Abstract
Background:
The objective of this study was to compare the pharmacokinetics and safety between newly developed sildenafil (Please Orally Soluble Film) and sildenafil citrate (VIAGRA®) after single oral administration in healthy Korean male subjects.
Methods:
A randomized, open-label, single dose, 2-way crossover study was conducted in 50 healthy male subjects. Each sequence group consisted of 25 subjects, received a single oral 50 mg dose of Please Orally Soluble Film (test formulation) or VIAGRA® (reference formulation) by study period. Blood samples were obtained during a 24-hour period after dosing. Sildenafil and its metabolite concentrations were determined using validated LC-MS/MS. A non-compartmental pharmacokinetic analysis was performed. Safety was assessed through monitoring of adverse events, vital sign check-up, physical examination, laboratory tests and electrocardiography.
Results:
All enrolled participants completed the study. The point estimates and 90 % confidence intervals of log transformed Cmax and AUClast of the test formulation in comparison to those of reference formulation were 0.9294(0.8353 - 1.0341) and 0.9415 (0.8869 - 0.9994) respectively. The analysis of variance showed no significant influences of formulation, sequence and period on the pharmacokinetic parameters. The frequencies of adverse events were not statistically different between the formulations. No serious adverse event was observed or reported.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Kim TH, Chung TG, Ahn TY. Relation between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction epidemiologic study in Jeong-Eup. Kor J Androl. 1998; 16(1):87–91.
2. Woodwell DA, Cherry DK. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2002 summary. Advance data. 2004; 26(346):1–44.
3. Ryu SB, Min KD, Park KS, Park YI, Rhee JA, Kweon SS. Epidemiologic study of the male erectile dysfunction with risk, factors in rural area. Korean J Androl. 2001; 19:125–31.
4. Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Kranae RJ, McKinlay JB. Importence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994; 151(1):54–61.
5. Lee U, Lee MH, Kim SY, Ji YH, Hong JH, Ahn TY. Clinical efficacy and safety of sildenafil in the men with erectile dysfunction in Korea. Korean J Urol. 2001; 42(4):435–440.
6. Price DE, Gingell JC, Gepi-Attee S, Wareham K, Yates P, Boolell M. Sildenafil: study of a novel oral treatment for erectile dysfunction in diabetic men. Diabet Med. 1998; 15(10):821–825.

7. Nichols DJ, Muirhead GJ, Harness JA. Pharmacokinetics of sildenafil citrate after single oral doses in healthy male subjects: absolute bioavailability, food effects and dose proportionality. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002; 53:5S–12S.
Go to : 
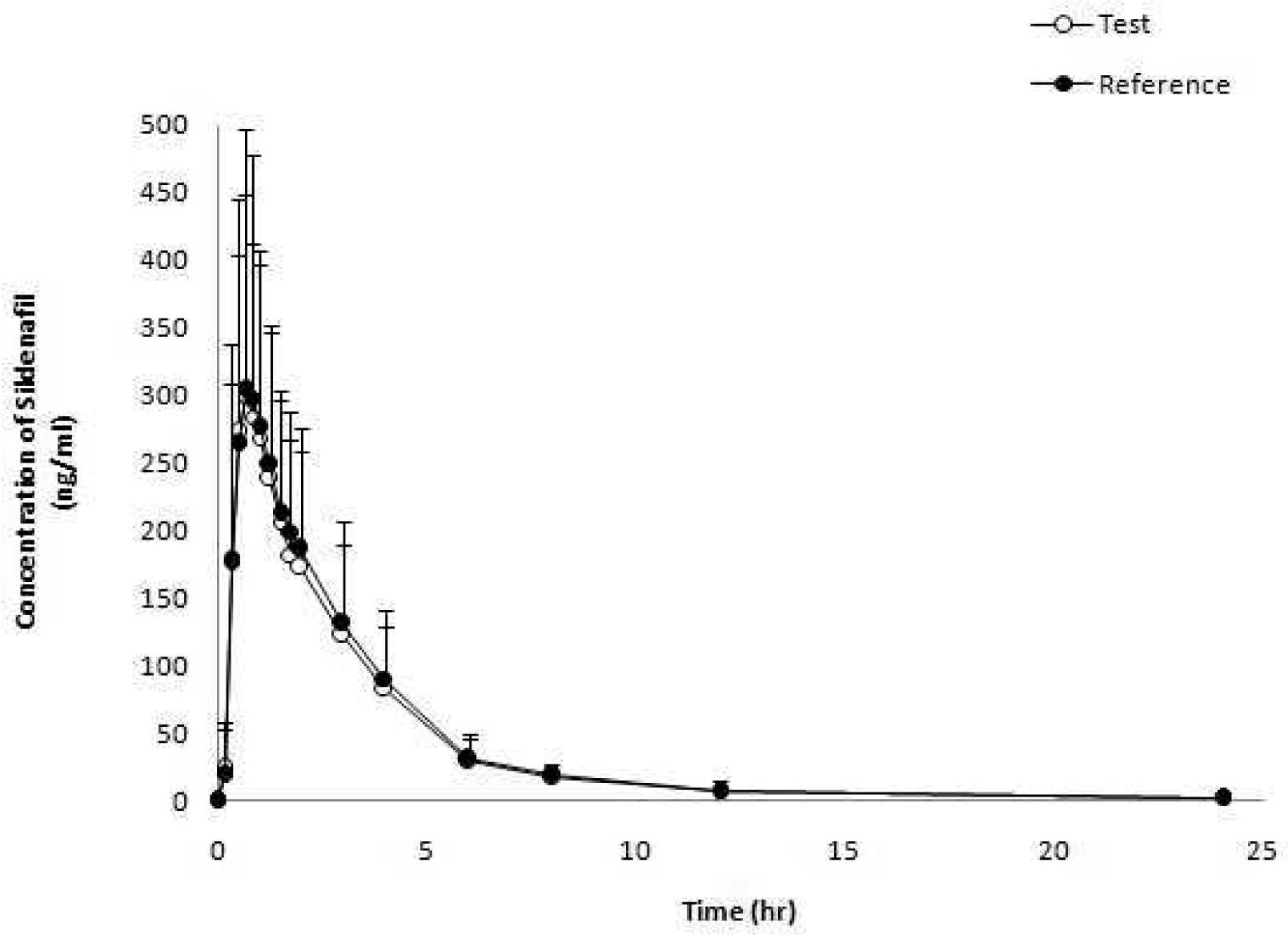 | Figure 1.Mean (standard deviation) plasma concentration-time profile of reference (VIAGRA®) and test (Please Orally Soluble Film) formulation after a single oral administration. |
Table 1.
Subject demographics
Table 2.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of sildenafil and N-desmethyl sildenafil in reference (VIAGRA®) and test (Please Orally Soluble Film) formulation
Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation (CV(%)). Cmax: maximum plasma concentration. AUClast: area under the plasma concentration-time curve from zero time until last measurable concentration. AUGinf: area under the plasma concentration-time curve from zero time to infinity. Tmax: time to maximum plasma concentration. t1/2: terminal elimination half-life. λZ: terminal elimination rate constant.
Table 3.
Geometric mean ratio and 90 % confidence interval for Cmax and AUClast of sildenafil and N-desmethyl sildenafil in test (Please Orally Soluble Film) and reference (VIAGRA®) formulations in healthy male volunteers
Table 4.
Analysis of variance for pharmacokinetic parameters of sildenafil between reference (VIAGRA®) and test (Please Orally Soluble Film) formulations
Table 5.
Analysis of variance for pharmacokinetic parameters of N-desmethyl sildenafil between reference (VIAGRA®) and test (Please Orally Soluble Film) formulations




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download