Abstract
Background
Dutasteride is an inhibitor of both types I and II 5 alpha-reductase and was approved in Korea in April 2004. This post-marketing surveillance was to assess the safety of dutasteride in Korean patients with benign prostate hyperplasia in real life and to elucidate the risk factors related adverse events.
Methods
From December 2004 to January 2010, 3,977 patients were enrolled by 184 urologists. According to post-marketing surveillance regulation, patients were enrolled consecutively. Patients administered dutasteride at least once were included in safety assessment. The incidences of any adverse events and serious adverse events were evaluated. Multiple logistic regression method was used to identify risk factors related to adverse events.
Results
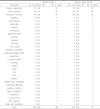
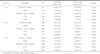
The safety assessment included 3,870 patients with the mean age of 67.3 years. The incidence of adverse events was 3.8 %. The most frequent adverse event was impotence (75 cases, 1.9 %), libido decrease (49 cases, 1.3 %), ejaculation disorder (30 cases, 0.8 %), and gynecomastia (5 cases, 0.1 %). The incidence of unexpected adverse events was 0.5 % and cerebral infarction, lung cancer, pulmonary embolism, and diarrhea were reported as serious adverse events.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Welch G, Weinger K, Barry MJ. Quality-of-life impact of lower urinary tract symptom severity: results from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study* 1. Urology. 2002. 59(2):245–250.

2. Roehrborn CG, Bruskewitz R, Nickel GC, Glickman S, Cox I. Urinary retention in patients with BPH treated with finasteride or placebo over 4 years. Eur Urol. 2000. 37(5):528–536.

3. Lepor H, Williford WO, Barry MJ, Brawer MK, Dixon CM, Gormley G, Haakenson C, Machi M, Narayan P, Padley RJ. The efficacy of terazosin, finasteride, or both in benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 1996. 335(8):533–539.

4. McConnell JD, Bruskewitz R, Walsh P, Andriole G, Lieber M, Holtgrewe HL, Haakenson C, Machi M, Narayan P, Padley RJ. Finasteride Long-Term Efficacy and Safety Study Group. The effect of finasteride on the risk of acute urinary retention and the need for surgical treatment among men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 1998. 338(9):557–563.

5. Frye S, Bramson H, Hermann D, Lee F, Sinhababu A, Tian G. Discovery and Development of GG745, a Potent Inhibitor of Both Isozymes of 5α-Reductase. Pharm Biotechnol. 1998. 11:393–422.
6. Bramson HN, Hermann D, Batchelor KW, Lee FW, James MK, Frye SV. Unique preclinical characteristics of GG745, a potent dual inhibitor of 5AR. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997. 282(3):1496–1502.
7. Roehrborn CG, Boyle P, Nickel JC, Hoefner K, Andriole G. Efficacy and safety of a dual inhibitor of 5 alpha-reductase types 1 and 2 in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia* 1. Urology. 2002. 60(3):434–441.

8. Montorsi F, Roehrborn C, Garcia Penit J, Borre M, Roeleveld TA, Alimi JC, et al. The effects of dutasteride or tamsulosin alone and in combination on storage and voiding symptoms in men with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): 4 year data from the Combination of Avodart and Tamsulosin (CombAT) study. BJU Int. 2011. 107(9):1426–1431.

9. Oh CY, Lee SH, Yoo SJ, Chung BH. Korean urologist's view of practice patterns in diagnosis and management of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a nationwide survey. Yonsei Med J. 2010. 51(2):248–252.

10. Nickel JC, Gilling P, Tammela TL, Morrill B, Wilson TH, Rittmaster RS. Comparison of dutasteride and finasteride for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia: the Enlarged Prostate International Comparator Study (EPICS). BJU Int. 2011. 108(3):388–394.

11. Andriole GL, Kirby R. Safety and Tolerability of the Dual 5 [alpha]-Reductase Inhibitor Dutasteride in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2003. 44(1):82–88.

12. Roehrborn CG, Siami P, Barkin J, Damiao R, Major-Walker K, Nandy I, Morrill BB, Gagnier RP, Montsori F. CombAT Study Group. The effects of combination therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin on clinical outcomes in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 4-year results from the CombAT study. Eur Urol. 2010. 57(1):123–131.

13. Vallancien G, Emberton M, Harving N, van Moorselaar RJ. Sexual dysfunction in 1,274 European men suffering from lower urinary tract symptoms. J Urol. 2003. 169(6):2257–2261.

14. Roehrborn CG, Siami P, Barkin J, Damiao R, Major-Walker K, Morrill B, Montorsi F. The effects of dutasteride, tamsulosin and combination therapy on lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic enlargement: 2-year results from the CombAT study. J Urol. 2008. 179(2):616–621.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print







 XML Download
XML Download