Abstract
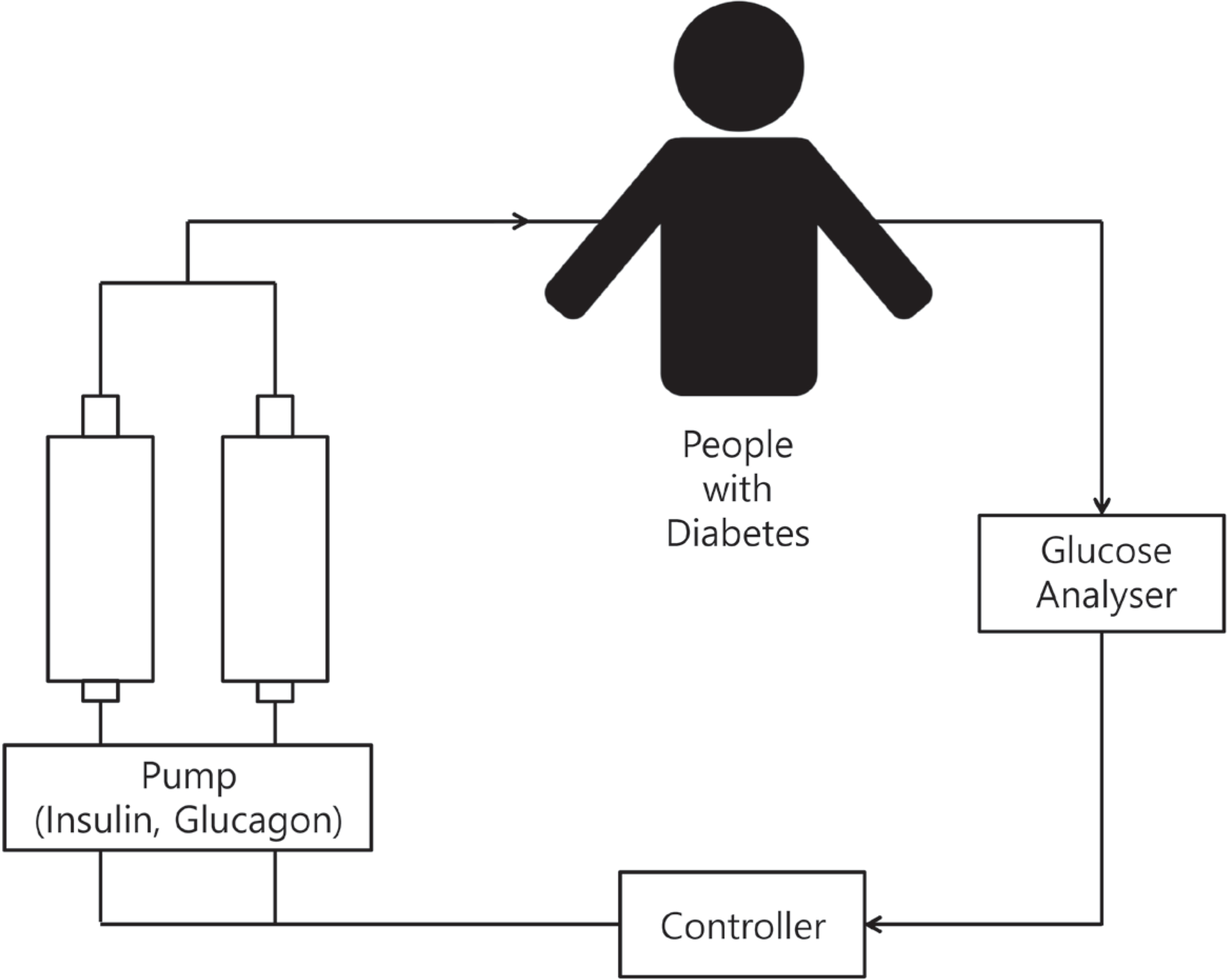
Artificial pancreas is a technique developed to automatically control blood glucose in people with diabetes by providing an endocrine function instead of a healthy pancreas. The technique was developed for the replacement of insulin secretion deficiencies among various exocrine and endocrine functions of the pancreas and is mainly used for people with type 1 diabetes or those who need intensive insulin treatment. This review briefly summarizes the working principles, components, recent clinical research, and future perspectives of artificial pancreas.
References
1. Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL, Kneteman NM, Rajotte RV. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:230–8.

2. Sutherland DE, Gruessner RW, Gruessner AC. Pancreas transplantation for treatment of diabetes mellitus. World J Surg. 2001; 25:487–96.

3. Humar A, Kandaswamy R, Granger D, Gruessner RW, Gruessner AC, Sutherland DE. Decreased surgical risks of pancreas transplantation in the modern era. Ann Surg. 2000; 231:269–75.

4. Shapiro AM. Islet transplantation in type 1 diabetes: ongoing challenges, refined procedures, and longterm outcome. Rev Diabet Stud. 2012; 9:385–406.

5. Huh KB. Artificial pancreas. Korean J Int Med. 1978; 21:1071–6.
6. Cobelli C, Renard E, Kovatchev B. Artificial pancreas: past, present, future. Diabetes. 2011; 60:2672–82.

7. Kobayashi N. Bioartificial pancreas for the treatment of diabetes. Cell Transplant. 2008; 17:11–7.

8. Ricordi C, Edlund H. Toward a renewable source of pancreatic beta-cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2008; 26:397–8.
9. Farmer TG Jr, Edgar TF, Peppas NA. The future of open- and closed-loop insulin delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2008; 60:1–13.

10. Bode BW. Clinical utility of the continuous glucose monitoring system. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2000; 2(Suppl 1):S35–41.

12. Haidar A, Legault L, Messier V, Mitre TM, Leroux C, Rabasa-Lhoret R. Comparison of dual-hormone artificial pancreas, single-hormone artificial pancreas, and conventional insulin pump therapy for glycaemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes: an open-label randomised controlled crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015; 3:17–26.

13. Russell SJ, El-Khatib FH, Sinha M, Magyar KL, McKeon K, Goergen LG, Balliro C, Hillard MA, Nathan DM, Damiano ER. Outpatient glycemic control with a bionic pancreas in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371:313–25.

14. Cobelli C, Man CD, Sparacino G, Magni L, De Nicolao G, Kovatchev BP. Diabetes: models, signals, and control. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2009; 2:54–96.

15. Steil GM, Rebrin K, Darwin C, Hariri F, Saad MF. Feasibility of automating insulin delivery for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2006; 55:3344–50.

16. Hovorka R. The future of continuous glucose monitoring: closed loop. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2008; 4:269–79.

17. Rhee SY, Chon S, Koh G, Paeng JR, Oh S, Woo JT, Kim SW, Kim JW, Kim YS. Clinical experience of an iontophoresis based glucose measuring system. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:70–3.

18. Bailey T, Bode BW, Christiansen MP, Klaff LJ, Alva S. The performance and usability of a factory-calibrated flash glucose monitoring system. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2015; 17:787–94.

19. Ólafsdóttir AF, Attvall S, Sandgren U, Dahlqvist S, Pivodic A, Skrtic S, Theodorsson E, Lind M. A clinical trial of the accuracy and treatment experience of the flash glucose monitor freestyle libre in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2017; 19:164–72.

20. Clemens AH, Chang PH, Myers RW. The development of biostator, a glucose controlled insulin infusion system (GCIIS). Horm Metab Res. 1977; (Suppl 7):23–33.
21. LeBlanc H, Chauvet D, Lombrail P, Robert JJ. Glycemic control with closed-loop intraperitoneal insulin in type I diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1986; 9:124–8.

22. Pickup JC, Keen H, Parsons JA, Alberti KG. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion: an approach to achieving normoglycaemia. Br Med J. 1978; 1:204–7.

23. Bally L, Thabit H, Kojzar H, Mader JK, Qerimi-Hyseni J, Hartnell S, Tauschmann M, Allen JM, Wilinska ME, Pieber TR, Evans ML, Hovorka R. Day-and-night glycaemic control with closed-loop insulin delivery versus conventional insulin pump therapy in free-living adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes: an open-label, randomised, crossover study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017; 5:261–70.

24. Stewart ZA, Wilinska ME, Hartnell S, Temple RC, Rayman G, Stanley KP, Simmons D, Law GR, Scott EM, Hovorka R, Murphy HR. Closed-Loop insulin delivery during pregnancy in women with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:644–54.

25. Tauschmann M, Allen JM, Wilinska ME, Thabit H, Stewart Z, Cheng P, Kollman C, Acerini CL, Dunger DB, Hovorka R. Day-and-night hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a free-living, randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:1168–74.

26. Reddy M, Herrero P, Sharkawy ME, Pesl P, Jugnee N, Pavitt D, Godsland IF, Alberti G, Toumazou C, Johnston DG, Georgiou P, Oliver NS. Metabolic control with the Bio-inspired artificial pancreas in adults with type 1 diabetes: a 24-hour randomized controlled crossover study. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2015; 10:405–13.
27. Cherñavvsky DR, DeBoer MD, Keith-Hynes P, Mize B, McElwee M, Demartini S, Dunsmore SF, Wakeman C, Kovatchev BP, Breton MD. Use of an artificial pancreas among adolescents for a missed snack bolus and an underestimated meal bolus. Pediatr Diabetes. 2016; 17:28–35.

28. Thabit H, Tauschmann M, Allen JM, Leelarathna L, Hartnell S, Wilinska ME, Acerini CL, Dellweg S, Benesch C, Heinemann L, Mader JK, Holzer M, Kojzar H, Exall J, Yong J, Pichierri J, Barnard KD, Kollman C, Cheng P, Hindmarsh PC, Campbell FM, Arnolds S, Pieber TR, Evans ML, Dunger DB, Hovorka R. APCam Consortium; AP@home Consortium. Home use of an artificial beta cell in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2129–40.

29. Kropff J, Del Favero S, Place J, Toffanin C, Visentin R, Monaro M, Messori M, Di Palma F, Lanzola G, Farret A, Boscari F, Galasso S, Magni P, Avogaro A, Keith-Hynes P, Kovatchev BP, Bruttomesso D, Cobelli C, DeVries JH, Renard E, Magni L. AP@home consortium. 2 month evening and night closed-loop glucose control in patients with type 1 diabetes under free-living conditions: a randomised crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015; 3:939–47.

30. Dassau E, Brown SA, Basu A, Pinsker JE, Kudva YC, Gondhalekar R, Patek S, Lv D, Schiavon M, Lee JB, Dalla Man C, Hinshaw L, Castorino K, Mallad A, Dadlani V, McCrady-Spitzer SK, McElwee-Malloy M, Wakeman CA, Bevier WC, Bradley PK, Kovatchev B, Cobelli C, Zisser HC, Doyle FJ 3rd. Adjustment of open-loop settings to improve closed-loop results in type 1 diabetes: a multicenter randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 100:3878–86.

31. Ly TT, Roy A, Grosman B, Shin J, Campbell A, Monirabbasi S, Liang B, von Eyben R, Shanmugham S, Clinton P, Buckingham BA. Day and night closed-loop control using the integrated medtronic hybrid closed-loop system in type 1 diabetes at diabetes camp. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:1205–11.

32. Brown SA, Kovatchev BP, Breton MD, Anderson SM, Keith-Hynes P, Patek SD, Jiang B, Ben Brahim N, Vereshchetin P, Bruttomesso D, Avogaro A, Del Favero S, Boscari F, Galasso S, Visentin R, Monaro M, Cobelli C. Multinight "bedside" closed-loop control for patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2015; 17:203–9.

33. Thabit H, Elleri D, Leelarathna L, Allen JM, Lubina-Solomon A, Stadler M, Walkinshaw E, Iqbal A, Choudhary P, Wilinska ME, Barnard KD, Heller SR, Amiel SA, Evans ML, Dunger DB, Hovorka R. Unsupervised home use of an overnight closed-loop system over 3–4 weeks: a pooled analysis of randomized controlled studies in adults and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015; 17:452–8.

34. Nimri R, Muller I, Atlas E, Miller S, Fogel A, Bratina N, Kordonouri O, Battelino T, Danne T, Phillip M. MD-Logic overnight control for 6 weeks of home use in patients with type 1 diabetes: randomized crossover trial. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:3025–32.

35. Leelarathna L, Dellweg S, Mader JK, Allen JM, Benesch C, Doll W, Ellmerer M, Hartnell S, Heinemann L, Kojzar H, Michalewski L, Nodale M, Thabit H, Wilinska ME, Pieber TR, Arnolds S, Evans ML, Hovorka R. AP@ home Consortium. Day and night home closed-loop insulin delivery in adults with type 1 diabetes: three-center randomized crossover study. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:1931–7.

36. Thabit H, Lubina-Solomon A, Stadler M, Leelarathna L, Walkinshaw E, Pernet A, Allen JM, Iqbal A, Choudhary P, Kumareswaran K, Nodale M, Nisbet C, Wilinska ME, Barnard KD, Dunger DB, Heller SR, Amiel SA, Evans ML, Hovorka R. Home use of closed-loop insulin delivery for overnight glucose control in adults with type 1 diabetes: a 4-week, multicentre, randomised crossover study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014; 2:701–9.

Fig. 2.
The main components of the closed loop artificial pancreas system, and the three key technical limitations that need to be overcome.
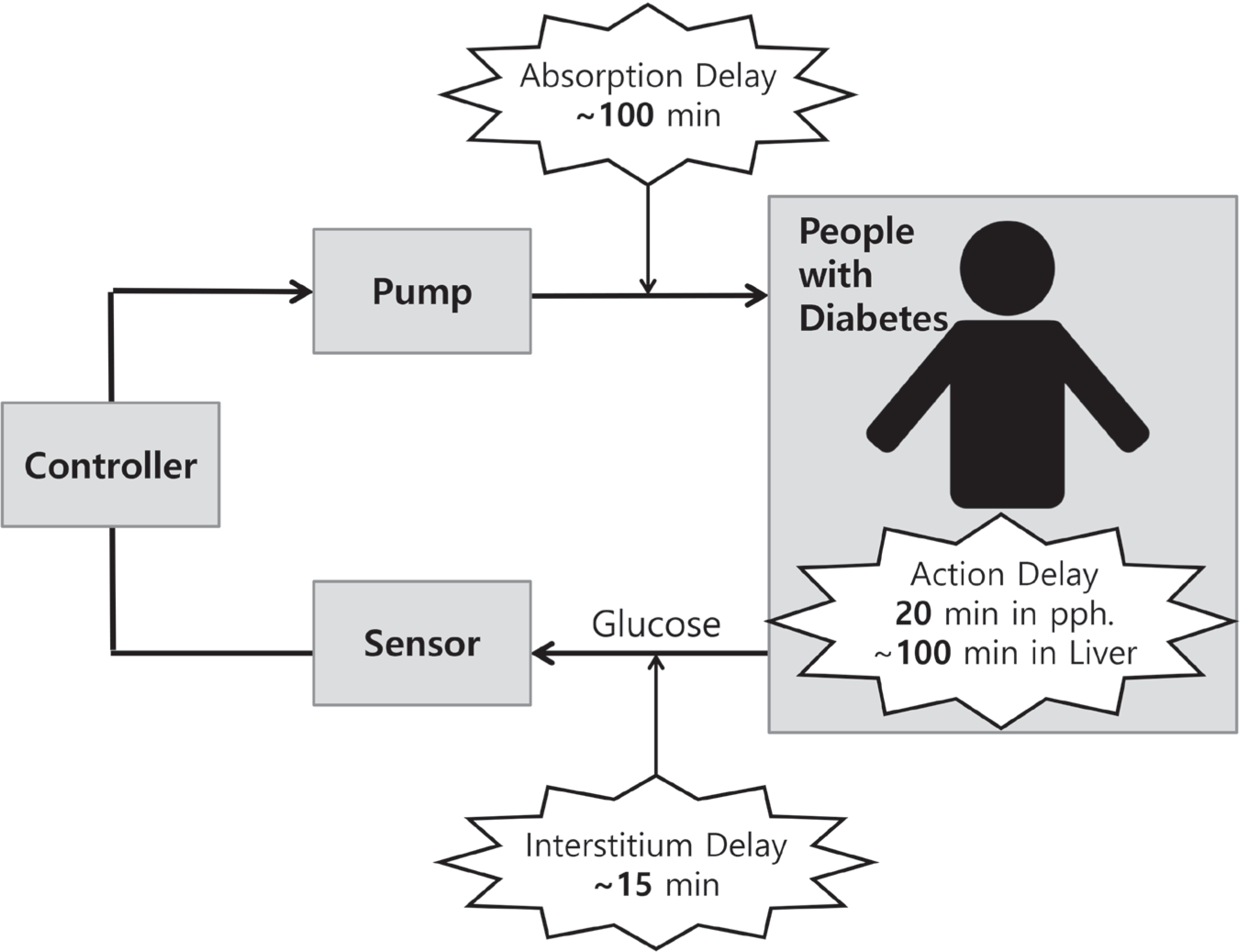
Table 1.
Clinical trials of the latest ‘closed loop’ artificial pancreas performed since 2010. Most studies were performed with an open label, randomized design, and the control group was a conventional insulin pump treatment group




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download