Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the microtensile bond strength (µTBS), failure modes and bonding interfaces of self-etching and three self-adhesive resin cements to dentin and indirect composite resin.
Cylindrical composite blocks (Tescera, Bisco Inc.) were luted with resin cements (PA: Panavia F 2.0, Kuraray Medical Inc., RE: RelyX Unicem Clicker, 3M ESPE., MA: Maxem, Kerr Co., BI: BisCem, Bisco Inc.) on the prepared occlusal dentin surfaces of 20 extracted molars. After storage in distilled water for 24 h, 1.0 mm × 1.0 mm composite-dentin beams were prepared. µTBS was tested at a cross-head speed of 0.5 mm/min. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Tukey's HSD test. Dentin sides of all fractured specimens and interfaces of resin cements-dentin or resin cements-composite were examined at FE-SEM (Field Emission-Scanning Electron Microscope).
In conclusion, PA and RE showed higher bond strength and closer adaptation than MA and BI when indirect composite blocks were luted to dentin using a self-etching and three self-adhesive resin cements.
Figures and Tables
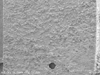 | Figure 1SEM micrograph of dentin side showing a representative cohesive failure within Panavia F 2.0 (× 130). |
 | Figure 2SEM micrograph showing remnant fractured filler (F) and cement (C) on the surface of fractured Panavia F 2.0 (× 5,000). |
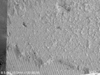 | Figure 3SEM micrograph of dentin side showing a representative mixed failure with a thin layer of RelyX Unicem Clicker on the dentin surface (× 130). |
 | Figure 4SEM micrograph of dentin side showing a representative adhesive failure of Maxcem along dentin surface (× 130). |
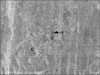 | Figure 5SEM micrograph showing remnant a few small sized filler (F) and cement (C) on the dentin surface and fractured Maxem (× 5,000). |
 | Figure 6SEM micrograph of dentin side showing a representative adhesive failure of BisCem along dentin surface (× 130). |
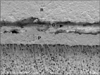 | Figure 7SEM micrograph showing gap (G), about 5 µm wide, between the composite resin (R)-Panavia F 2.0 (P), and close adaptation with numerous short and long resin tags between the Panavia F 2.0-dentin (D) (× 600). |
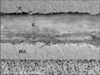 | Figure 8SEM micrograph showing wide gap (G), about 70 µm wide, between the composite resin (R)-RelyX Unicem Clicker (RU), and close adaptation with a few short resin tags between RelyX Unicem Clicker-dentin (D) (× 600). |
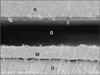 | Figure 9SEM micrograph showing wide gap (G), about 60 µm wide, between the composite resin (R)-Maxcem (M), and discontinuous 1-2 µm wide gaps(g) between Maxem-dentin (D) (× 600). |
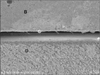 | Figure 10SEM micrograph showing gap (G), about 15 µm wide, and a few short resin tags between BisCem (B)-dentin (D) (× 600). |
References
1. Hikita K, Van Meerbeek B, De Munck J, Ikeda T, Van Landuyt K, Maida T, Lambrechts P, Peumans M. Bonding effectiveness of adhesive luting agents to enamel and dentin. Dent Mater. 2007. 23:71–80.

2. Lutz F, Krejci I, Barbaknow F. Quality and durability of marginal adaptation in bonded composite restorations. Dent Mater. 1991. 7:107–113.

3. El Zohairy AA, De Gee AJ, Mohsen MM, Feilzer AJ. Microtensile bond strength testing of luting cements to prefabricated CAD/CAM ceramic and composite blocks. Dent Mater. 2003. 19:575–583.

4. Song MH, Park SJ, Cho HG, Hwang YC, Oh WM, Hwang IN. Influence of adhesive application on shear bond strength of the resin cement to indirect resin composite. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2008. 33:419–426.

5. Duarte S, Botta AC, Meire M, Saden A. Microtensile bond strength and scanning electron microscopic evaluation of self-adhesive and self-etch resin cements to intact and etched enamel. J Prosthet Dent. 2008. 100:203–210.

6. Mak YF, Lai SCN, Cheung GSP, Chan AWK, Tay FR, Pashley DH. Micro-tensile bond testing of resin cements to dentin and indirect resin composite. Dent Mater. 2002. 18:609–621.

7. Goracci C, Cury AH, Cantoro A, Papacchini F, Tay FR, Ferrari M. Microtensile bond strength and interfacial properties of self-etching and self-adhesive resin cements used to lute composite onlays under different seating forces. J Adhes Dent. 2006. 8:327–335.
8. Hiraishi N, Yiu CKY, King NM, Tay FR. Effect of pulpal pressure on the microtensile bond strength of luting resin cements to human dentin. Dent Mater. 2009. 25:58–66.

9. Jayasooriya PR, Perira PN, Nikaido T, Tagami J. Efficacy of a resin coating on bond strengths of resin cement to dentin. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2003. 15:105–113.

10. De Munck J, Vargas M, Van Landuyt K, Hikita K, Lambrechts P, Van Meerbeek B. Bonding of an auto-adhesive luting material to enamel and dentin. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:963–971.

11. Al-Assaf K, Chakmakchi M, Palaghias G, Karanika-Kouma A, Eliades G. Interfacial characteristics of adhesive luting resins and composites with dentine. Dent Mater. 2007. 23:829–839.

12. Yang B, Ludwig K, Adelung R, Kern M. Micro-tensile bond strength of three luting resins to human regional dentin. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:45–56.

13. Della Bona A, van Noort R. Shear vs tensile bond strength of resin composite bonded to ceramic. J Dent Res. 1995. 74:1591–1596.

14. Chersoni S, Suppa P, Grandini S, Goracci G, Monticelli F, Yiu C. In vivo and vitro permeability of one-step self-etch adhesives. J Dent Res. 2004. 83:459–464.

15. Han SH, Cho YG. Effect of a desensitizer on dentinal bond strength in cementation of composite resin inlay. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2009. 34:223–231.

16. Kim DS, Park SH, Choi KW, Choi KK. The effect of bonding resin on bond strength of dual-cure resin cements. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2007. 32:426–436.

17. Abo-Hamar SE, Hiller KA, Jung H, Federlin M, Friedl KH, Schmalz G. Bond strength of a new universal self-adhesive resin luting cement to dentin and enamel. Clin Oral Investig. 2005. 9:161–167.

18. Monticelli F, Osorio R, Mazzitelli C, Ferrari M, Toledano M. Limited decalcification/diffusion of self-adhesive cements into dentin. J Dent Res. 2008. 87:974–976.

19. Mazzitelli C, Monticelli F, Osorio R, Casucci A, Toledano M, Ferrari M. Effect of simulated pulpal pressure on self-adhesive cements bonding to dentin. Dent Mater. 2008. 24:1156–1163.

20. Moszner N, Salz U, Zimmermann J. Chemical aspects of self-etching enamel-dentin adhesives: a systematic review. Dent Mater. 2005. 21:895–910.

21. Shortall AC, Baylis RL, Wilson HJ. Composite inaly/luting resin bond strength-surface tratment effects. J Dent. 1996. 24:129–135.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download