Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy and the consistency of four different electronic apex locators in an in vitro model.
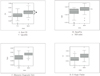
Fourty extracted premolars were used for the study. Four electronic apex locators (EAL) were Root ZX, SmarPex, Elements Diagnostic Unit (EDU), and E-Magic Finder Deluxe (EMF). After access preparation, the teeth were embedded in an alginate model and the length measurements were carried out at "0.5"and "Apex"mark using four EALs. The file was cemented at the location of the manufacturers'instruction (Root ZX, EDU, EMF: 0.5 mark, SmarPex: Apex mark). The apical 4mm of the apex was exposed and the distance from the file tip to the major foramen was measured by Image ProPlus (× 100). The distance from the file tip to the major foramen was calculated at 0.5 and Apex mark and the consistency of 0.5 and Apex mark was compared by SD and Quartile of Box plots.
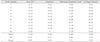
In this study, Root ZX and EMF located the apical constriction accurately within ± 0.5 mm in 100%, whereas SmarPex and EDU located in 90% and in 70% respectively. For Root ZX and EMF, there was no significant difference between the consistency of 0.5 and Apex mark. However, for the EDU and SmarPex, Apex mark was more consistent than 0.5 mark.
From the evaluation of the consistency in this study, for Root ZX and EMF, both 0.5 and Apex mark can be used as a standard mark. And for EDU and SmarPex, the Apex mark can be recommended to be used as a standard mark.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Grove C. Why canals should be filled to the dentinocemental junction. J Am Dent Assoc. 1930. 17:293–296.
2. Ricucci D, Langeland K. Apical limit of root canal instrumentation and obturation. Int Endod J. 1998. 31:394–409.
3. Suzuki K. Experimental study on iontophoresis. Jpn J Stomatol. 1942. 16:411–429.
4. Sunada I. New method for the measuring the length of the root canal. J Dent Res. 1962. 41:375–387.

5. Ushiyama J. New Principle and method for measuring the root canal length. J Endod. 1983. 9:97–104.

6. Hasegawa K, Iizuka H, Takei M, Goto N, Nihei M, Ohashi M. A new method and apparatus for measuring root canal length. J Nihon Univ Sch Dent. 1986. 28:117–128.

7. Frank AL, Torabinejad M. An in vivo evaluation of Endex electronic apex locator. J Endod. 1993. 19:177–179.
8. Kobayashi C, Okiji T, Kaqwashima N, Suda H, Sunada I. A basic study on the electronic root canal length measurement: Part 3. Newly designed electronic root canal length measuring device using division method. Jpn J Conserv Dent. 1991. 34:1442–1448.
9. Kobayashi C, Suda H. New electronic canal measuring device based on the ratio method. J Endod. 1994. 20:111–114.

10. Kobayashi C. Electronic canal length measurement. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995. 79:226–231.

11. Shabahang S, Goon WW, Gluskin AH. An in vivo evaluation of Root ZX electronic apex locator. J Endod. 1996. 22:616–618.
12. Dunlap CA, Remeikis NA, BeGole EA, Rauschenberger CR. An in vivo evaluation of an electronic apex locator that uses the ratio method. J Endod. 1998. 24:48–50.

13. Welk AR, Baumgartner JC, Marshall JG. An in vivo comparison of two frequency-based electronic apex locator. J Endod. 2003. 29:497–500.
14. Meares WA, Steiman HR. The influence of sodium hypochlorite irrigation on the accuracy of the Root ZX electronic apex locator. J Endod. 2002. 28:595–598.

15. Jenkins JA, Walker WA 3rd, Schindler WG, Flores CM. An in vitro evaluation of the accuracy of the Root ZX in the presence of various irrigants. J Endod. 2001. 27:209–211.

16. Lee SJ, Nam KC, Kim YJ, Kim DW. Clinical accuracy of a new apex locator with an automatic compensation circuit. J Endod. 2002. 28:706–709.

17. Kaufman AY, Keila S, Yoshpe M. Accuracy of a new apex locator: an in vitro study. Int Endod J. 2002. 35:186–192.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download