139–143.
3. Aguiló L, Gandía JL. Transient red discoloration: report of case. ASDC J Dent Child. 1998. Sep-Oct. 65(5):346–348. 356
4. Yoon MJ, Kim E, Lee SJ, Bae YM, Kim S, Park SH. Pulpal blood flow measurement with ultrasound Doppler imaging. J Endod. 2010. 36(3):419–422.

5. Andreasen JO. Textbook and color atlas of Traumatic injuries to the teeth. 4th ed. UK: Oxford.
6. Ozçelik B, Kuraner T, Kendir B, Aşan E. Histopathological evaluation of the dental pulps in crown-fractured teeth. J Endod. 2000. 26(5):271–273.

7. Andreasen FM. Pulpal healing after luxation injuries and root fracture in the permanent dentition. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1989. 5(3):111–131.

8. Cohen S, et al. Pathways of the pulp. 9th ed. St. Louis: Mosby.
9. Petersson K, Söderström C, Kiani-Anaraki M, Lévy G. Evaluation of the ability of thermal and electrical tests to register pulp vitality. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1999. 15(3):127–131.

10. Berson M, Grégoire JM, Gens F, Rateau J, Jamet F, Vaillant L, Tranquart F, Pourcelot L. High frequency(20MHz) ultrasonic devices : advantages and applications. Eur J Ultrasound. 1999. 10(1):53–63.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download