Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of fiber direction on the polymerization shrinkage of fiber-reinforced composite. The disc-shaped flowable composite specimens (d = 10 mm, h = 2 mm, Aeliteflo A2, Bisco, Inc., IL, USA) with or without glass fiber bundle (X-80821P Glass Fiber, Bisco, Inc., IL, USA) inside were prepared, and the longitudinal and transversal polymerization shrinkage of the specimens on radial plane were measured with strain gages (Linear S-series 350ω, CAS, Seoul, Korea). In order to measure the free polymerization shrinkage of the flowable composite itself, the disc-shaped specimens (d = 7 mm, h = 1 mm) without fiber were prepared, and the axial shrinkage was measured with an LVDT (linear variable differential transformer) displacement sensor. The cross-section of the polymerized specimens was observed with a scanning electron microscope to examine the arrangement of the fiber bundle in composite. The mean polymerization shrinkage value of each specimen group was analyzed with ANOVA and Scheffe post-hoc test (α=0.05).
The radial polymerization shrinkage of fiber-reinforced composite was decreased in the longitudinal direction of fiber, but increased in the transversal direction of fiber (p<0.05). We can conclude that the polymerization shrinkage of fiber-reinforced composite splint or restoratives is dependent on the direction of fiber.
Figures and Tables
 | Figure 1a) Experimental setup for the measurement of radial linear shrinkage using a strain gage.
b) Definition of directions on a disc shaped specimen in the measurement.
|
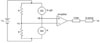 | Figure 2Electric circuit design for the strain measurement (Vo: output voltage, Va: voltage between two fixed resistances, Vb: voltage between two strain gages, Vs: input voltage, R: fixed resistance, ΔR: resistance difference, SG: strain gage). |
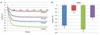 | Figure 4a) Representative curves of radial shrinkage strains for composite specimens as a function of time.
b) Post-gel shrinkage strains for four groups.
|
References
1. Giachetti L, Scaminaci Russo D, Bambi C, Grandini R. A review of polymerization shrinkage stress: current techniques for posterior direct resin restorations. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2006. 7:79–88.

2. Vallittu PK, Lassila VP, Lappalainen R. Acrylic resin-fiber composite-Part I: The effect of fiber concentration on fracture resistance. J Prosthet Dent. 1994. 71:607–612.

3. Vallittu PK. Acrylic resin-fiber composite--Part II: The effect of polymerization shrinkage of polymethyl methacrylate applied to fiber roving on transverse strength. J Prosthet Dent. 1994. 71:613–617.

4. Goldberg AJ, Burstone CJ. The use of continuous fiber reinforcement in dentistry. Dent Mater. 1992. 8:197–202.

5. Butterworth C, Ellakwa AE, Shortall A. Fibre-reinforced composites in restorative dentistry. Dent Update. 2003. 30:300–306.

6. Dyer SR, Lassila LV, Jokinen M, Vallittu PK. Effect of cross-sectional design on the modulus of elasticity and toughness of fiber-reinforced composite materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2005. 94:219–226.

7. Tezvergil A, Lassila LV, Vallittu PK. The effect of fiber orientation on the polymerization shrinkage strain of fiber-reinforced composites. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:610–616.

8. Sakaguchi RL, Versluis A, Douglas WH. Analysis of strain gage method for measurement of post-gel shrinkage in resin composites. Dent Mater. 1997. 13:233–239.

9. Versluis A, Tantbirojn D, Douglas WH. Distribution of transient properties during polymerization of a light-initiated restorative composite. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:543–553.

10. Lassila LV, Vallittu PK. The effect of fiber position and polymerization condition on the flexural properties of fiber-reinforced composite. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2004. 5:14–26.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download