Abstract
A variety files made of stainless steel (S-S) or nickel-titanium (Ni-Ti) are used during endodontic treatment. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the corrosion susceptibility of S-S and Ni-Ti endodontic files. Three brands of files were used for this study: K-flex® S-S files (Maillefer, USA), Profile® Ni-Ti files (Maillefer, USA), K-3® Ni-Ti files (SybronEndo, USA). 120 files of each brands (21mm, ISO size #20) were divided into 12 groups according to 1) sterilization methods using Autoclave or Ethylene Oxide (E-O) gas, 2) Irrigation solutions using 5.25 % NaOCl or Saline, 3) the number of sterilization (1, 5, 10 times). After above procedures, each of the files was inspected by three examiners with a light microscope and camera at X25. Each file was judged and ranked according to the following criteria: 0; no corrosion, 1; mild corrosion, 2; moderate corrosion, and 3; severe corrosion. The files of high score were examined under the Scanning Electron Microscope.
Data were statistically analyzed with the Kruskal-Wallis test (p < 0.05). Most of the ten time-autoclaved files had showed mild to moderate corrosion. But, one or five time-autoclaved files did not show corrosive surface. NaOCl treatment and E-O gas sterilization did not influence on corrosion. There was a significant difference in corrosion susceptibility between sterilization methods and the number of autoclaving. However, there was no significant difference between brands and file materials.
Figures and Tables
 | Figure 2SEM photographs of K-flex® file treated with sodium hypochlorite and autoclaved ten-times (left arrow; fissure line, right arrows; pitting). |
 | Figure 3Low magnification (left) and high magnification (right) of Profile® treated with sodium hypochlorite and autoclaved ten-times (arrow; pitting) |
 | Figure 4Low magnification (left) and high magnification (right) of K-3® file treated with sodium hypochlorite and autoclaved ten-times (arrows; pitting). |
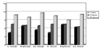 | Figure 5Sum of corrosion scores of autoclaved files (O; NaOCl, X; Saline).
Ten times-autoclaved files had significantly different from one or five times-autocaved files (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference between brands and file materials.
|
References
1. Bahcall JK, Barss JT. Understanding and evaluating the endodontic file. Gen Dent. 2000. 48:690–692.
2. Walia HM, Brantley WA, Gerstein H. An initial investigation of the bending and torsional properties of nitinol root canal files. J Endod. 1988. 14:346–351.

3. Assad M, Chernyshov AV, Jarzem P, Leroux MA, Coillard C, Charette S, Rivard CH. Porous titanium-nickel for Intervertebral fusion in a sheep model: part 2. Surface analysis and nickel release assessment. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2003. 64:121–129.

4. Mize SB, Pruett JP, Clement DJ, Carnes DL. Effect to sterilization on cyclic fatigue of rotary nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J Endod. 1998. 24:843–847.

5. Filho IB, Esberard RM, Leonardo RT, Del Rio CE. Microsopic evaluation of three endodontic files pre- and postinstrumentation. J Endod. 1998. 24:461–464.

6. Stokes OW, Di Fiore PM, Barss JT, Koerber A, Gilbert JL, Lautenschlager EP. Corrosion in stainless-steel and nickel titanium files. J Endod. 1999. 25:17–20.
7. Neal RG, Craig RG, Powers JM. Effects of sterilization and irrigants on the cutting ability of stainless steel files. J Endod. 1983. 9:93–96.

8. Haikel Y, Serfaty R, Speisser WJM, Alleman C. Cutting efficiency of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments and the effect of sodium hypochlorite treatment. J Endod. 1998. 24:736–739.

9. Busslinger A, Sener B, Barbakow F. Effects of sodium hypochlorite on nickel-titanium Lightspeed instruments. Int Endod J. 1998. 31:290–294.

10. Haikel Y, Serfaty R, Speisser WJM, Alleman C. Mechanical properties of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments and the effect of sodium hypochlorite treatment. J Endod. 1998. 24:731–735.

11. Sarkar NK, Redmond W, Schwaninger B, Goldberg AJ. The chloride corrosion behaviour of four orthodontic wires. J Oral Rehabil. 1983. 10:121–128.

13. Charles , et al. Sterilization or disinfection of dental instruments. Accepted dental therapeutics 40th. 1984. Chicago, IL: American Dental Association;134–150.
14. Willet NP, White RR, Rosen S. Disinfection and sterilization. Essential Dental Mocrobiology. 1991. Appletin & Lange, East Norwalk, CO;58–61.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download