Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the correlation between hybrid layer thickness and bond strength using confocal laser scanning microscope and microtensile bond strength test of two adhesive systems.
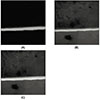
The dentin surface of human molars, sectioned to remove the enamel from the occlusal surface. Either Scotchbond Multi-Purpose(3M Dental Product, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A) or Clearfil SE Bond(Kuraray, Osaka, Japan) was bonded to the surface, and covered with resin-composite. The resin-bonded teeth were serially sliced perpendicular to the adhesive interface to measure the hybrid layer thickness by confocal laser scanning microscope. The specimen were trimmed to give a bonded cross-sectional surface area of 1mm2, then the micro-tensile bone test was performed at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min. All fractured surfaces were also observed by stereomicroscope.
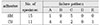
There was no significant differences in bond strengths the materials(p>0.05). However, the hybrid layers of three-step dentin adhesive system, SM, had significantly thicker than self-etching adhesive system, CS(p<0.05). Pearson's correlation coefficient showed no correlation between hybrid layer thickness and bond strengths(p>0.05). Bond strengths of dentin adhesive systems were not dependent on the thickness of hybrid layer.
Figures and Tables
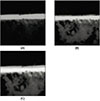
Fig. 1
Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (3M)
A; Adhesive layer(rhodamine)
B; Primer layer(fluorescene)
C; Adhesive layer+Primer layer
References
1. Buonocore MG. A simple method of increasing the adhesion of acrylic filling materials to enamel surfaces. J Dent Res. 1955. 34:849–853.

2. Van Meerbeek B, Perdigao J, Lambrechts P, Vanherle G. The clinical performance of adhesives. J Dent. 1998. 26(1):1–20.

3. Bouillaguet S, Gysi P, Wataha JC, Ciucchi B, Cattani M, Godin Ch, Meyer JM. Bond strength of composite to dentin using conventional, one-step, and self-etching adhesive systems. J Dent. 2001. 29:55–61.

4. Perdigao J, Lopes M. Dentin Bonding-Questions for the new millennium. J Adhes Dent. 1999. 1:191–209.
5. Yoshiyama M, Matsuo T, Ebisu S, Pashley D. Regional bond strengths of self-etching/self-priming adhesive systems. J Dent. 1998. 26:609–616.

6. Yoshiyama M, Sano H, Ebisu S, Tagami J, Ciucchi B, Carvalho RM, Johnson MH, Pashley DH. Regional strengths of bonding agents to cervical sclerotic root dentin. J Dent Res. 1996. 75:1404–1413.

7. Frankenberger R, Perdigao J, Rosa BT, Lopes M. 'No-bottle' vs 'multi-bottle' dentin adhesives-a microtensile bond strength and morphological study. Dent Mater. 2001. 17:373–380.

8. Gwinnett AJ. Quantitative contribution of resin infiltration/hybridization to dentin bonding. Am J Dent. 1993. 6:7–9.
9. Gwinnett AJ. Altered tissue contribution to interfacial bond strength with acid conditioned dentin. Am J Dent. 1994. 7:243–246.
10. Inai N, Kanemura N, Tagami J, Watanabe LG, Marshall SJ, Marshall GW. Adhesion between collagen depleted dentin and dentin adhesive. Am J Dent. 1998. 11:123–127.
11. Kanca J, Sandrik J. Bonding to dentin. Clues to the mechanism of adhesion. Am J Dent. 1998. 11:154–159.
12. Finger WJ, Inoue M, Asmussen E. Effect of wettability of adhesive resins on bonding to dentin. Am J Dent. 1994. 7:35–38.
13. Perdigao J, May KN Jr, Wilder AD Jr, Lopes M. The effect of depth of dentin demineralization of bond strengths and morphology of the hybrid layer. Oper Dent. 2000. 25:186–194.
14. Hashimoto M, Ohno H, Endo K, Kaga M, Sano H, Oguchi H. The effect of hybrid layer thickness on bond strength: demineralized dentin zone of the hybrid layer. Dent Mater. 2000. 16:406–411.

15. Nakabayashi N. Resin reinforced dentin due to infiltration of monomers into the dentin adhesive interface. J Jpn Dent Mat Devices. 1982. 1:78–81.
16. Harnirattisai C, Inokoshi S, Shimada Y, Hosoda H. Adhesive interface between resin and etched dentin of cervical erosion/abrasion lesions. Oper Dent. 1993. 18:138–143.
17. Kwong SM, Cheung GSP, Kei LH, Ittagarun A, Smales RJ, Tay FR, Pashley DH. Micro-tensile bond strengths to sclerotic dentin using a self-etching and a total-etching technique. Dent Mater. 2002. 18:359–369.

18. Phrukkanon S, Burrow MF, Hartley PG, Tyas MJ. The influence of the modification of etched bovine dentin on bond strengths. Dent Mater. 2000. 16:255–265.

19. Pashley DH, Sano H, Ciucchi B, Yoshiyama M, Carvalho RM. Adhesion testing of dentin bonding agents: A review. Dent Mater. 1995. 11:117–125.

20. Erickson RL, Glasspoole EA. Bonding to tooth structure: a comparison of glass-ionomer and composite-resin systems. J Esthet Dent. 1994. 6:227–244.

21. Schreiner RF, Chappell RP, Glaros AG, Eick JD. Microtensile testing of dentin adhesives. Dent Mater. 1998. 14:194–201.

22. Tanumiharja M, Burrow MF, Tyas MJ. Microtensile bond strengths of seven dentin adhesives systems. Dent Mater. 2000. 16:180–187.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download