Abstract
For the groups with tubules perpendicular to bonded surface, funnel shape of resin tag was observed in all specimen. However, resin tags were more prominent in phosphoric acid etching system (ALL BOND® 2 and PQ1) than self etching system (CLEARFIL™ SE BOND).
For the groups with tubules parallel to bonded surface, rhodamine-labeled primer penetrated into peritubular dentin parallel to the orientation of dentinal tubules. But rhodamine-labeled primer of PQ1 diffused more radially into surrounding intertubular dentin than other dentin adhesive systems.
For the groups with tubules oblique to bonded surface, resin tags appeared irregular and discontinuous. But they penetrated deeper into dentinal tubules than other groups.
Figures and Tables
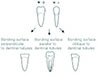 | Fig. 1Preparation of specimens with the bonding surface perpendicular, parallel or oblique to the dentinal tubules (B-L = bucco-lingual view, M-D = mesio-distal view). |
 | Fig. 3Overlapped image of fluorescent mode of the interface between ALL-BOND® 2 and dentin. Resin tags with characteristic funnel cone shape were observed. ×1200. |
 | Fig. 4CLSM image scanned parallel to interface at a depth below 3 µm interval. The Red area indicate the penetration of rhodamine-labeled primer into dentinal tubules and White arrows also indicate their side branchs. ×2400. |
 | Fig. 5Overlapped image of fluorescent mode of the interface between CLEARFIL™ SE BOND and dentin. Resin tags is less prominent than other dental adhesive systems. ×2100. |
 | Fig. 6CLSM image scanned parallel to interface at a depth below 3 µm interval. The Red area indicate the penetration of rhodamine-labeled primer into dnetinal tubules. ×2400. |
 | Fig. 7Overlapped image of fluorescent mode of the interface between PQ1 and dentin. Resin tags with characteristic funnel cone shape were observed. ×1200. |
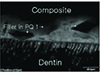 | Fig. 8Overlapped image of fluorescent mode of the interface between PQ1 and dentin. The white arrow indicate the filler of PQ1. ×1200. |
 | Fig. 9Overlapped image of fluorescent mode of the interface betweenALL-BOND® 2 and dentin. The penetration pattern of rhodamine-labeled primer is different from perpendicular group. ×1200. |
 | Fig. 10CLSM image scanned parallel to interface at a depth below 3 µm interval. There were few resin tags like perpendicular group. ×2100. |
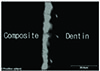 | Fig. 11Overlapped image of fluorescent mode of the interface between CLEARFIL™ SE BOND and dentin. The direction of dentinal tubule and rhodamine-labeled primer is parallel. ×2100. |
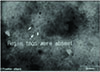 | Fig. 12CLSM image scanned parallel to interface at a depth below 3 µm interval. There were few resin tags like prependicular group. ×2100. |
 | Fig. 13Overlapped image of fluorescent mode of the interface between PQ1 and dentin. Rhodamine-labeled primer diffuses more radially into surrounding intertubular dentin. ×2100. |
 | Fig. 14Schematic illustration of Fig. 13. |
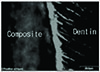 | Fig. 15Overlapped image of fluorescent mode of the interface betweenALL-BOND® 2 and dentin. Irregular shape resin tags were observed. ×1200. |
 | Fig. 16CLSM image scanned parallel to interface at a depth below 16 µm interval. The white arrow indicate resin tags. ×2100. |
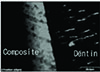 | Fig. 17Overlapped image of fluorescent mode of the interface between CLEARFIL™ SE BOND and dentin. Resin tags were not continuous. ×1200. |
 | Fig. 18CLSM image scanned parallel to interface at a depth below 16 µm interval. The white arrow indicate resin tags. ×2100. |
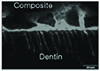 | Fig. 19Overlapped image of fluorescent mode of the interface between PQ1 and dentin. Irregular shape resin tags were observed. ×1200. |
Table 1

Abbreviation:
HEMA = 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate
Bis-GMA = Bis-phenol A diglycidylmethycrylate
BPDM = Biphenyl dimethacrylate
CQ = d,l-Camphorquinone
MDP = 10-meth ryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate
NTG-GMA = N-tolyglycine-glycidyl methacrylate
UDMA = Urethane dimethacrylate
TEGDMA = Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download