Abstract
The revised Clinical Practice Guideline (5th edition) for patients with diabetes was released in November 2015 by the Korean Diabetes Association. Strict glycemic control is emphasized for the prevention and progression of diabetes-related vascular complications. The recommended target goal of HbA1c is less than 6.5%, especially for patients with recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes. To achieve this target goal, various classes of oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin should be initiated promptly, according to the patient's clinical situation. Accurate and up-to-date information about the available oral hypoglycemic agents will help increase glycemic control and diabetes management.
References
1. Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes. 5th ed.Seoul: Gold' Planning and Development;2015.
2. Korean Academy of Medical Sciences. Evidence-based guideline for type 2 diabetes in primary care. Seoul: Korean Academy of Medical Sciences;2014.
3. Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes. 5th ed.Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2015. p. 24–6.
4. Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes. 5th ed.Seoul: Gold' Planning and Development;2011.
5. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) group. Lancet. 1998; 352:854–65.
6. Bennett WL, Maruthur NM, Singh S, Segal JB, Wilson LM, Chatterjee R, Marinopoulos SS, Puhan MA, Ranasinghe P, Block L, Nicholson WK, Hutfless S, Bass EB, Bolen S. Comparative effectiveness and safety of medications for type 2 diabetes: an update including new drugs and 2-drug combinations. Ann Intern Med. 2011; 154:602–13.

7. Yoon KH, Shin JA, Kwon HS, Lee SH, Min KW, Ahn YB, Yoo SJ, Ahn KJ, Park SW, Lee KW, Sung YA, Park TS, Kim MS, Kim YK, Nam MS, Kim HS, Park IeB, Park JS, Woo JT, Son HY. Comparison of the efficacy of glimepiride, metformin, and rosiglitazone monotherapy in Korean drug-naïve type 2 diabetic patients: the practical evidence of antidiabetic monotherapy study. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:26–33.

8. Phung OJ, Sobieraj DM, Engel SS, Rajpathak SN. Early combination therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and metaanalysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:410–7.

9. Kim HS, Kim DM, Cha BS, Park TS, Kim KA, Kim DL, Chung CH, Park JH, Jang HC, Choi DS. Efficacy of glimepiride/metformin fixed-dose combination vs metformin uptitration in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled on low-dose metformin monotherapy: a randomized, open label, parallel group, multicenter study in Korea. J Diabetes Investig. 2014; 5:701–8.

Fig. 1.
Treatment algorithm of newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes. DPP-4, dipeptidylpeptidase-4; SU, sulfonylurea; GLN, meglitinide; TZD, thiazolidinedione; SGLT-2, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2; GLP-1A, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; OHA, oral hypoglycemic agents.
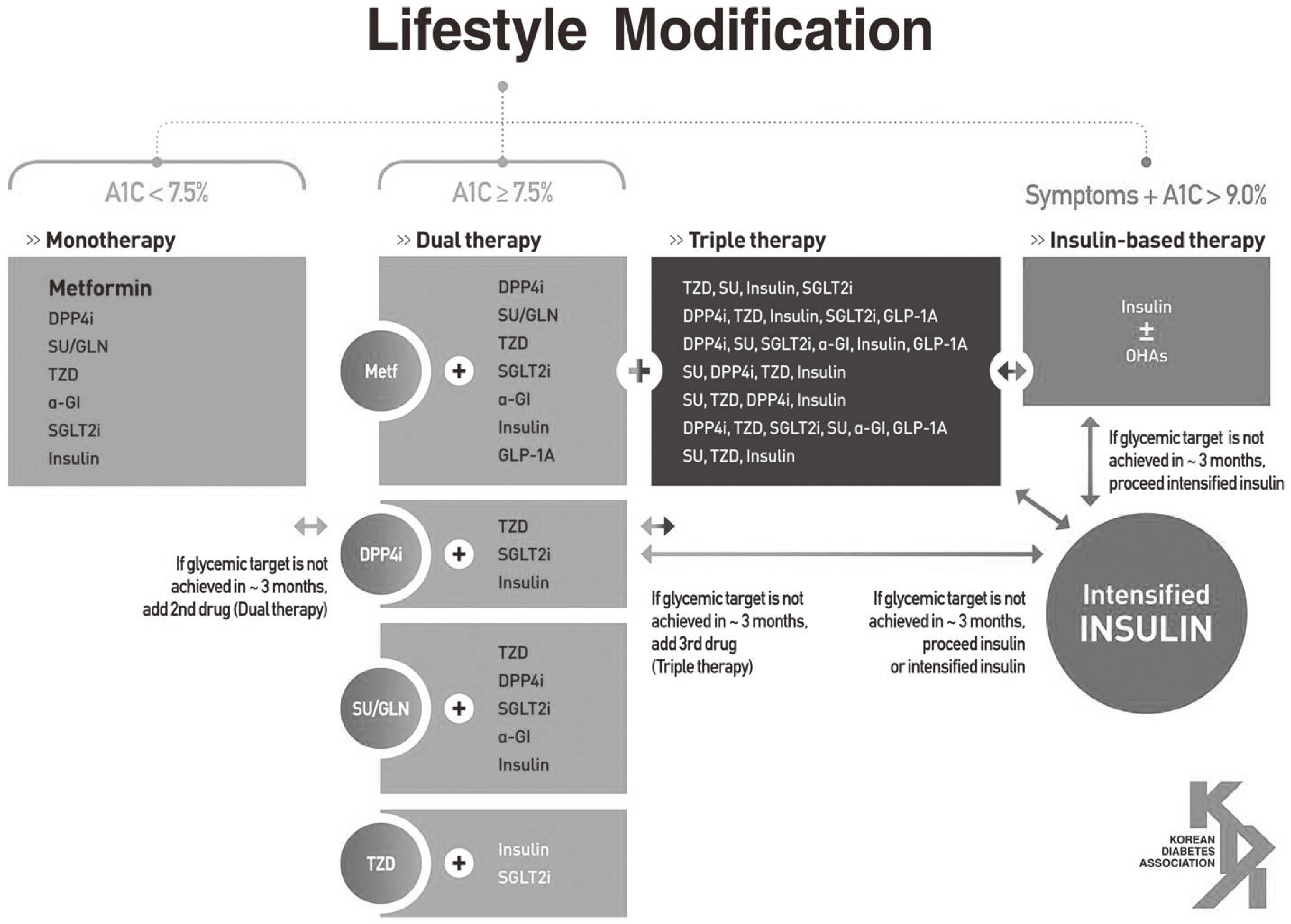
Table 1.
Clinical recommendation for antihyperglycemic treatment in type 2 diabetes
Table 2.
Characteristics of oral hypoglycemic agents for patients with type 2 diabetes




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download