Abstract
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the sealing effect of several root-end filling materials using spectrophotometric analysis. 180 single root teeth with one canal were instrumented and canal filled. Root resected and root end preparation was made. Teeth were randomly classified to 5 experimental group(MTA, EBA, IRM, TCP, ZOE) and 1 control group according to root-end filling material MTA group used PRO ROOT MTA, EBA group used Super EBA, TCP group used NEW APATITE LINER TYPE II main component of which is α-tricalcium phosphate(TCP). According to manufacture's instruction experimental material was mixed and retrfilled. After 2% methylene blue solution penetration absorbance for each test sample was measured with spectrophotometer (JASCO UV-530, Japan).
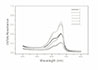
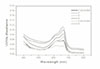
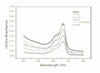
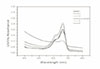
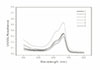
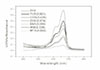
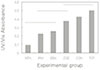
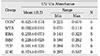
The mean absorbance of control and experimental group was as follows;
MTA : 0.092, IRM : 0.226, Super EBA : 0.255, ZOE : 0.374, Control : 0.425, TCP : 0.501 and the result analyzed by Turkey test at P=0.05 level.
Conclusions of this study are as follows;
Figures and Tables
References
1. Torabinejad M, Watson TF, Pitt Ford TR. Sealing ability of a mineral trioxide aggregate when used as a root end filling material. J Endod. 1993. 19(12):591–595.

2. Rapp EL, Brown CE Jr, Newton CW. An analysis of success and failure of apicoectomies. J Endod. 1991. 17(10):508–512.

3. Kaplan SD, Tanzilli JP, Raphael D, Moodnik RM. A comparison of the marginal leakage of retrograde techniques. Oral Surg. 1982. 54(5):583–585.

4. Bramwell JD, Hicks ML. Sealing ability of four retrofilling techniques. J Endod. 1986. 12(3):95–100.

5. Carr GB, Bentkover SB. Cohen S, Burns RC, editors. Surgical endodontics. Pathways of the pulp. 1998. St Louis: CV Mosby Co;608–656.
6. King KT, Anderson RW, Pashley DH, Pantera EA Jr. Longitudinal evaluation of the seal of endodontic retrofillings. J Endod. 1990. 16(7):307–310.

7. Tuggle ST, Anderson RW, Pantera EA Jr, Neaverth EJ. A dye penetration study of retrofilling materials. J Endod. 1989. 15(3):122–124.

8. Vertucci FJ, Beatty RG. Apical leakage associated with retrofilling techniques: a dye study. J Endod. 1986. 12(8):331–336.

9. Johnson BR. Considerations in the selection of a root-end filling material. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999. 87(4):398–404.

11. Gartner AH, Dorn SO. Advances in endodontic surgery. Dent Clin North Am. 1992. 36(2):357–378.
12. Pitt Ford TR, Andreasen JO, Dorn SO, Kariyawasam SP. Effect of various zinc oxide materials as root-end fillings on healing after replantation. Int Endod J. 1995. 28(6):273–278.

13. Wu MK, Kontakiotis EG, Wesselink PR. Long-term seal provided by some root-end filling materials. J Endod. 1998. 24(8):557–560.

14. Zhu Q, Safavi KE, Spangberg LS. Cytotoxic evaluation of root-end filling materials in cultures of human osteoblast-like cells and periodontal ligament cells. J Endod. 1999. 25(6):410–412.

15. Fischer EJ, Arens DE, Miller CH. Bacterial leakage of mineral trioxide aggregate as compared with zincfree amalgam, intermediate restorative material, and Super-EBA as a root-end filling material. J Endod. 1998. 24(3):176–179.

16. Torabinejad M, Higa RK, McKendry DJ, Pitt Ford TR. Dye leakage of four root end filling materials: effects of blood contamination. J Endod. 1994. 20(4):159–163.

17. Torabinejad M, Hong CU, Pitt Ford TR, Kettering JD. Cytotoxicity of four root end filling materials. J Endod. 1995. 21(10):489–492.

18. Torabinejad M, Pitt Ford TR, McKendry DJ, Abedi HR, Miller DA, Kariyawasam SP. Histologic assessment of mineral trioxide aggregate as a root-end filling in monkeys. J Endod. 1997. 23(4):225–228.

19. Zhu Q, Haglund R, Safavi KE, Spangberg LS. Adhesion of human osteoblasts on root-end filling materials. J Endod. 2000. 26(7):404–406.

20. Barkhordar RA, Meyer JR. Histologic evaluation of a human periapical defect after implantation with tricalcium phosphate. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1986. 61(2):201–206.

21. Himel VT, Brady J Jr, Weir J Jr. Evaluation of repair of mechanical perforations of the pulp chamber floor using biodegradable tricalcium phosphate or calcium hydroxide. J Endod. 1985. 11(4):161–165.

22. Dorn SO, Gartner AH. Retrograde filling materials: a retrospective success-failure study of amalgam, EBA, and IRM. J Endod. 1990. 16(8):391–393.

23. Szeremeta-Browar TL, VanCura JE, Zaki AE. A comparison of the sealing properties of different retrograde techniques: an autoradiographic study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1985. 59(1):82–87.

24. Fitzpatrick EL, Steiman HR. Scanning electron microscopic evaluation of finishing techniques on IRM and EBA retrofillings. J Endod. 1997. 23(7):423–427.

25. Torabinejad M, Falah Rastergar A, Kettering JD, Pitt Ford TR. Bacterial leakage of mineral trioxide aggregate as a root and filling material. J Endod. 1995. 21(3):109–112.

26. Goodell GG, Mork TO, Hutter JW, Nicoll BK. Linear dye penetration of a calcium phosphate cement apical barrier. J Endod. 1997. 23(3):174–177.

28. Chong BS, Pitt Ford TR, Watson TF. The adaptation and sealing ability of light-cured glass ionomer retrograde root fillings. Int Endod J. 1991. 24(5):223–232.

29. Oliver CM, Abbott PV. Correlation between clinical success and apical dye penetration. Int Endod J. 2001. 34(8):637–644.

30. Ahlberg KM, Assavanop P, Tay WM. A comparison of the apical dye penetration patterns shown by methylene blue and india ink in root-filled teeth. Int Endod J. 1995. 28(1):30–34.

31. Antonopoulos KG, Attin T, Hellwig E. Evaluation of the apical seal of root canal fillings with different methods. J Endod. 1998. 24(10):655–658.

32. Goldman M, Simmonds S, Rush R. The usefulness of dye-penetration studies reexamined. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1989. 67(3):327–332.

33. Spangberg LS, Acierno TG, Yongbum Cha B. Influence of entrapped air on the accuracy of leakage studies using dye penetration methods. J Endod. 1989. 15(11):548–551.

34. Oliver CM, Abbott PV. Entrapped air and its effects on dye penetration of voids. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1991. 7(3):135–138.

35. Peters LB, Harrison JW. A comparison of leakage of filling materials in demineralized and non-demineralized resected root ends under vacuum and non-vacuum conditions. Int Endod J. 1992. 25(6):273–278.

36. Wu MK, Kontakiotis EG, Wesselink PR. Decoloration of 1% methylene blue solution in contact with dental filling materials. J Dent. 1998. 26(7):585–589.

37. Torabinejad M, Smith PW, Kettering JD, Pitt Ford TR. Comparative investigation of marginal adaptation of mineral trioxide aggregate and other commonly used root-end filling materials. J Endod. 1995. 21(6):295–299.

39. Wu MK, Wesselink PR. Endodontic leakage studies reconsidered. Part I. Methology, application and relevance. Int Endod J. 1993. 26:37–43.

40. Veis A, Lambrianidies T, Nicolaou A. Area-metric analysis of dye leakage for evaluation of sealing ability of root canal obturation techniques. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1996. 12:222–226.

41. Brown WE, Chow LC. A new calcium phosphate settinh cement. J Dent Res. 1983. 62:672.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download